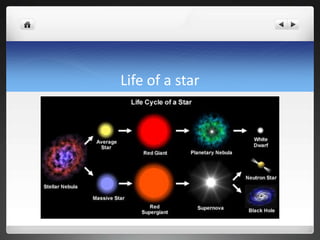
Stars are collections of dust and gas held together by gravity. They can be classified based on characteristics like temperature, luminosity, type, spectral class, and size. The main types of stars are main sequence, dwarf, giant, and supergiant stars. Nuclear fusion is the process by which stars generate energy by fusing hydrogen into helium. A star typically begins as a stellar nebula, collapses under gravity, and progresses through stages as a red giant or supergiant before exploding as a planetary nebula or supernova, eventually becoming a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole.