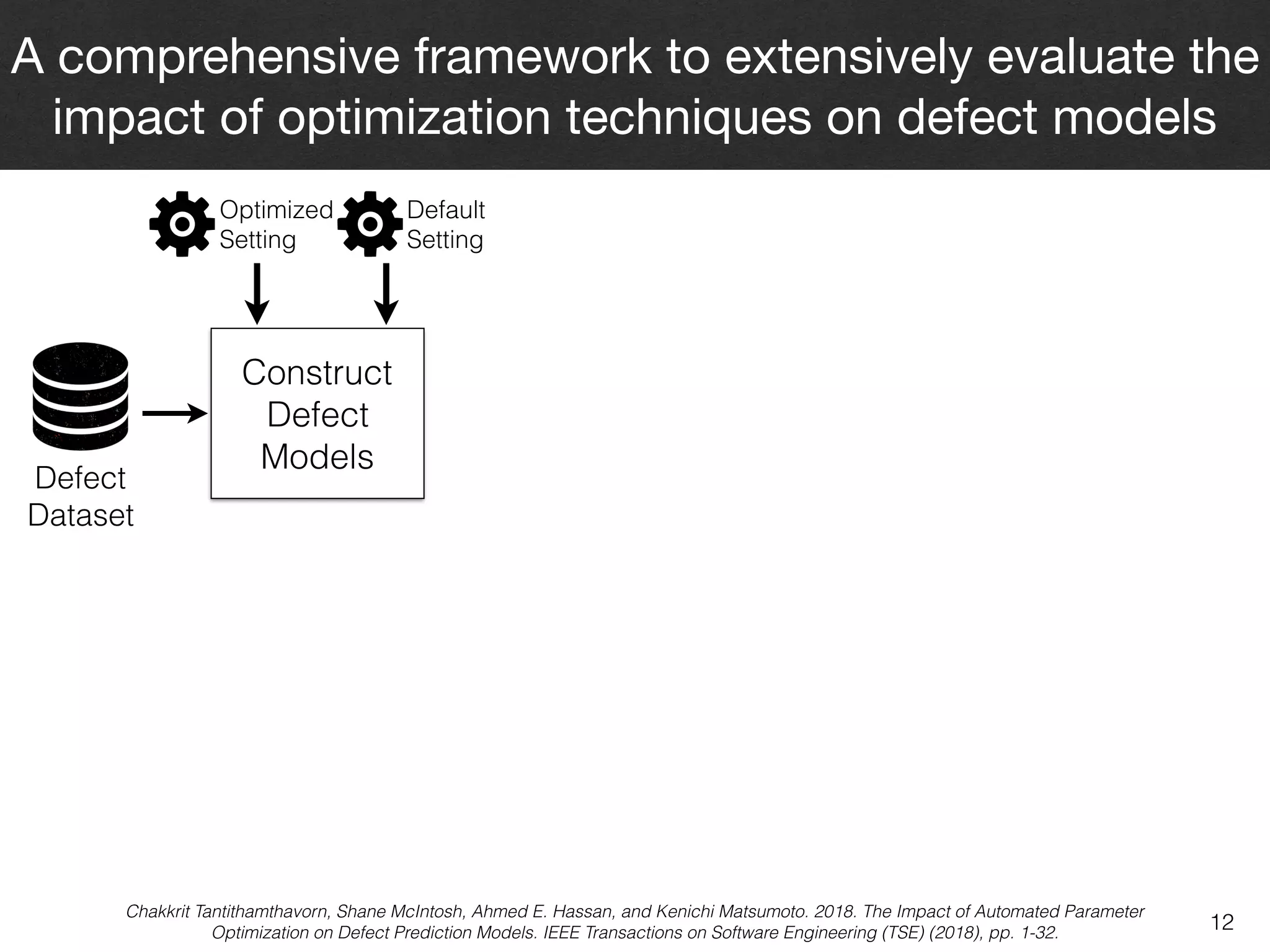
