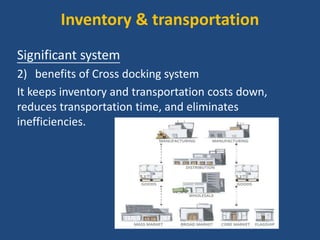
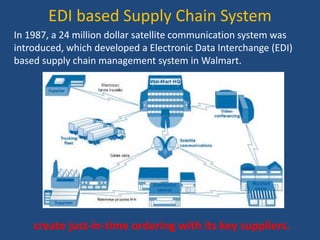
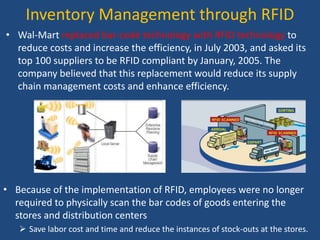
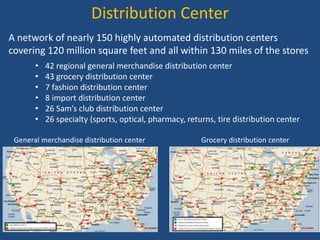
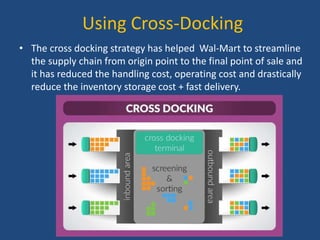
Walmart has highly efficient supply chain management that allows it to offer low prices. It uses various technologies and strategies like cross-docking, RFID, and direct sourcing to minimize costs. This includes operating a large network of distribution centers near stores for fast replenishment and avoiding storing inventory. Walmart also leverages its scale to negotiate lower prices from suppliers. As a result, it can pass cost savings on to customers through everyday low pricing.