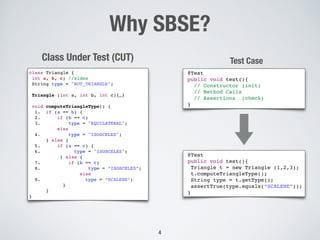
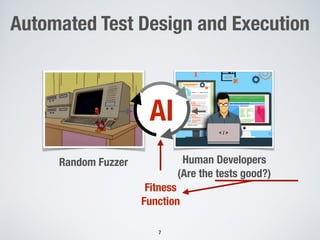
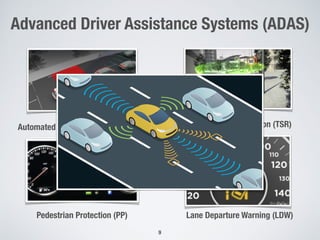
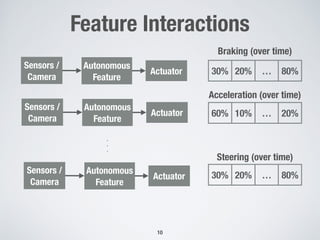
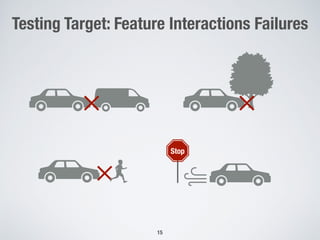
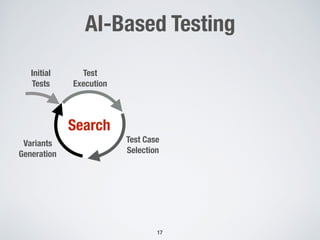
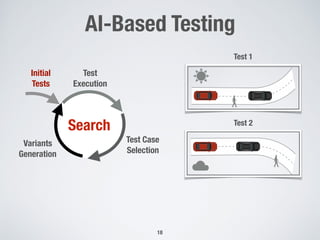
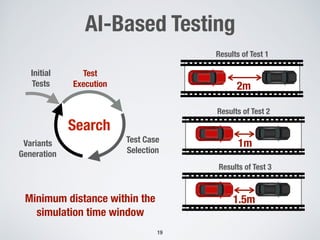
The document discusses the use of computational intelligence to enhance software testing, specifically through search-based software testing (SBST) techniques and their application in testing advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). It highlights various AI-based methodologies for automated test design, execution, and selection focused on optimizing test cases and discovering feature interaction failures. Additionally, the document provides insights into real-world case studies and tools developed for improving testing efficiency and effectiveness.











![References
[1] R. Abdessalem, A. Panichella, S. Nejati, L. Briand, T. Stifter, "Testing Autonomous Cars for Feature Interaction
Failures using Many-Objective Search". The 33rd IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software
Engineering (ASE 2018), Montpellier, France.
[2] D. Di Nucci, A. Panichella, A. Zaidman, A. De Lucia. "A Test Case Prioritization Genetic Algorithm guided by the
Hypervolume Indicator". Transactions on Software Engineering (TSE) 2018 | To appear.
[3] A. Panichella, F. M. Kifetew, P. Tonella. " A Large Scale Empirical Comparison of State-of-the-art Search-based
Test Case Generators". Information and Software Technology (IST) 2018 | To appear
[4] D. Appelt, C. D. Nguyen, A. Panichella, L. Briand. "A Machine Learning-Driven Evolutionary Approach for
Testing Web Application Firewalls". IEEE Transactions on Reliability (TR) 2018 | To appear.
[5] S. Jan, A. Panichella, A. Arcuri, L. Briand. Automatic Generation of Tests to Exploit XML Injection Vulnerabilities
in Web Applications. Transactions on Software Engineering (TSE) 2018. To appear
[6] A. Panichella, F. M. Kifetew, P. Tonella. Automated Test Case Generation as a Many-Objective Optimisation
Problem with Dynamic Selection of the Targets. Transactions on Software Engineering (TSE) 2018, volume 44,
issue 2, pp 122-158. doi:10.1109/TSE.2017.2663435
!29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sen2019-190204100826/85/Speeding-up-Software-Testing-With-Computational-Intelligence-29-320.jpg)