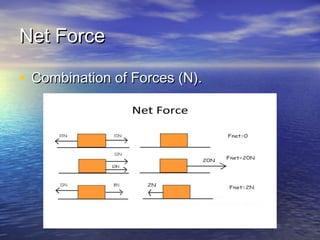
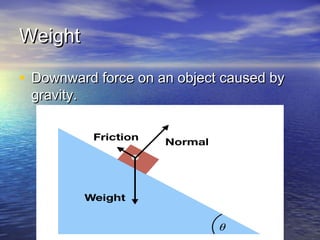
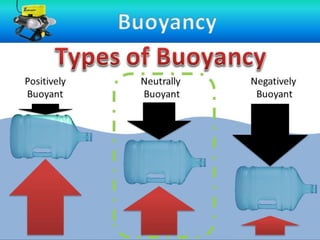
The document discusses the principles of buoyancy, weight, density, and their relationship with floating and sinking objects, using the Titanic as a case study. Key concepts include Archimedes' principle, the roles of net force and displacement, and how changes in density affect an object's ability to float or sink. It also outlines experiments and questions for further understanding of these principles.