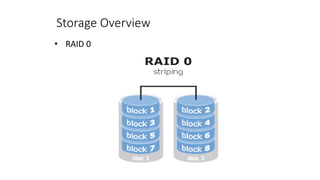
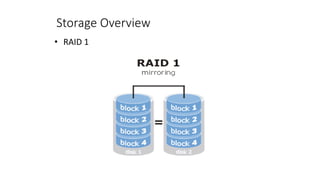
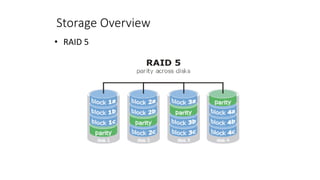
This document provides an overview of storage networking technologies, including storage area networks (SANs), fibre channel protocols, RAID configurations, and storage virtualization. It describes the basic components and functions of storage systems, such as primary and secondary storage, hard disk drives, RAID arrays, optical storage, and solid state drives. It also explains SAN fabrics, zoning, and how storage virtualization pools multiple storage devices to appear as a single device.