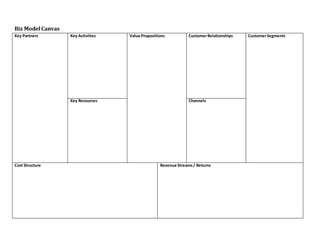
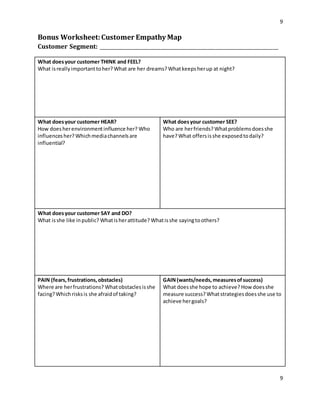
The document is a participant workbook for a startup thinking workshop focused on guiding attendees through key business model concepts and customer validation strategies. It includes worksheets for exploring customer challenges, analogs and antilogs, and developing a business model canvas, along with customer empathy mapping and validation planning. The document serves as a practical guide to help participants refine their startup ideas and strategies.








![11
11
Startup Thinking 101: Reference List
Blank, S. (2014). Steve Blank [blog]. Retrieved from http://steveblank.com
Blank, S. & Dorf, B. (2012). The Startup Owner’s Manual. Pescadero, CA: K&S Ranch
Cooper, B. & Vlaskovits, P. (2010). The Entrepreneur’s Guide to Customer
Development. Newport Beach, CA: Cooper-Vlaskovits
Komisar, J. & Mullins, R. (2009). Getting to Plan B. Cambridge, MA: Harvard Business.
MaRS. Entrepreneur’s Toolkit. Retrieved from http://www.marsdd.com/entrepreneurs-toolkit/
Mathews, B. (2012, April). Think like a Startup [white paper]. Retrieved from
http://vtechworks.lib.vt.edu/handle/10919/18649
Osterwalder, A. & Pigneur, Y. (2010). Business Model Generation. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley
Ries, E. (2011). The Lean Startup. New York: Crown.
Contact Info
Helen Kula
Librarian, Institute for Management and Innovation
University of Toronto Mississauga
helen.kula@utoronto.ca
Twitter: @helenkula
M.J. D’Elia
Head, Learning & Curriculum Support
University of Guelph
mdelia@uoguelph.ca
Twitter: @mjdelia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/il14startupthinking101workbook-141028093802-conversion-gate01/85/Startup-Thinking-101-for-Libraries-Workbook-11-320.jpg)
