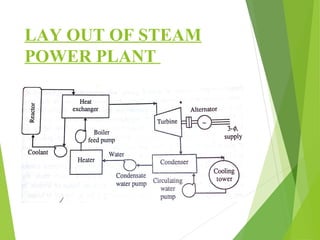
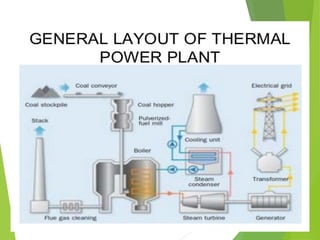
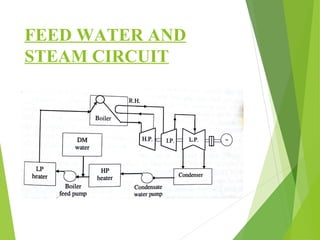
The document discusses the essential factors for selecting a site for steam power plants, including land availability, water supply, and future expansion needs. It details the layout and flow circuits within the plant such as fuel handling, cooling systems, and steam generation processes. Additionally, it highlights the advantages and disadvantages of hydrogen cooling systems for alternators in terms of efficiency and safety.