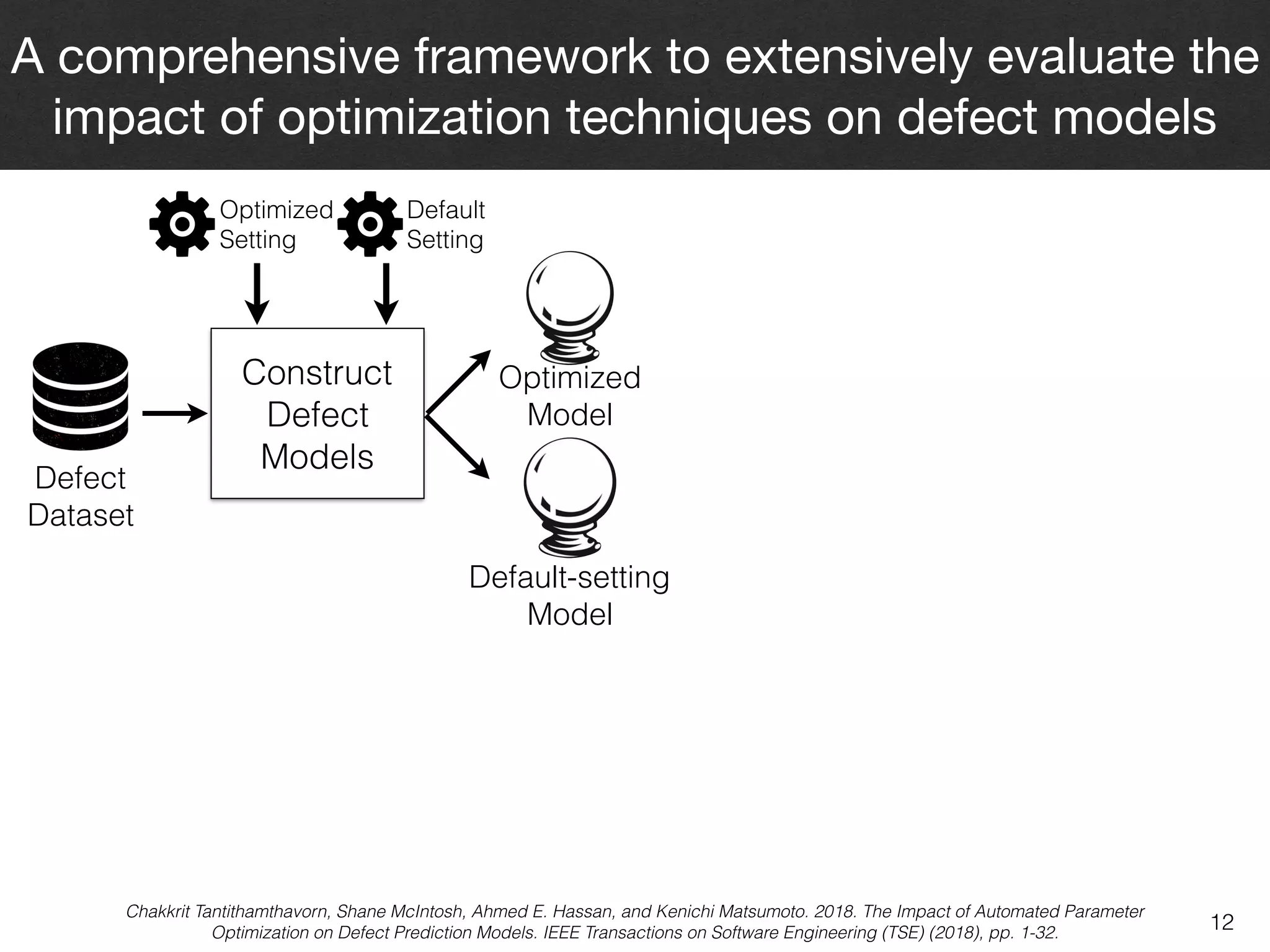
