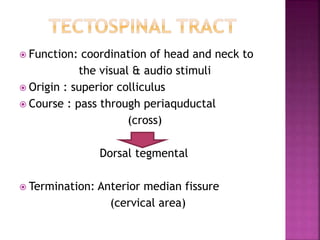
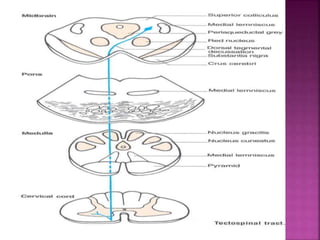
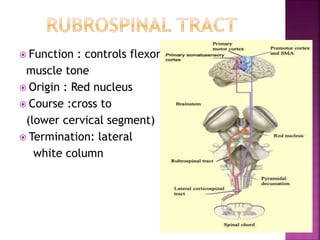
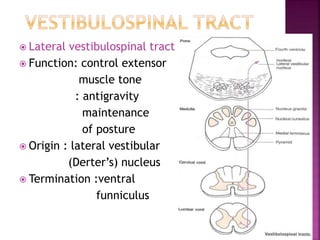
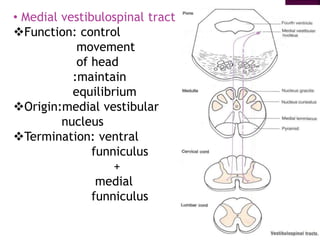
The document summarizes the structure and function of the spinal cord. It discusses the following key points:
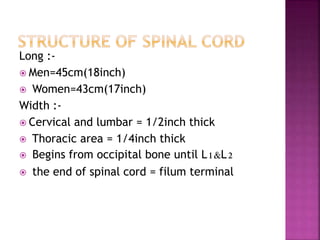
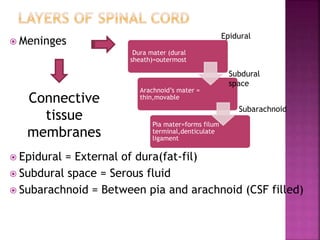
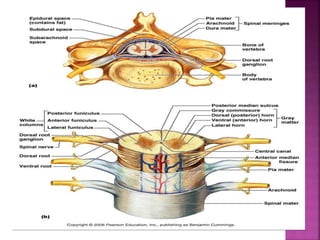
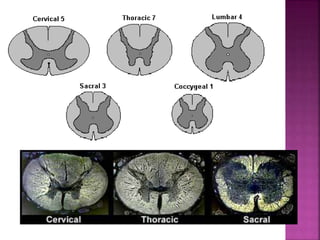
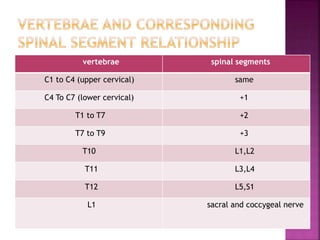
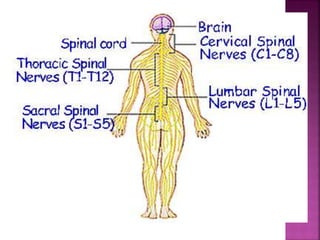
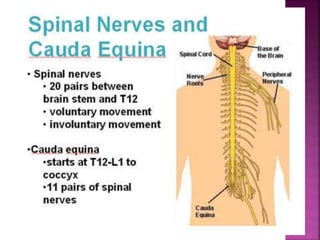
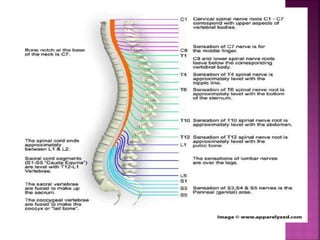
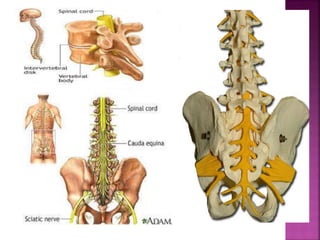
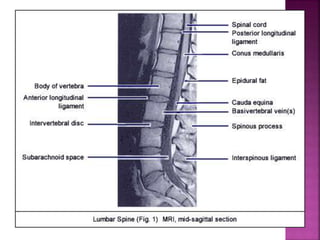
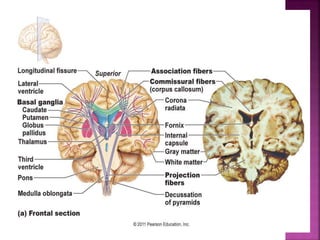
- The spinal cord is approximately 45cm long in men and 43cm in women, and is protected by three meninges. It contains 31 segments that contribute nerves to different parts of the body.
