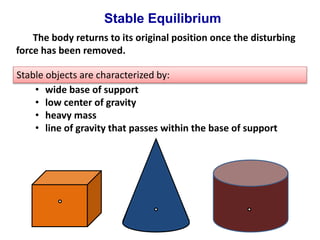
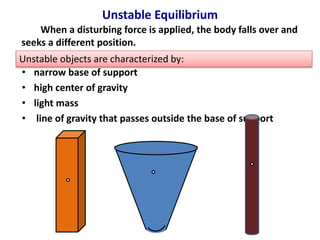
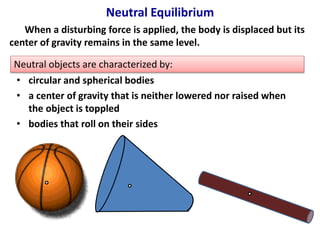
This document defines stability as the tendency of a body to return to its original state after being disturbed by restoring forces. It identifies four key factors that affect an object's stability: base of support, center of gravity, mass, and line of gravity. The document outlines the characteristics of stable, unstable, and neutral equilibrium and the types of objects that exhibit each state.