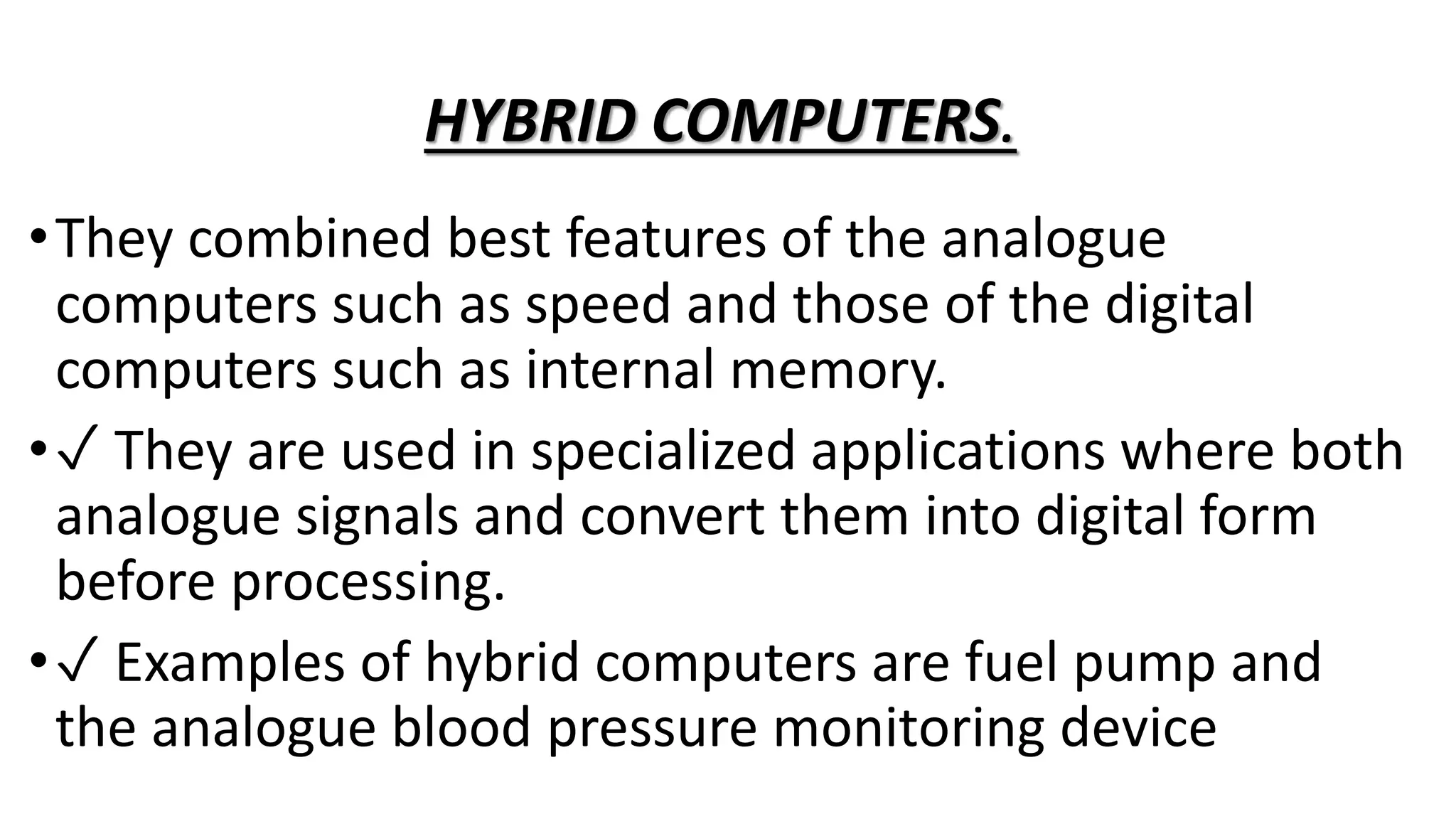
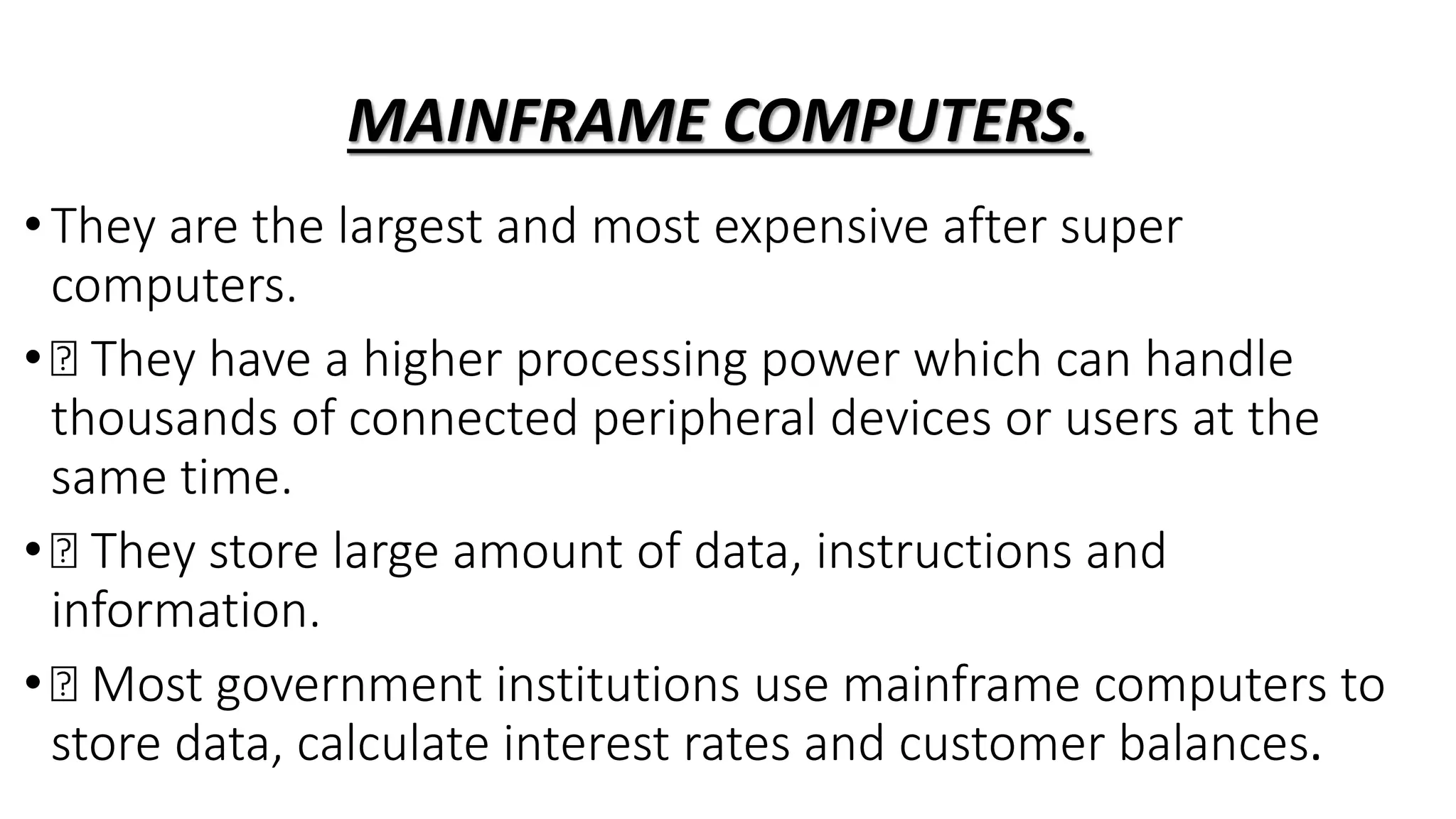
The document provides information about pretechnical studies, which involves acquiring practical skills in technical areas derived from computer science and business studies. It discusses the components of pretechnical studies, which includes pretechnical studies, computer science, and business studies. The document also outlines the role of pretechnical studies in daily life by providing skills for technical and digital futures and a wide range of career opportunities. Safety in the work environment and potential safety threats, both physical and online, are examined. Ways to mitigate physical threats to digital devices are proposed. The document concludes with discussing ideas to protect personal data online and general safety rules and regulations in the workplace.