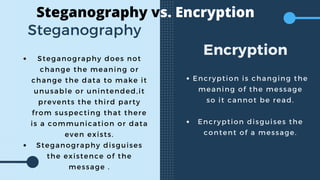
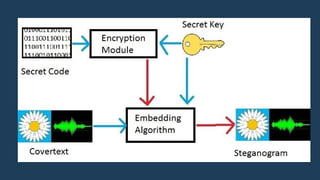
Steganography is the art of hiding secret messages within other files so that the existence of the message is concealed. There are various types of steganography that can be used to hide messages in images, audio, video, and text files. The document discusses different steganography techniques such as least significant bit encoding to modify pixel values in images or audio samples. It also compares steganography to encryption, noting that encryption disguises message content while steganography disguises the existence of the message itself.