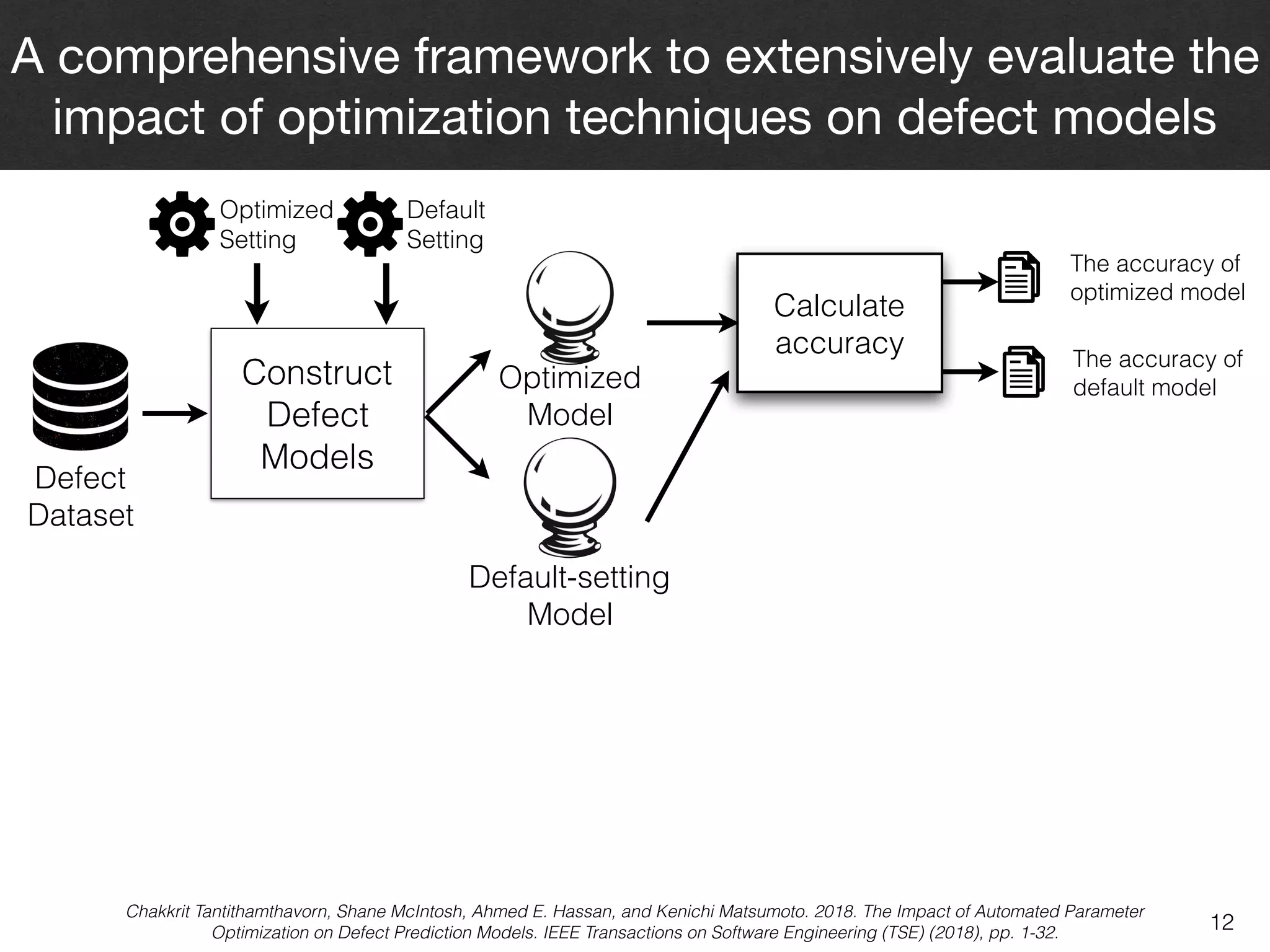