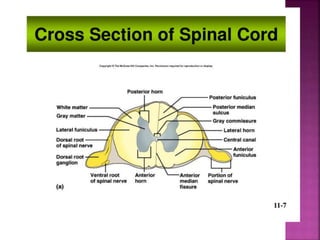
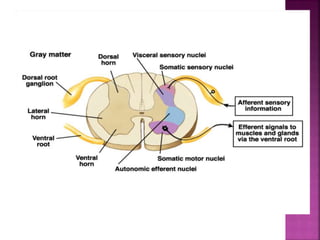
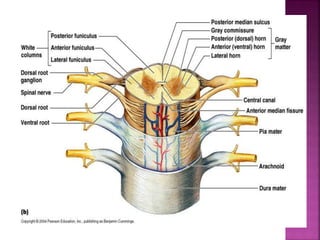
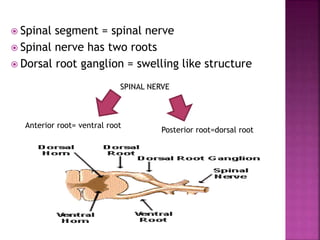
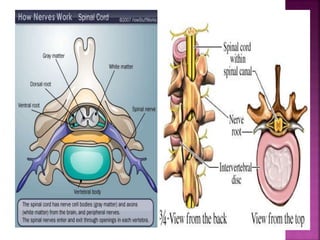
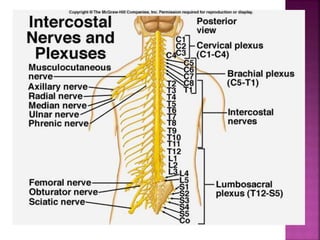
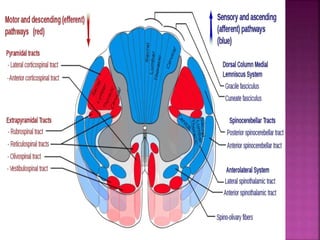
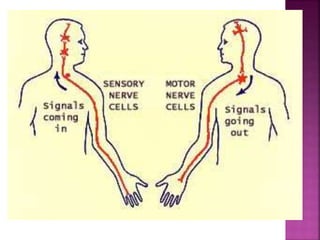
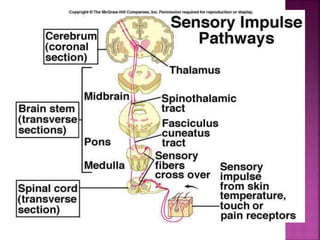
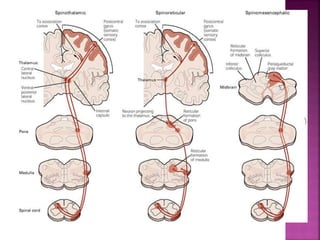
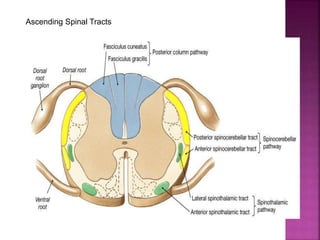
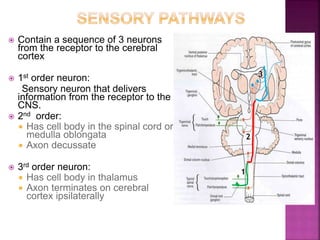
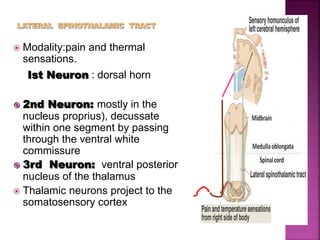
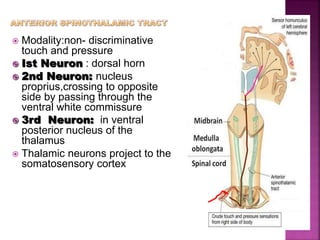
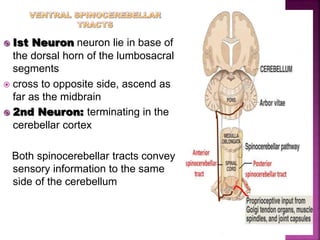
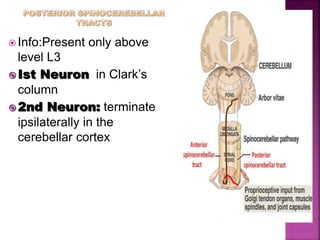
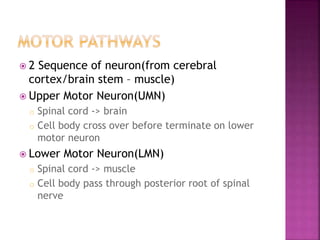
