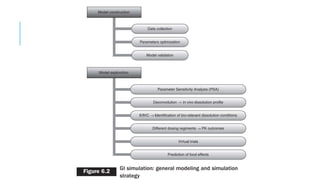
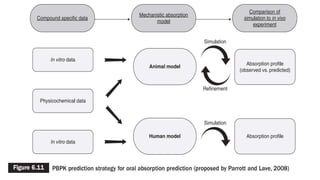
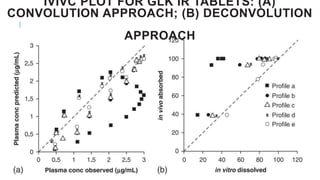
This document discusses using computer-aided modeling to simulate gastrointestinal absorption and predict oral drug bioavailability. Dynamic models can predict drug absorption rates and plasma concentration profiles. Such models can help evaluate formulations, screen compounds, and predict absorption when traditional methods are limited. The document describes how GastroPlus software simulates drug movement through the GI tract and how models are constructed and verified. It also discusses using models to predict food effects and establish in vitro-in vivo correlations to evaluate bioequivalence.