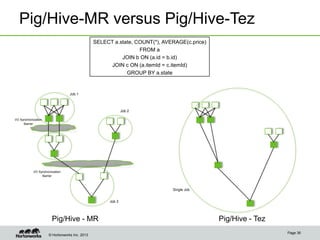
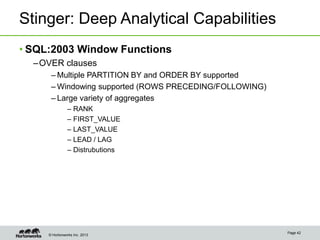
The document discusses the Stinger Initiative from Hortonworks to improve the performance and capabilities of interactive queries in Hive. The initiative takes a two-pronged approach, focusing on improvements to the query engine and the introduction of a new optimized column store file format called ORCFile. A new Tez execution engine is also introduced to avoid bottlenecks in MapReduce and enable lower latency queries. The goal is to extend Hive's ability to handle interactive queries with response times measured in seconds rather than minutes.