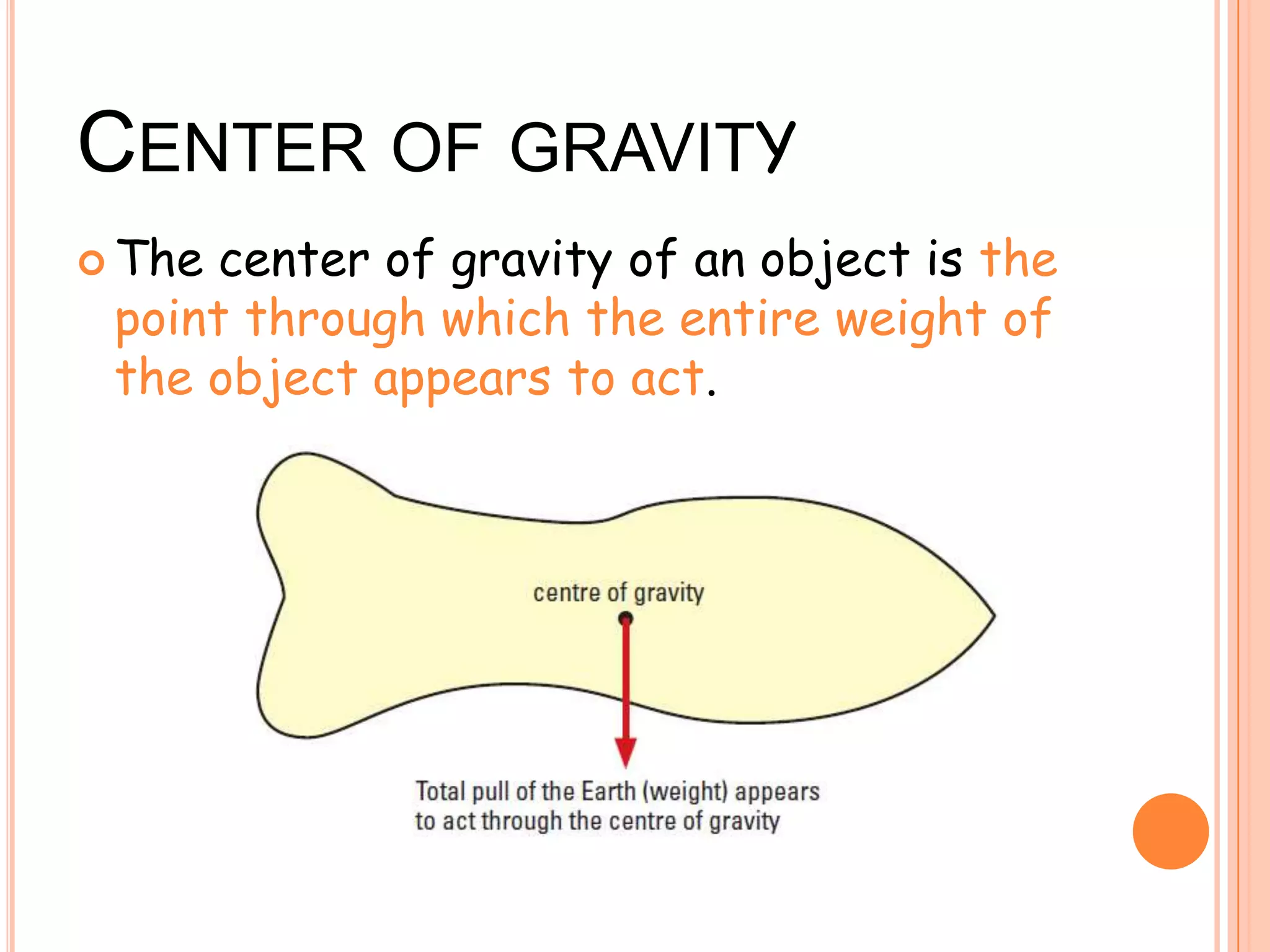
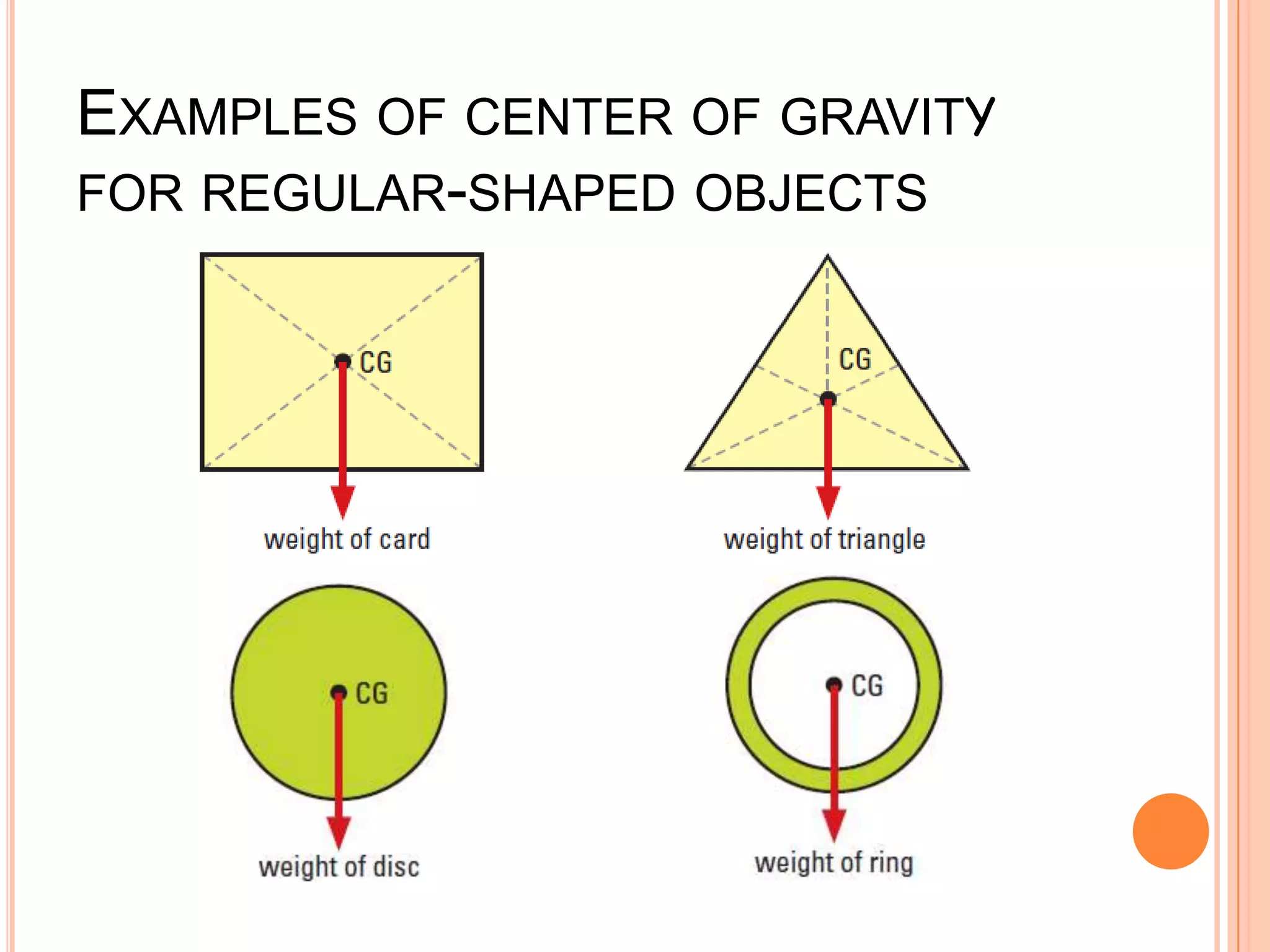
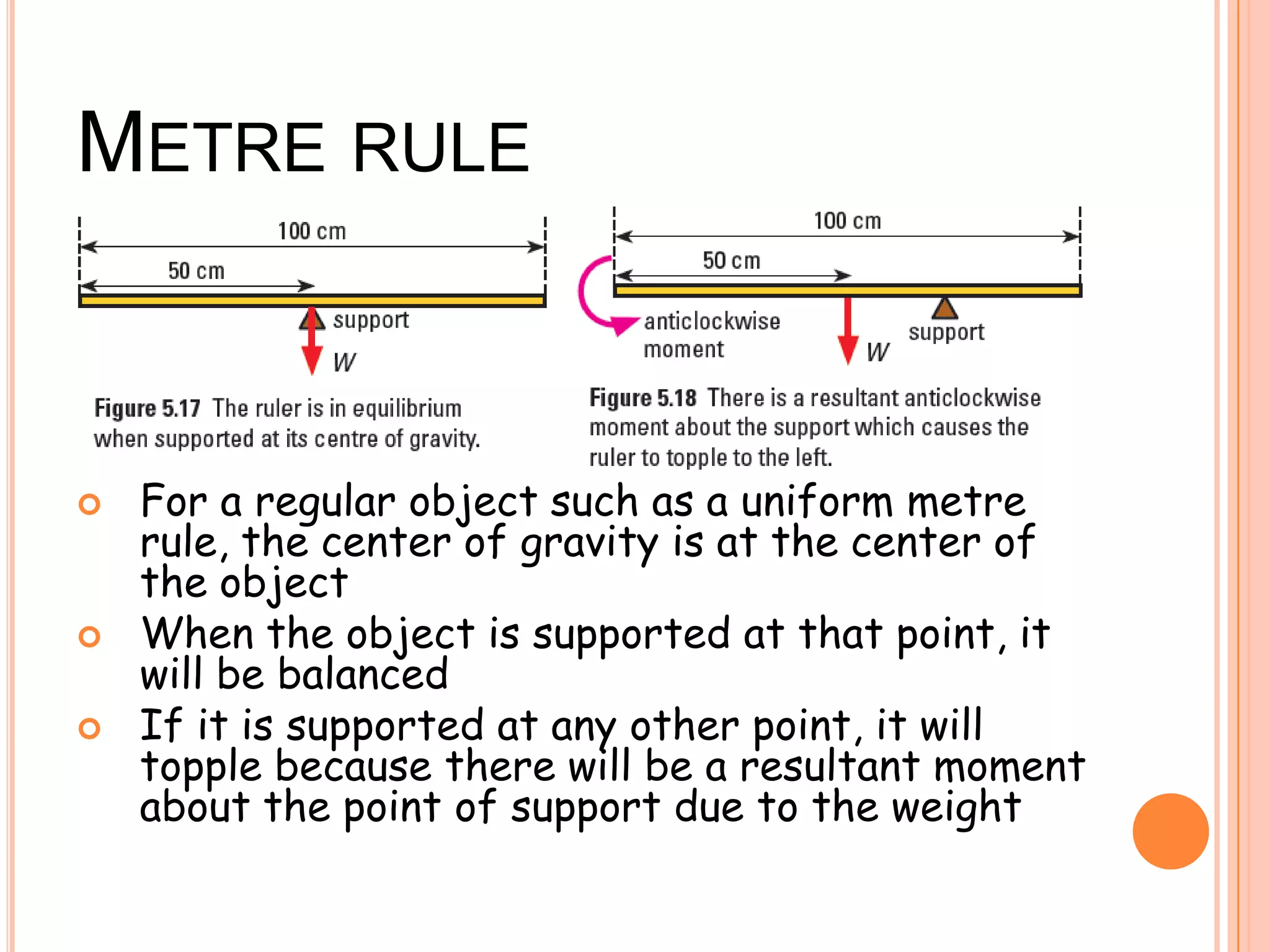
