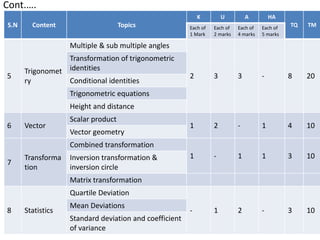
This document provides an overview of teaching optional mathematics. It discusses the nature and purpose of optional mathematics, including developing additional knowledge and skills beyond compulsory mathematics. It outlines general objectives like introducing functions and graphs. Techniques like demonstration, problem-solving, and cooperative learning are described. Materials include textbooks, practice books, and GeoGebra. Students will be evaluated through methods like observation, participation, practicums, tests, and formative/summative assessments.