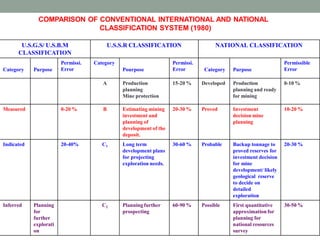
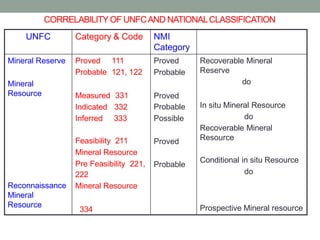
The document describes the four stages of mineral exploration:
1) Reconnaissance Surveys (G4 stage) involve wide-spaced regional surveys to identify areas for further study.
2) Preliminary Exploration (G3 stage) uses closer-spaced surveys over smaller areas to select target locations.
3) General Exploration (G2 stage) involves detailed mapping and sampling over small areas to identify economically viable zones.
4) Detailed Exploration (G1 stage) uses closely-spaced drilling to determine the precise shape, size, and grade of ore bodies.