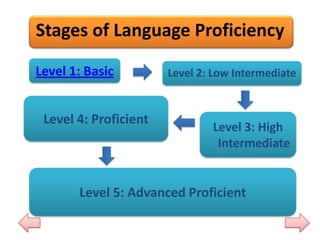
The document discusses mainstreaming English and language proficiency. It defines mainstreaming as the bridge to language proficiency, especially for listening skills. There are five stages of language proficiency from basic to advanced proficient levels. Mainstreaming is important because it acknowledges minority languages and allows students to learn in their native language before transitioning to English, helping ensure they do not fall behind in other subjects.