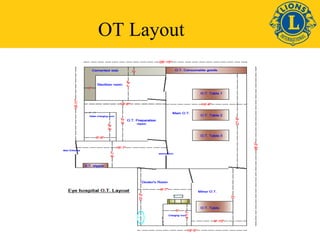
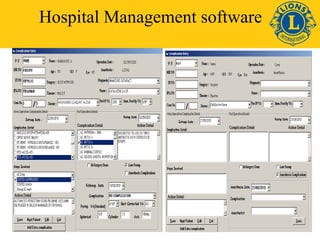
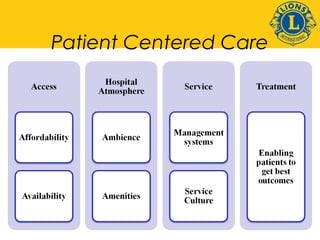
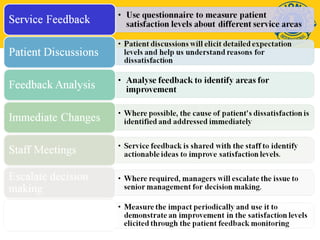
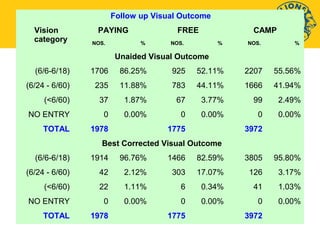
This document discusses standards for quality eye care services and infrastructure. It outlines key aspects of quality including professional performance, use of resources, risk management, and patient satisfaction. Key components of quality infrastructure are proper planning, equipment, trained staff, record maintenance, and accreditations. The document also discusses layout and facilities for outpatient departments, inpatient wards, operating theaters, and overall hospital infrastructure and emphasizes the importance of standardized procedures, staff training, and accreditation in ensuring quality of care.

![The American Medical Association defines the
quality of care services as “the degree to which
[these] services influence the probability of
optimal patient outcomes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/standardinfrastructureforqualityeyecareservices-141020160952-conversion-gate02/85/Standard-infrastructure-for-quality-eye-care-services-2-320.jpg)