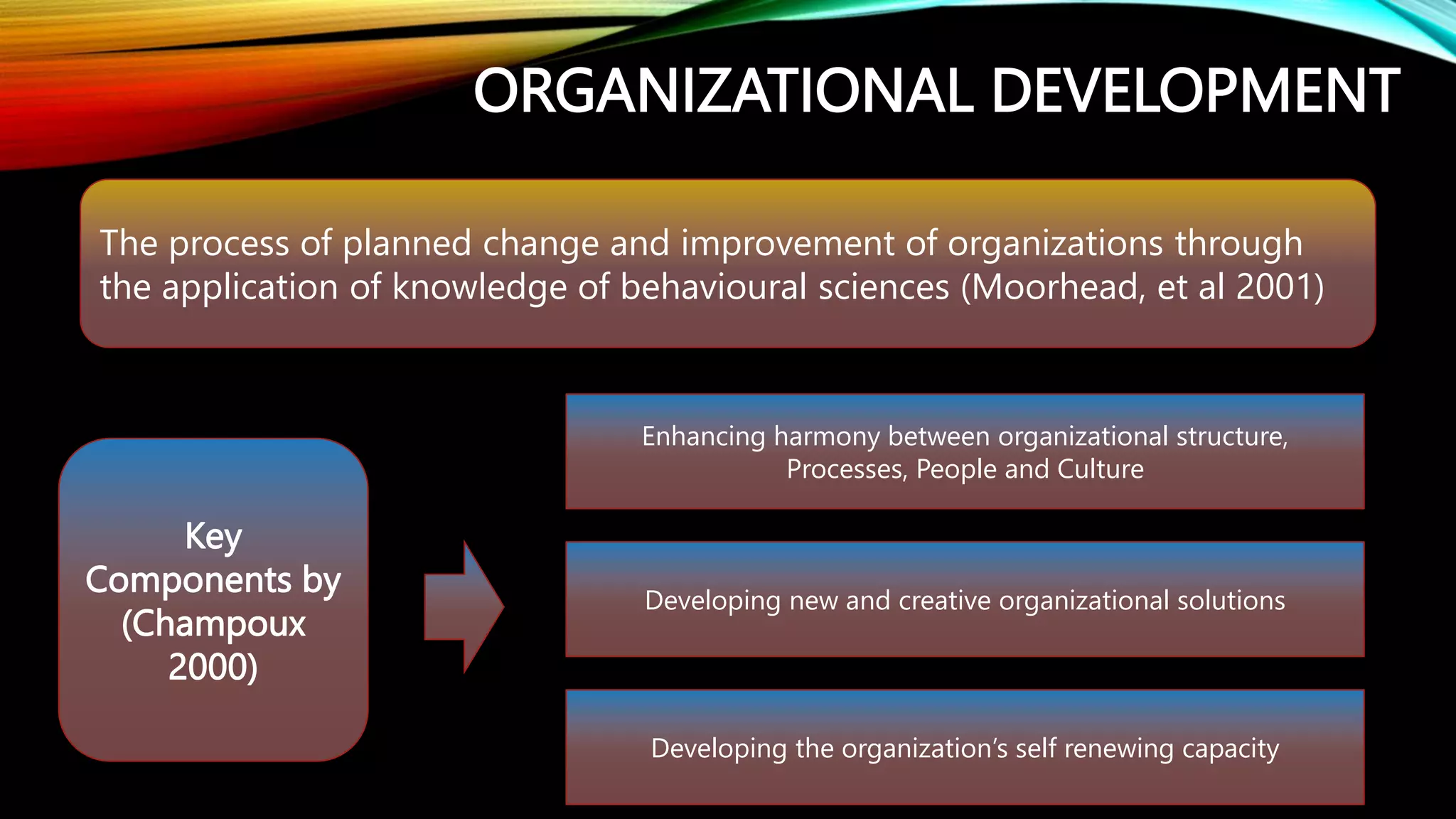
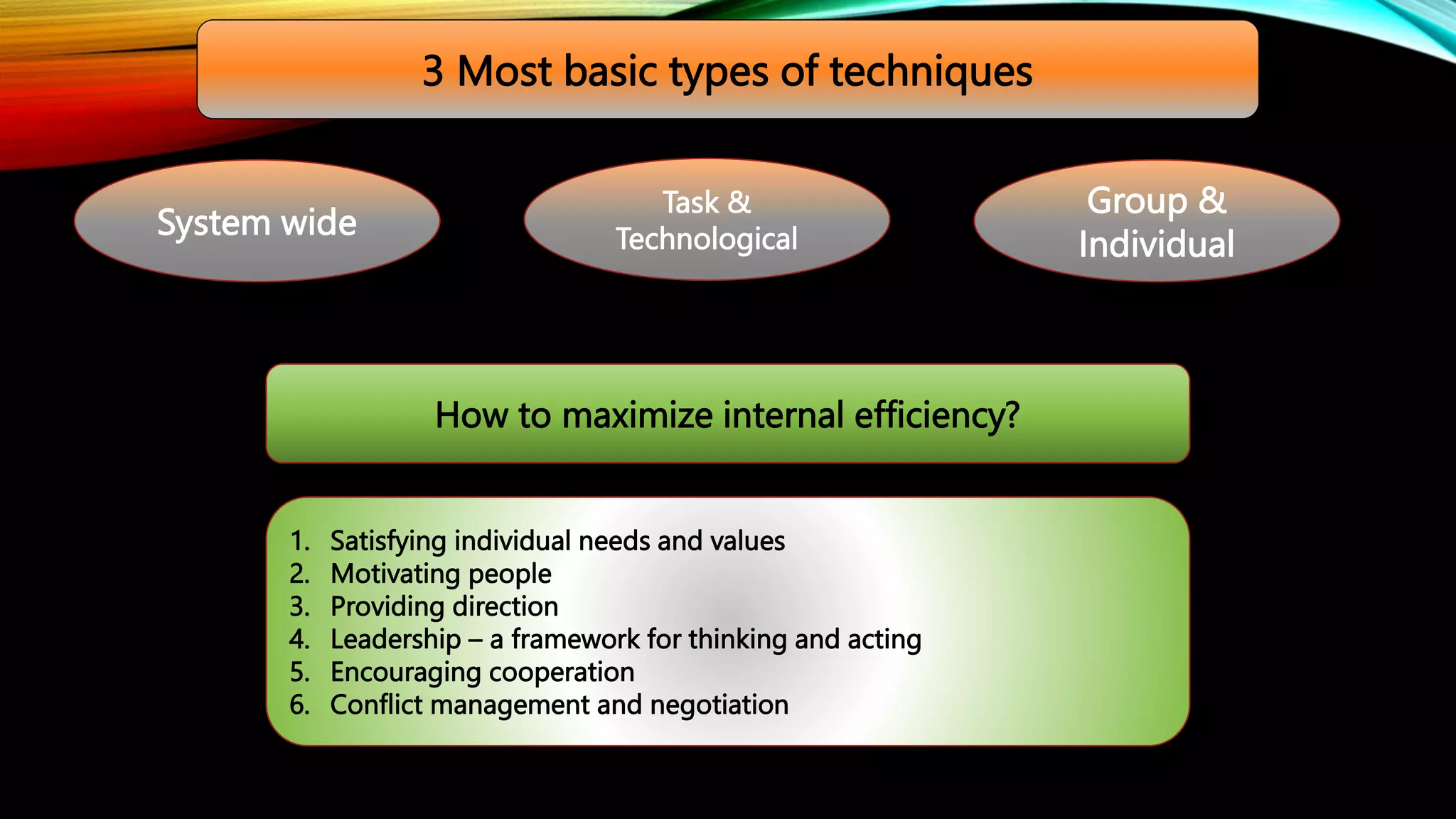
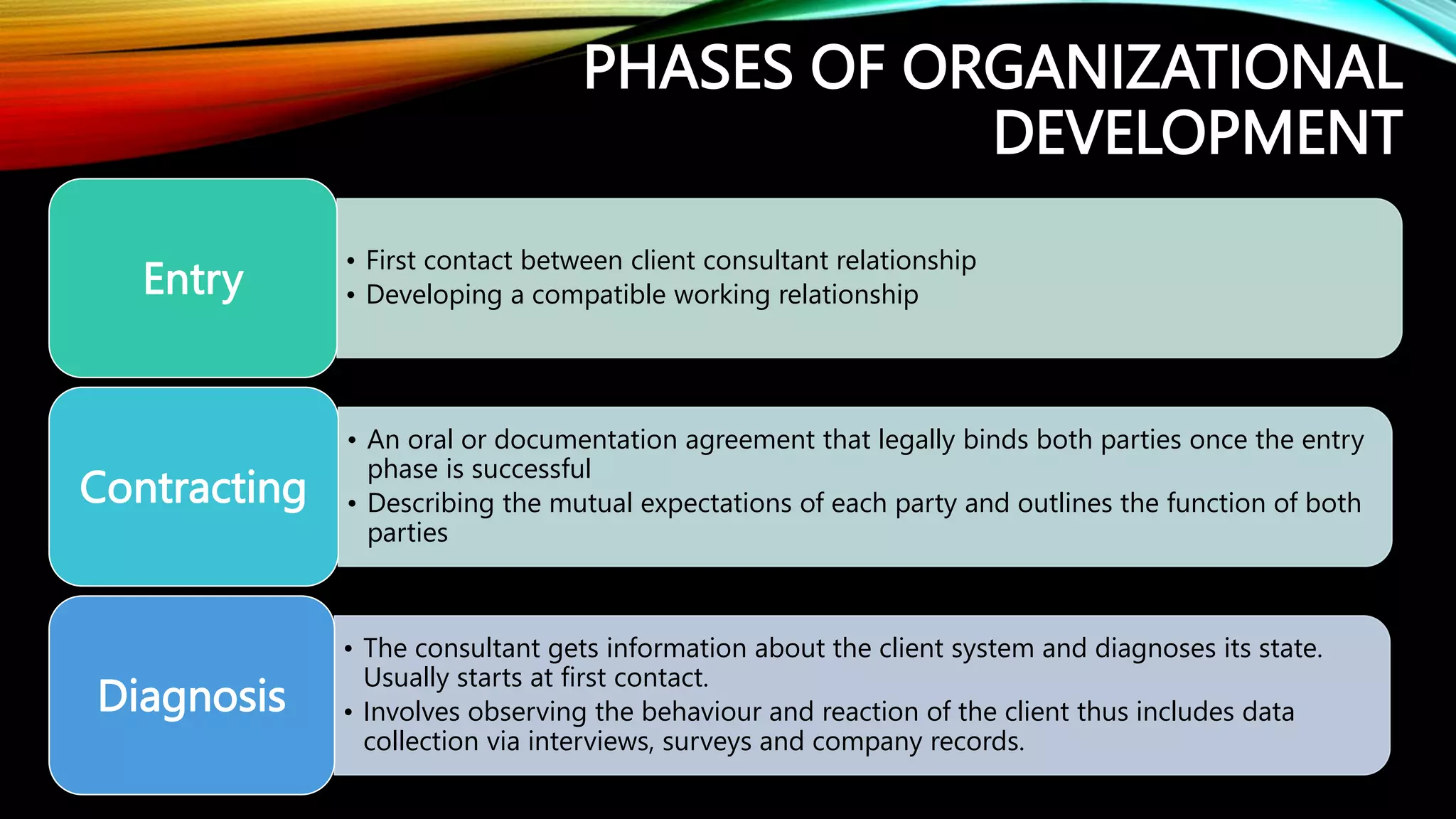
The document discusses organizational development as a systematic process aimed at creating planned change and enhancing internal efficiency through various techniques. It outlines key phases of organizational development, including diagnosis, feedback, intervention, and evaluation, emphasizing the importance of leadership, communication, and conflict management in achieving desired outcomes. Ultimately, it highlights the need for flexibility and adaptability within organizations to ensure continuous improvement and effective management of conflicts.