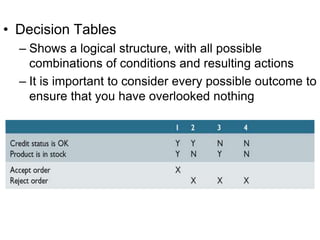
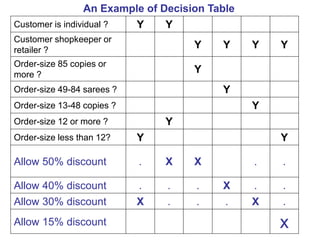
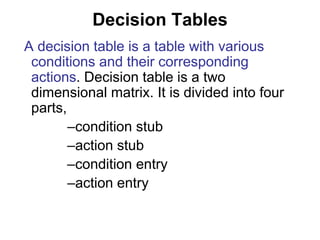
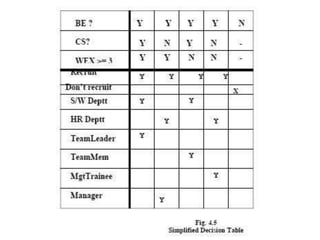
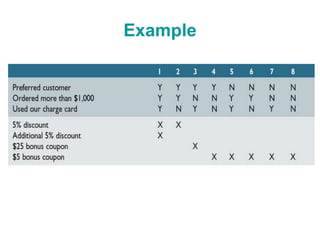
This document discusses decision tables and provides an example. It defines a decision table as a logical structure that considers all possible combinations of conditions and resulting actions. An example decision table is given showing different discount percentages given to orders based on customer type and order size. The document then provides more details on decision tables, including that they have condition and action stubs to specify the conditions being analyzed and actions taken. It outlines the steps for developing decision tables, including identifying essential factors/conditions and possible actions, calculating combinations, and filling in the table while eliminating impossible or consolidated rules.