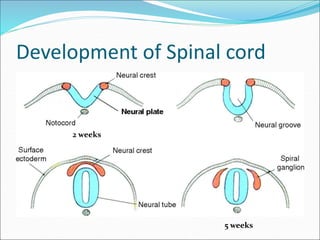
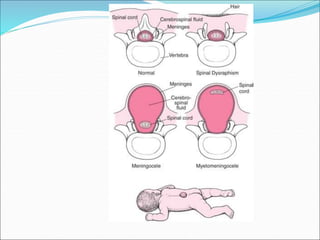
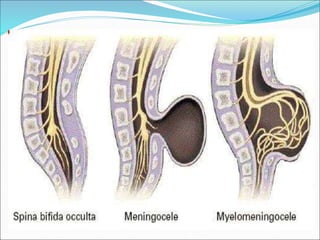
This document defines and describes different types of spina bifida, a congenital defect involving the posterior bony wall of the spinal canal. It notes that spina bifida occurs most commonly in the lumbosacral region due to a failure of fusion of vertebral arches during development. The main types discussed are spina bifida occulta, meningocele, myelomeningocele, syringomyelocele, and myelocele, with descriptions of their characteristics and clinical presentations. Neurological deficits vary depending on whether the spinal cord or meninges are involved in the protrusion.