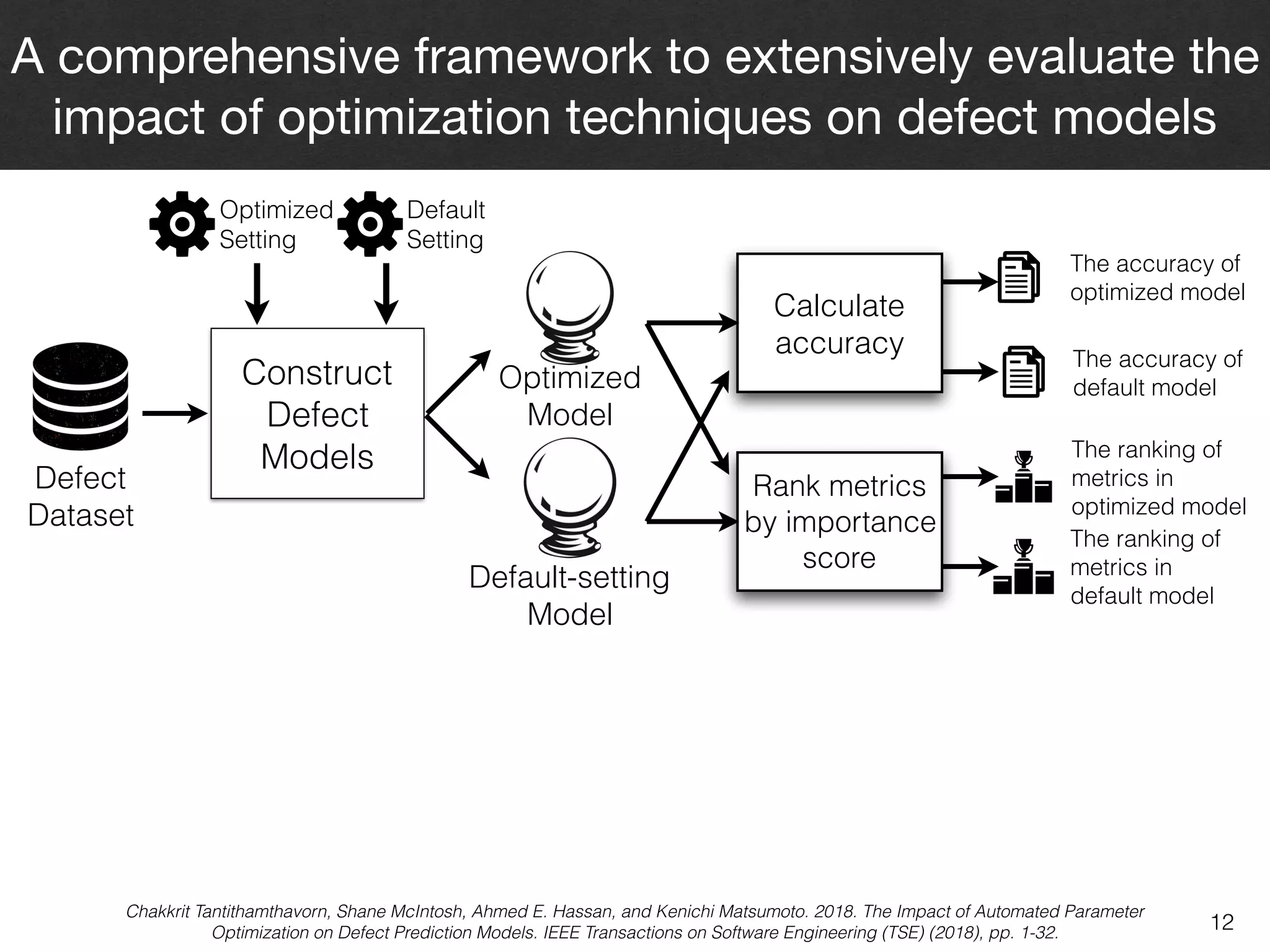
