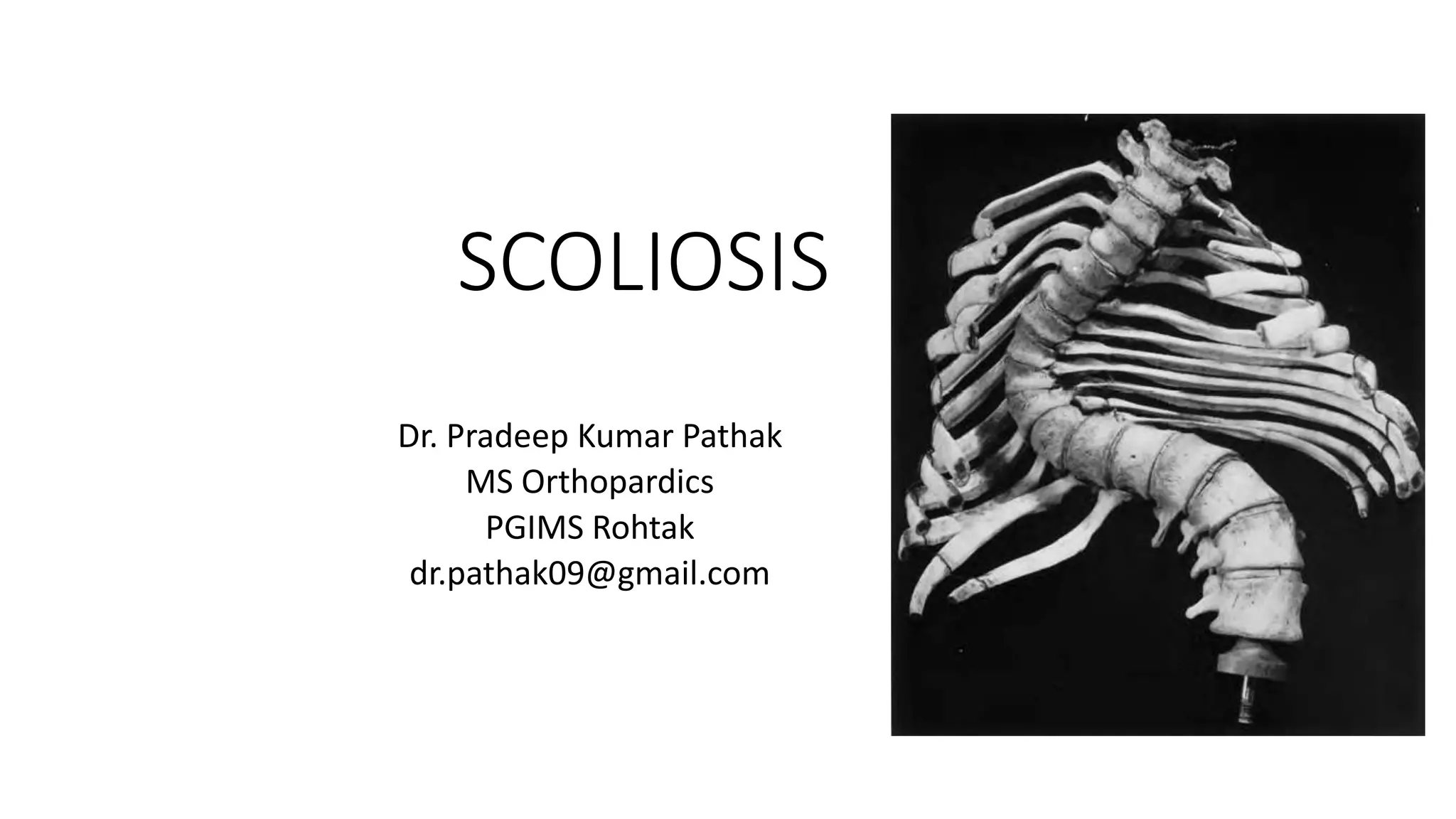
This document discusses different types of scoliosis including infantile, juvenile, adolescent, and adult scoliosis. It describes the key characteristics, assessment methods including radiographic evaluation, and treatment approaches for each type. Treatment may include bracing, casting, or surgery depending on the curve magnitude, progression risk, and remaining growth potential. Juvenile idiopathic scoliosis often progresses more than adolescent scoliosis and is less responsive to bracing, so surgery is more common. Infantile scoliosis is assessed using rib-vertebral angle difference and phase, and casting is used before bracing or surgery for progressive curves.