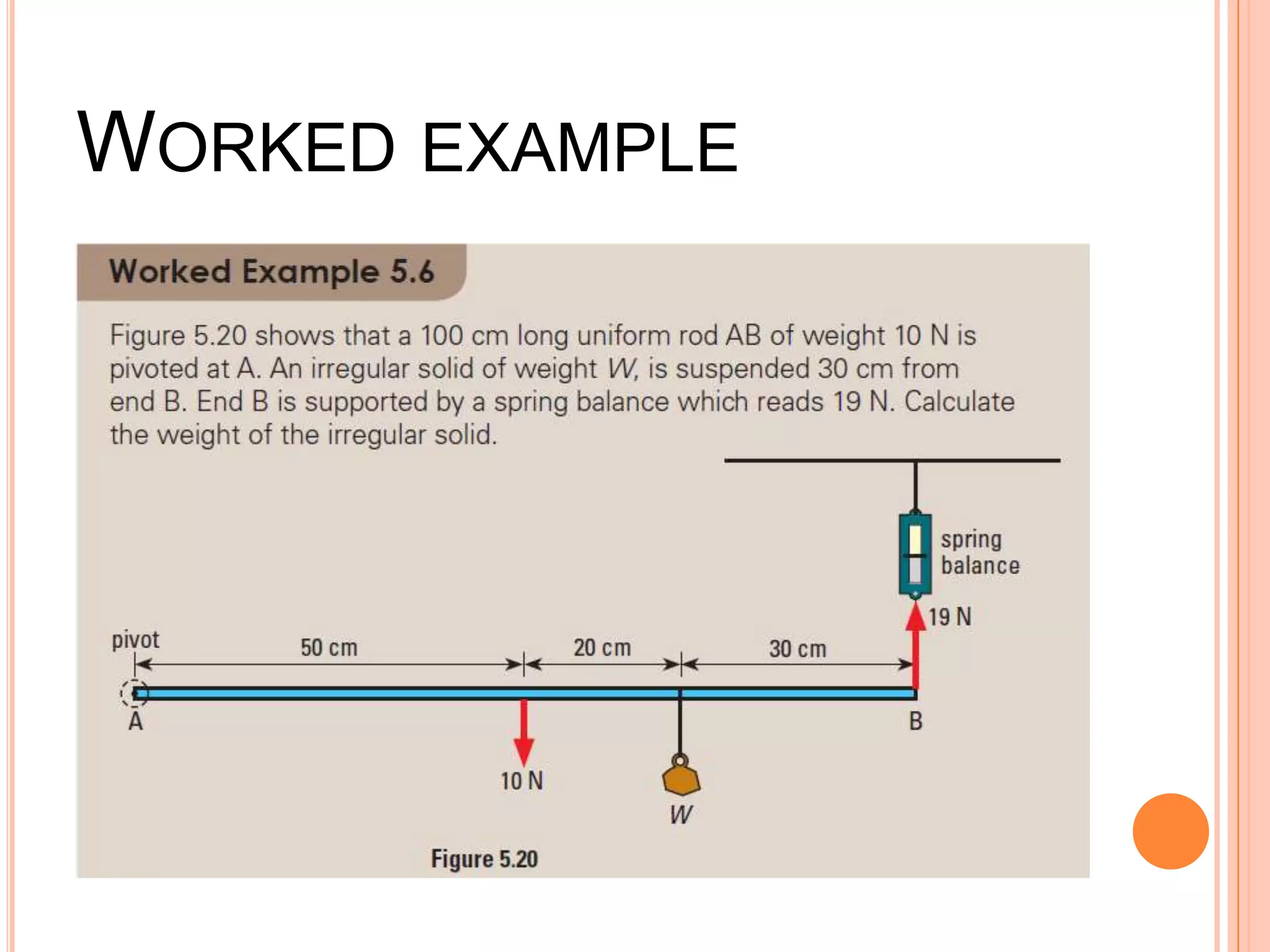
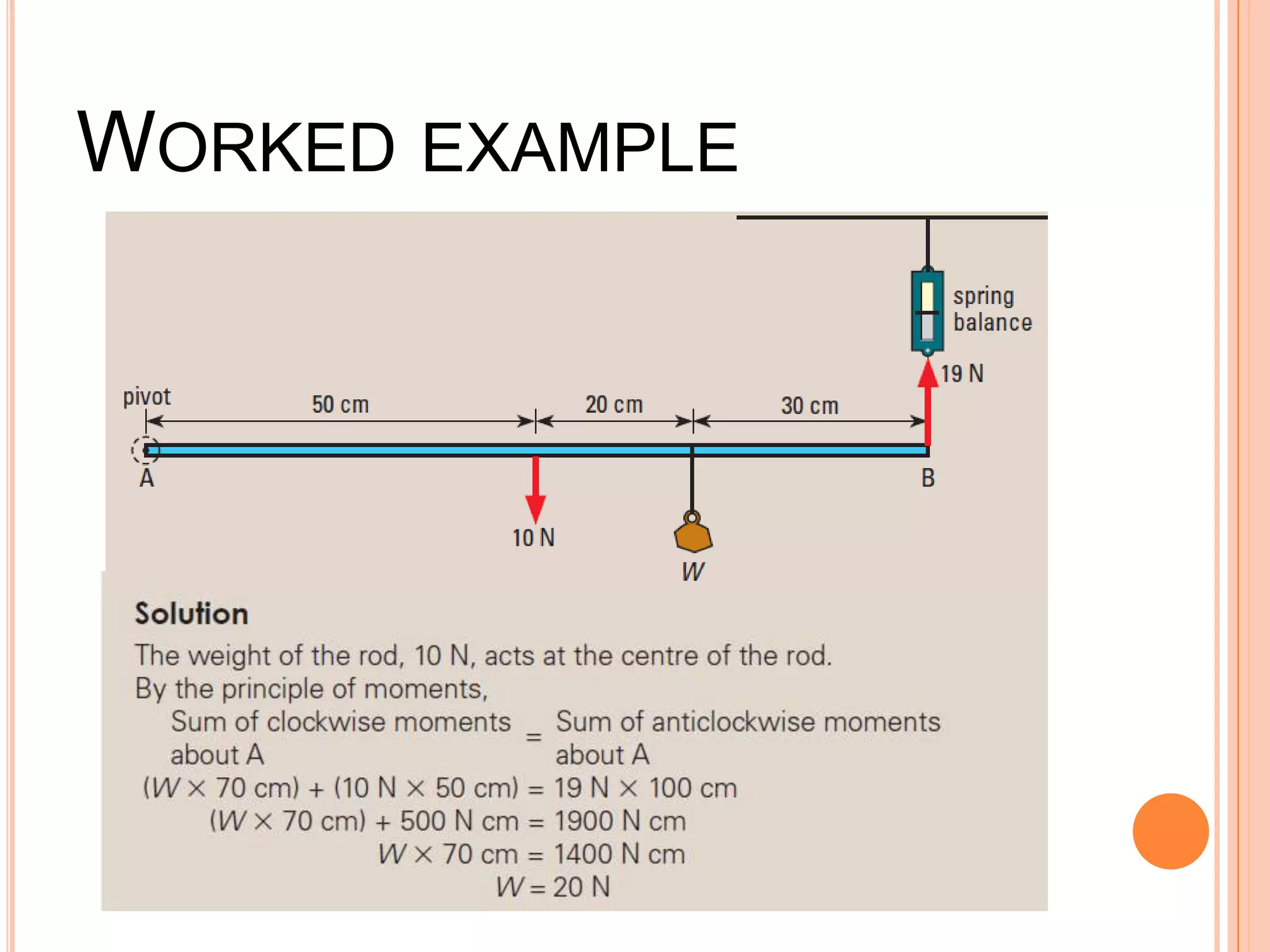
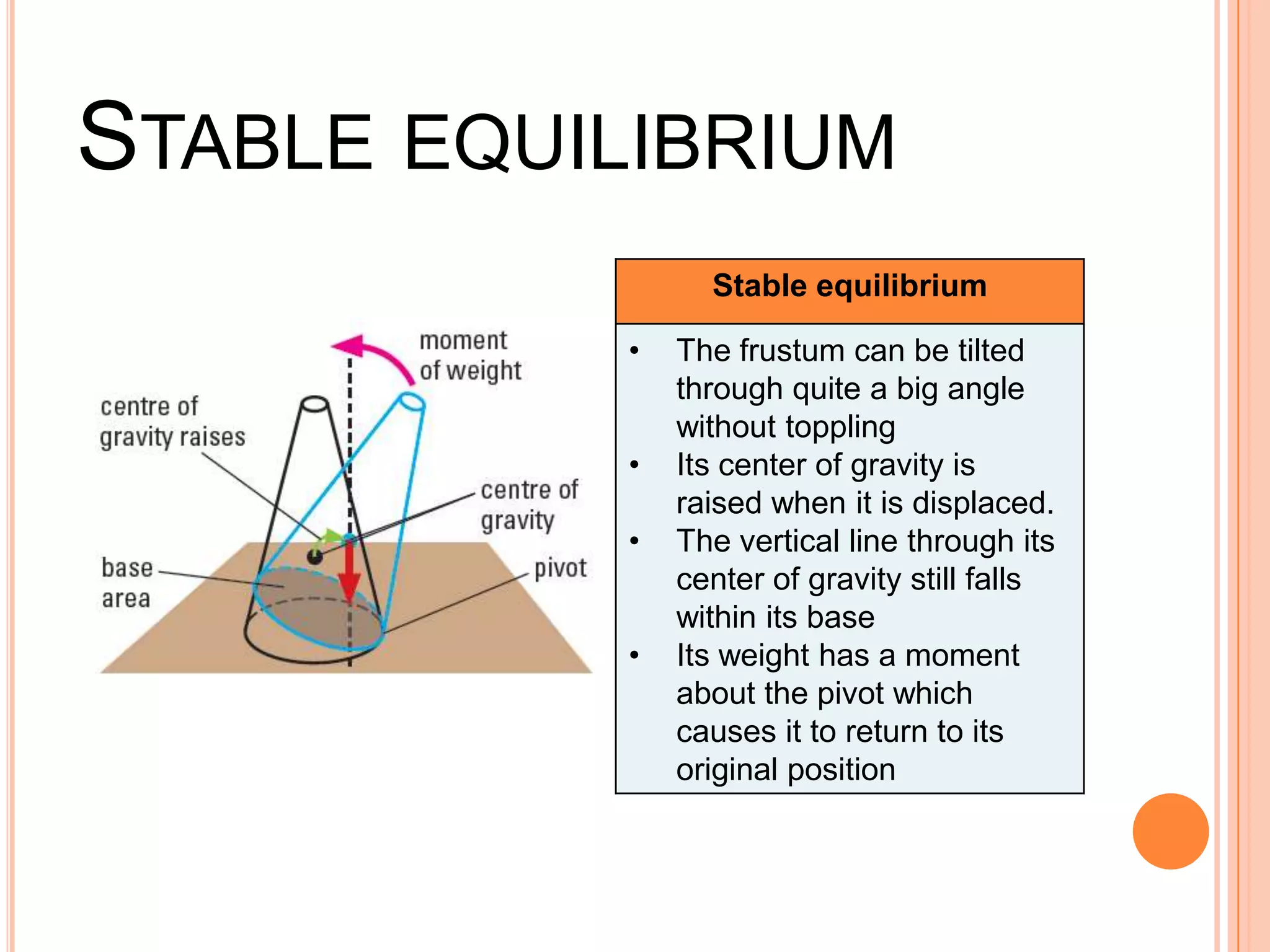
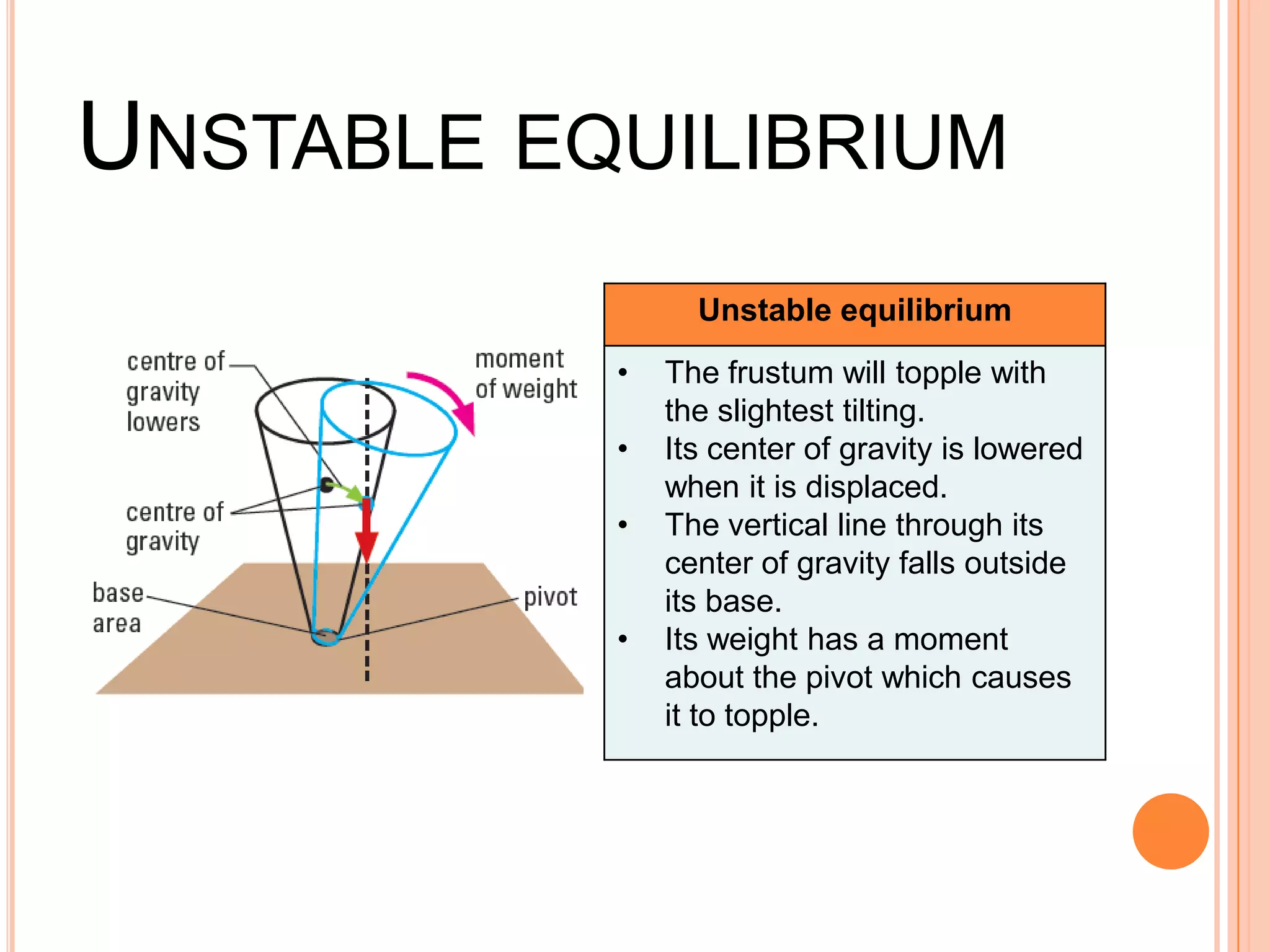
