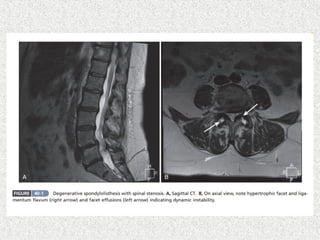
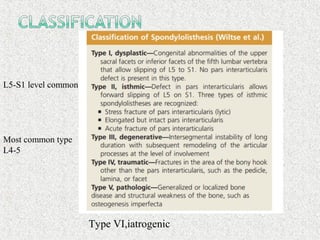
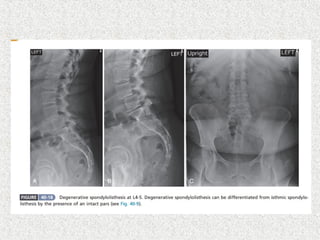
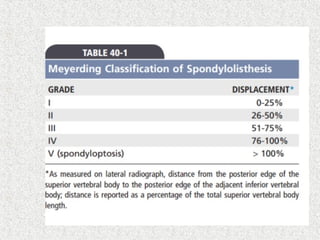
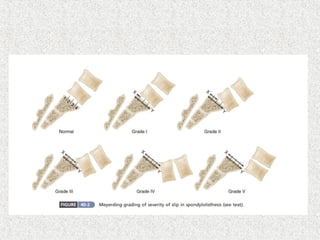
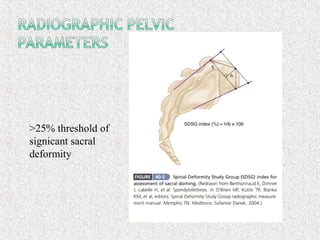
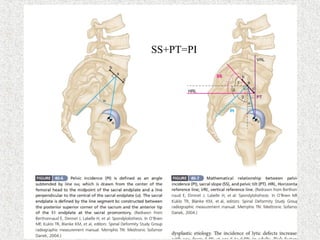
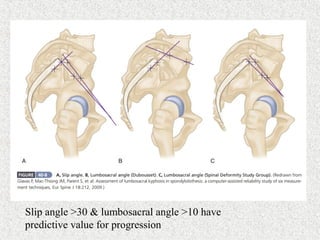
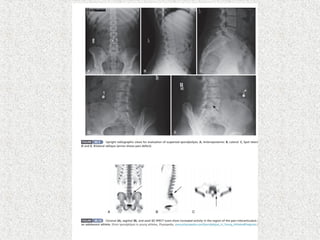
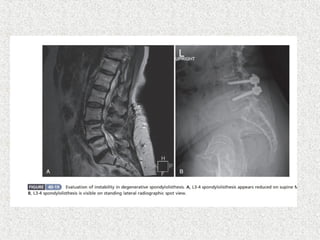
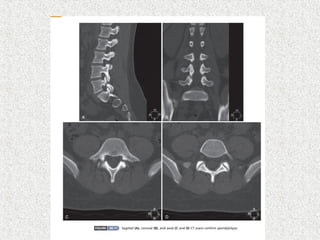
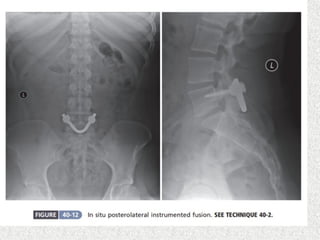
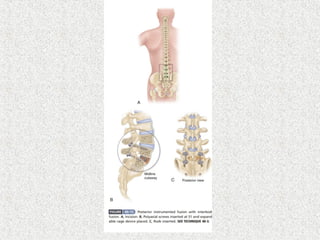
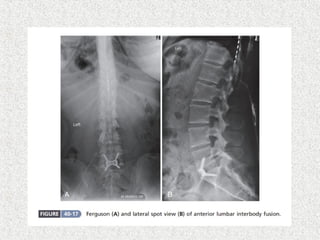
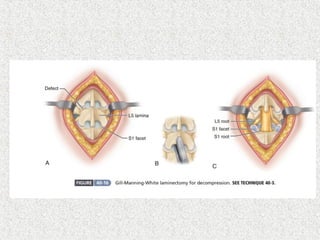
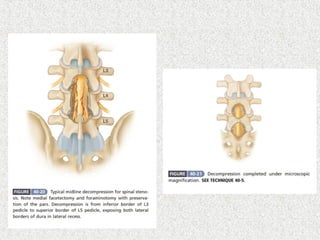
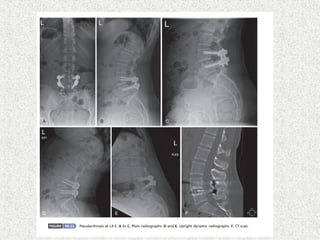
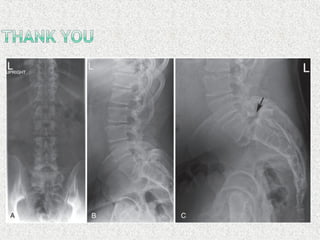
Spondylolisthesis is the anterior displacement of one vertebra over another and is usually caused by the failure of anatomical structures like facets or the posterior bony arch. It is most commonly seen at L4-L5 and L5-S1 levels. Symptoms include axial pain, neurogenic claudication, and radiculopathy. Treatment depends on the degree of slip and presence of neurological symptoms, ranging from conservative management to surgical procedures like fusion either with or without instrumentation.