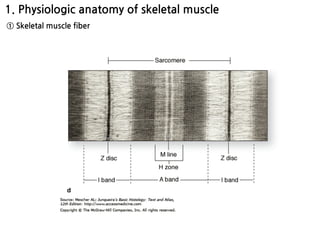
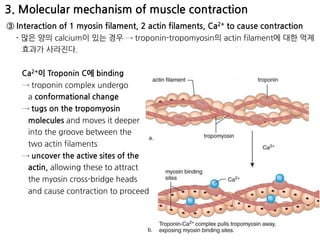
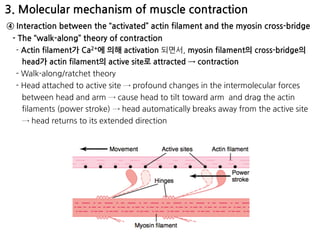
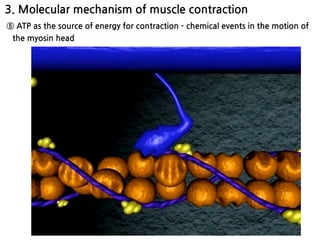
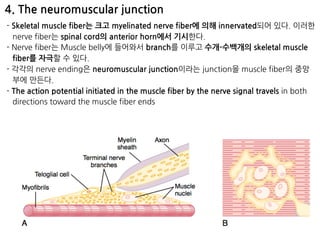
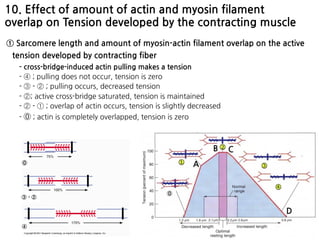
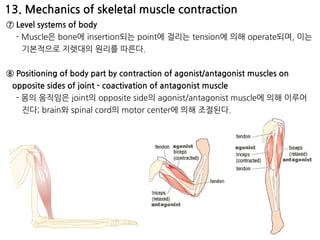
The document summarizes skeletal muscle contraction and excitation. It discusses the physiological anatomy of skeletal muscle fibers and their components. It then describes the general mechanism of muscle contraction initiated by a nerve impulse and action potential. On a molecular level, it explains the sliding filament theory and interactions between actin, myosin, calcium ions and ATP that cause contraction. Finally, it discusses the neuromuscular junction where motor neurons signal the muscle fiber and release acetylcholine to trigger muscle excitation.