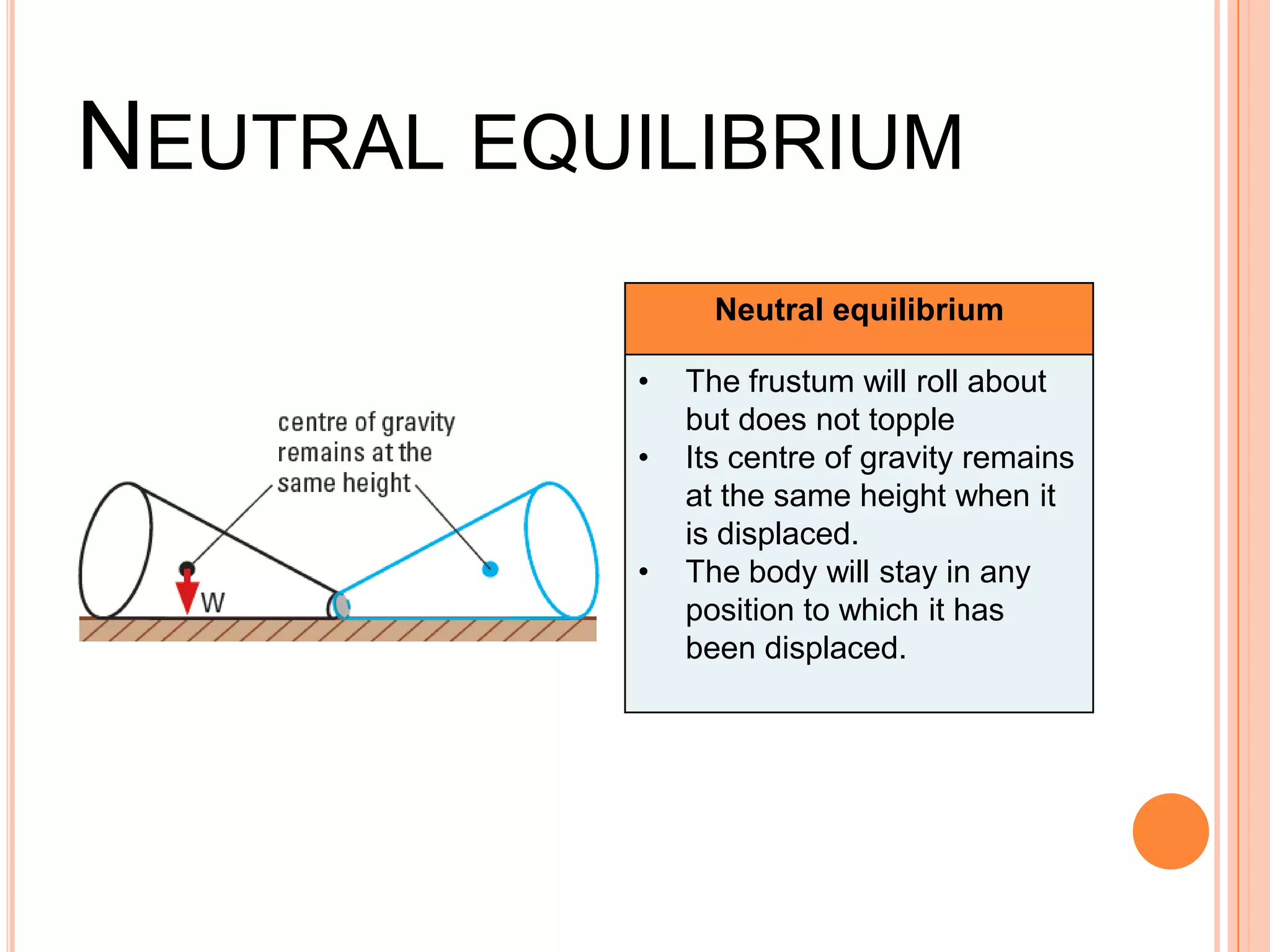
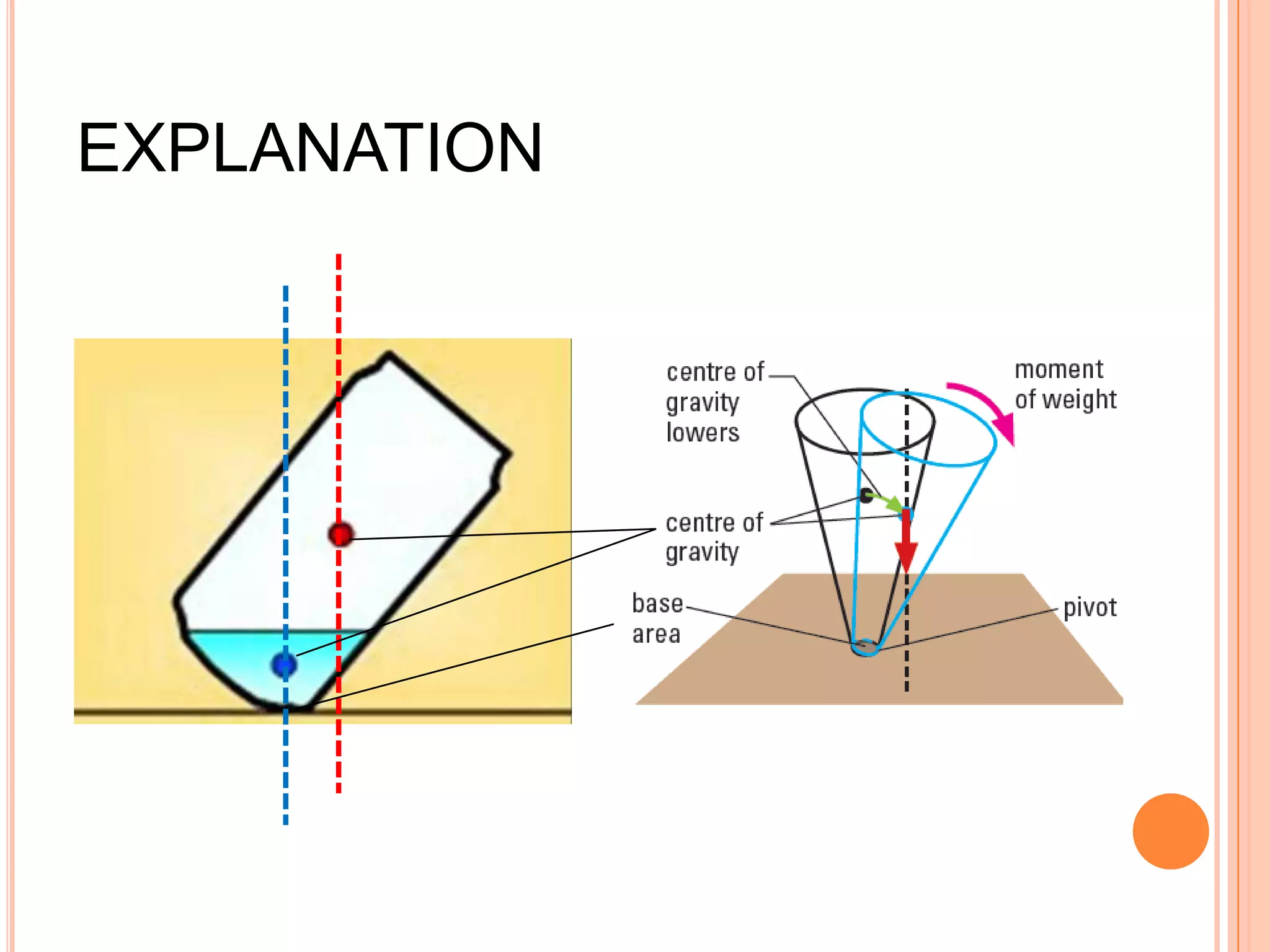
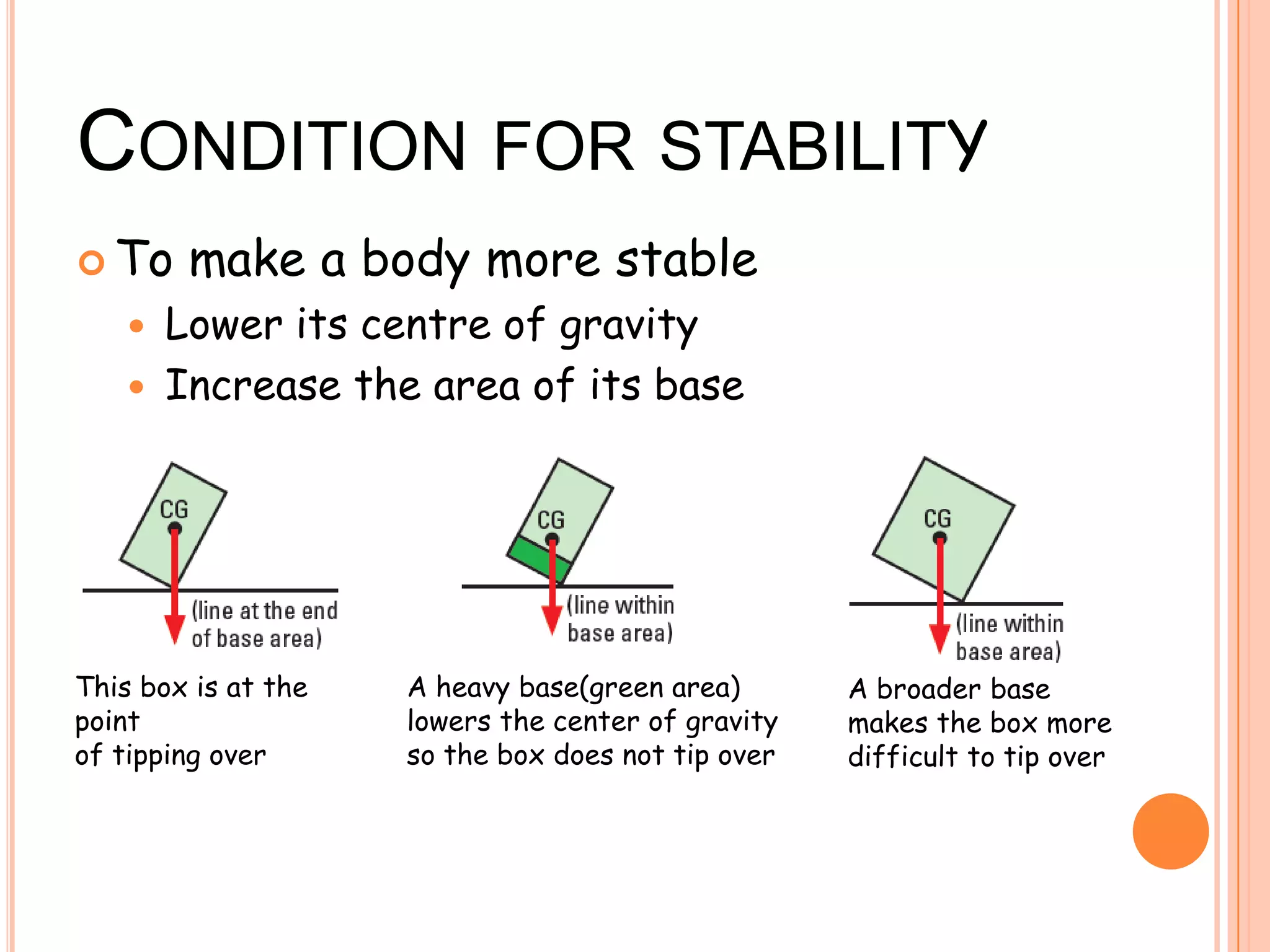
