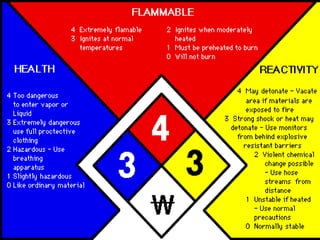
The document outlines workplace safety guidelines emphasizing the importance of protecting oneself and others from work-related injuries. It covers various safety protocols, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), emergency evacuation procedures, and proper operation of machinery like forklifts and manlifts. Additionally, it addresses specific hazards such as chemical handling, confined spaces, and fire safety measures, alongside the consequences of disregarding safety rules.