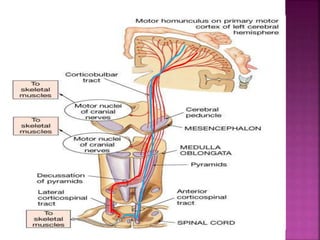
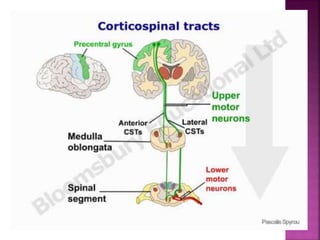
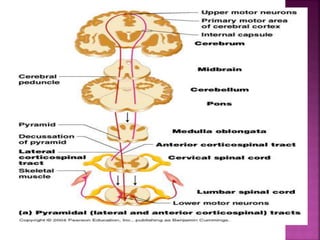
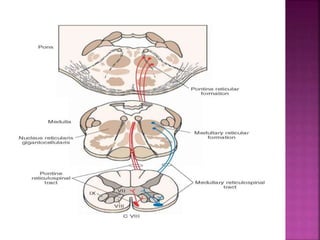
- Spinal nerves emerge from each segment and contain a dorsal root with sensory fibers and an anterior root with motor fibers. Ascending tracts transmit sensory information to the brain and descending tracts convey motor commands from the brain.
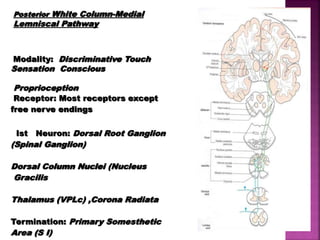
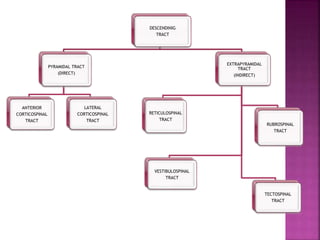
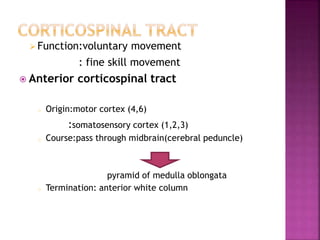
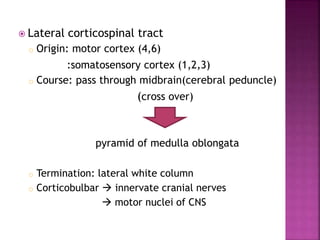
- The principal ascending tracts are the posterior white column, anterolateral system, and spinocerebellar tract. The main descending tracts include the pyramidal,