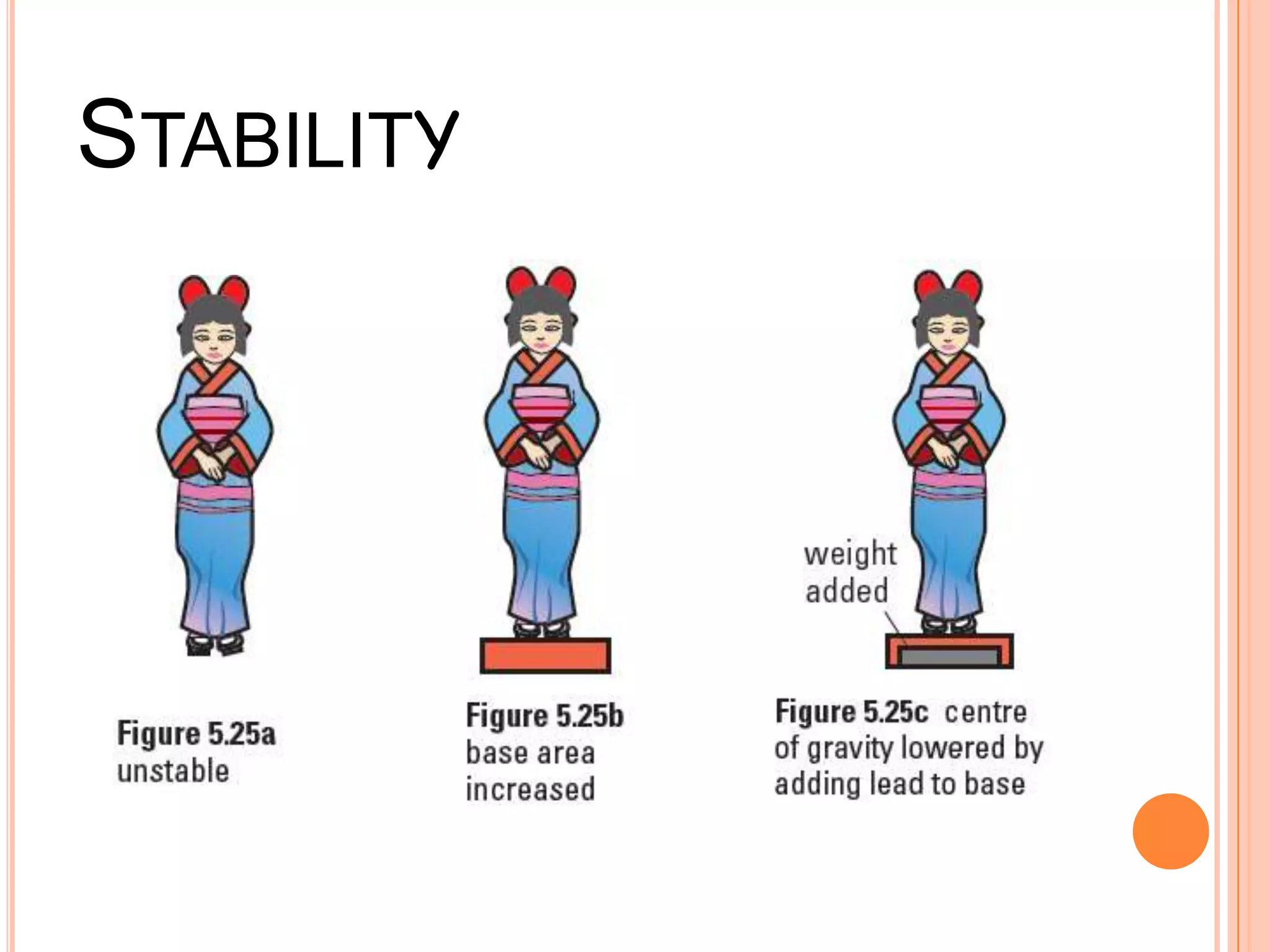
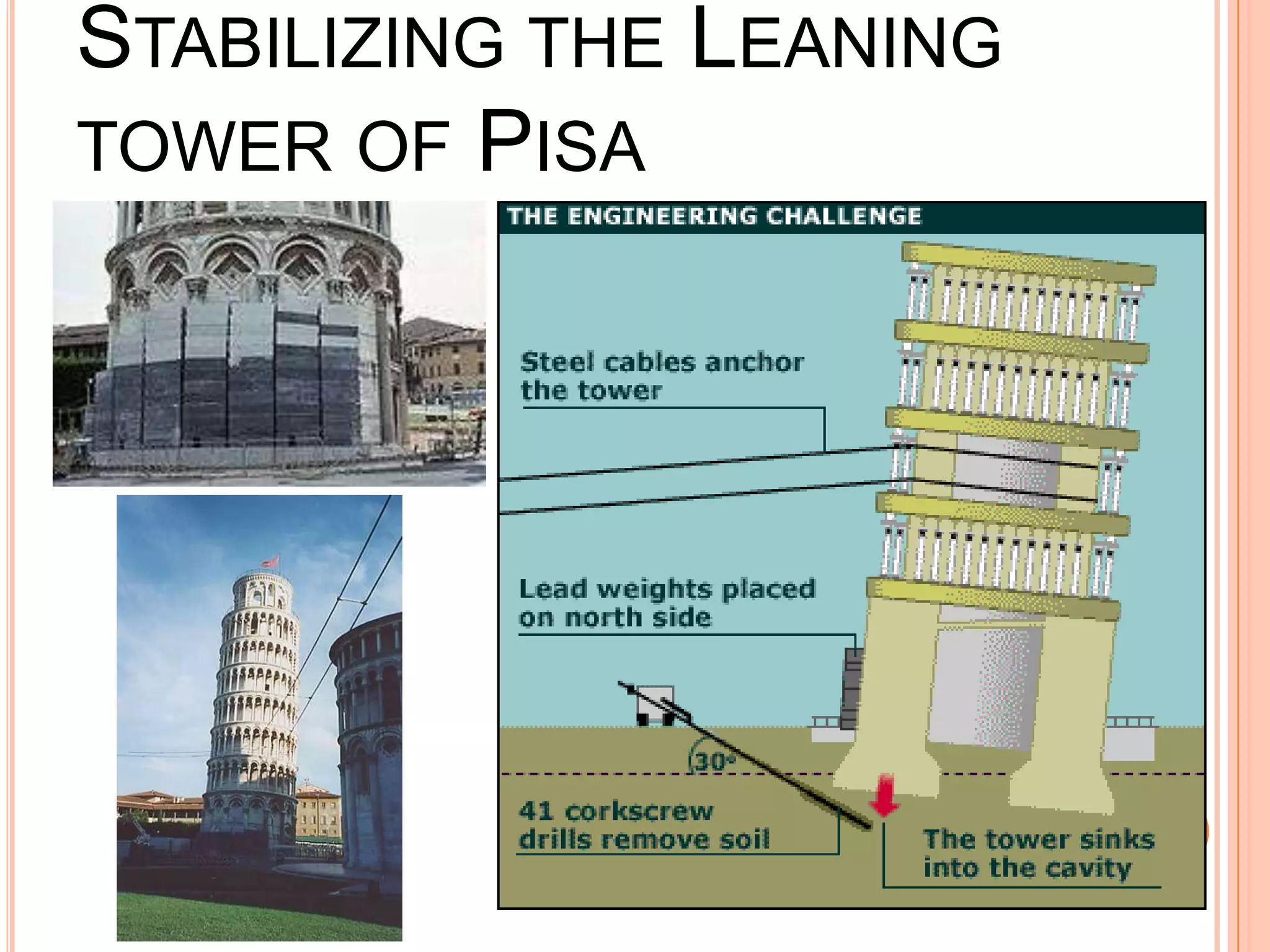
The document discusses the concept of center of gravity and how it relates to an object's stability. It defines center of gravity as the point where an object's entire weight seems to act and explains that an object's stability depends on the position of its center of gravity relative to its base. Specifically, an object will be stable if tilting moves the center of gravity higher within the base, unstable if tilting lowers it outside the base, and neutrally stable if tilting does not change the height. Real-life examples like buses and lamps are designed with low, broad bases to lower the center of gravity and increase stability.