This document introduces software requirement specification (SRS) and provides an example SRS for a Jazz Festival website. The key points are:
1. SRS is used to document system requirements through functional and non-functional requirements, use cases, scenarios, and other models.
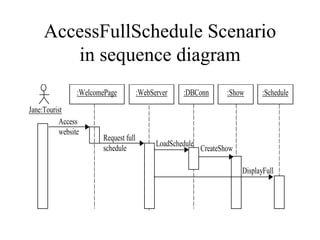
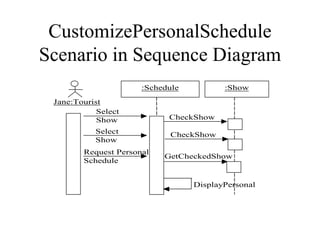
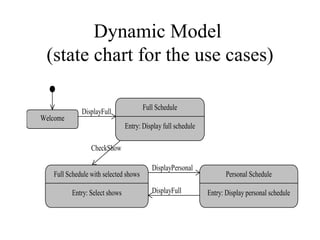
2. The example SRS is for a website that displays jazz festival show schedules and allows tourists to customize their own schedules.
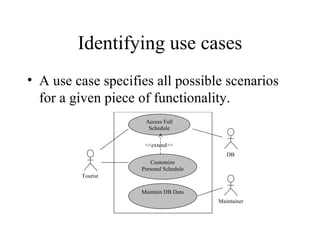
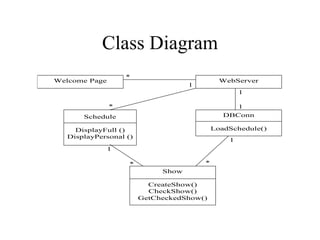
3. The SRS documents functional requirements, non-functional requirements, actors, scenarios, use cases, and class/dynamic models for the example jazz festival website system.