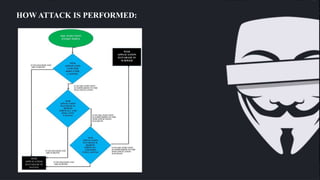
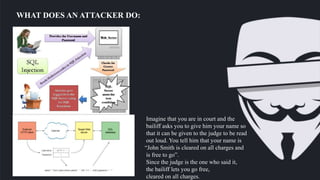
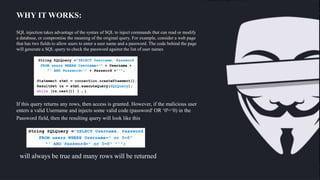
SQL injection allows attackers to execute malicious SQL statements to control a database server. This can allow attackers to access sensitive data like customer information and trade secrets. Attackers can bypass authentication, impersonate users, disclose all database data, and alter stored data affecting integrity. SQL injection works by exploiting how SQL syntax parses queries, allowing injected code to be treated as data. Developers can prevent SQL injection by using prepared statements, stored procedures, and escaping all user input.