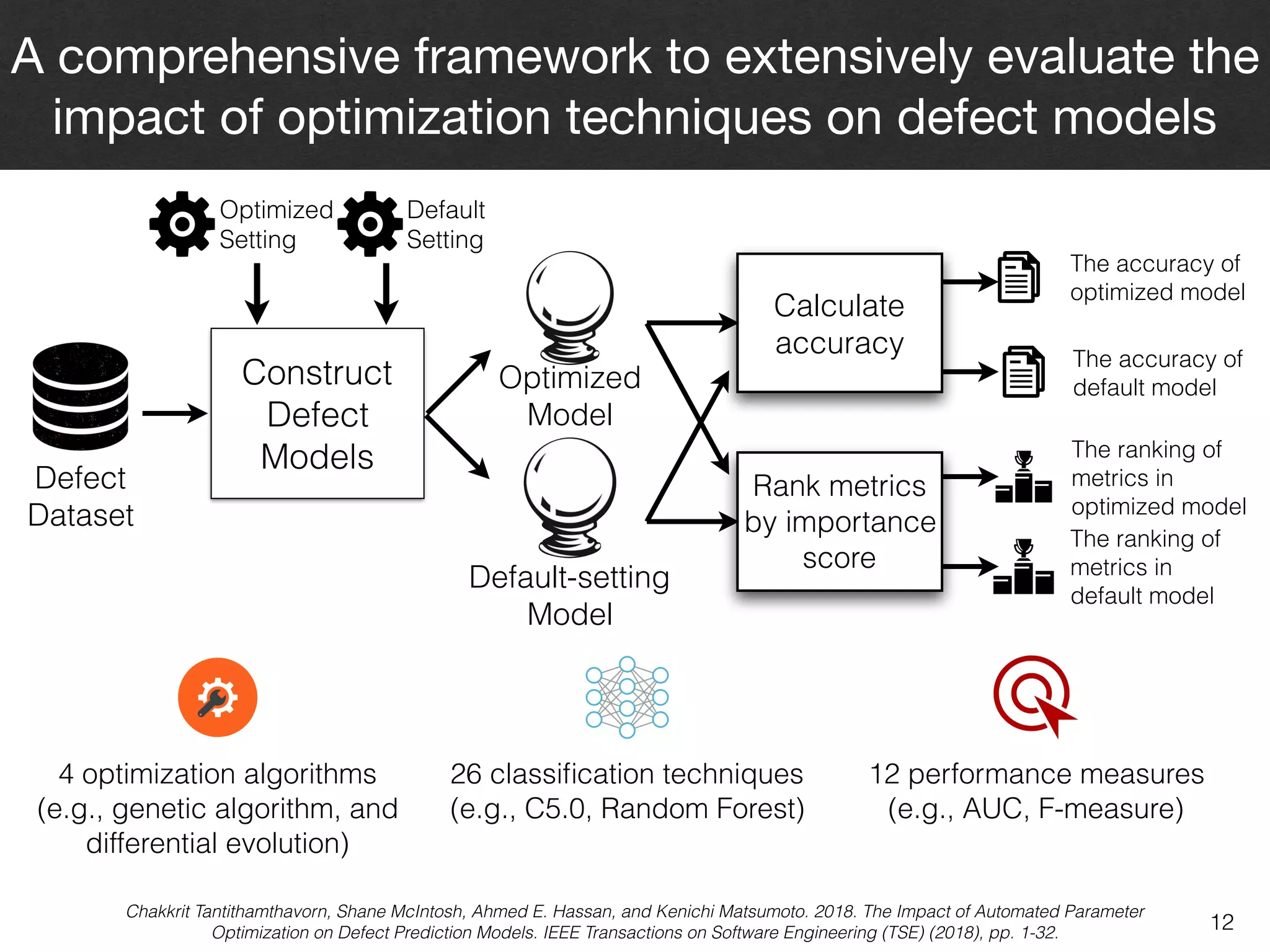
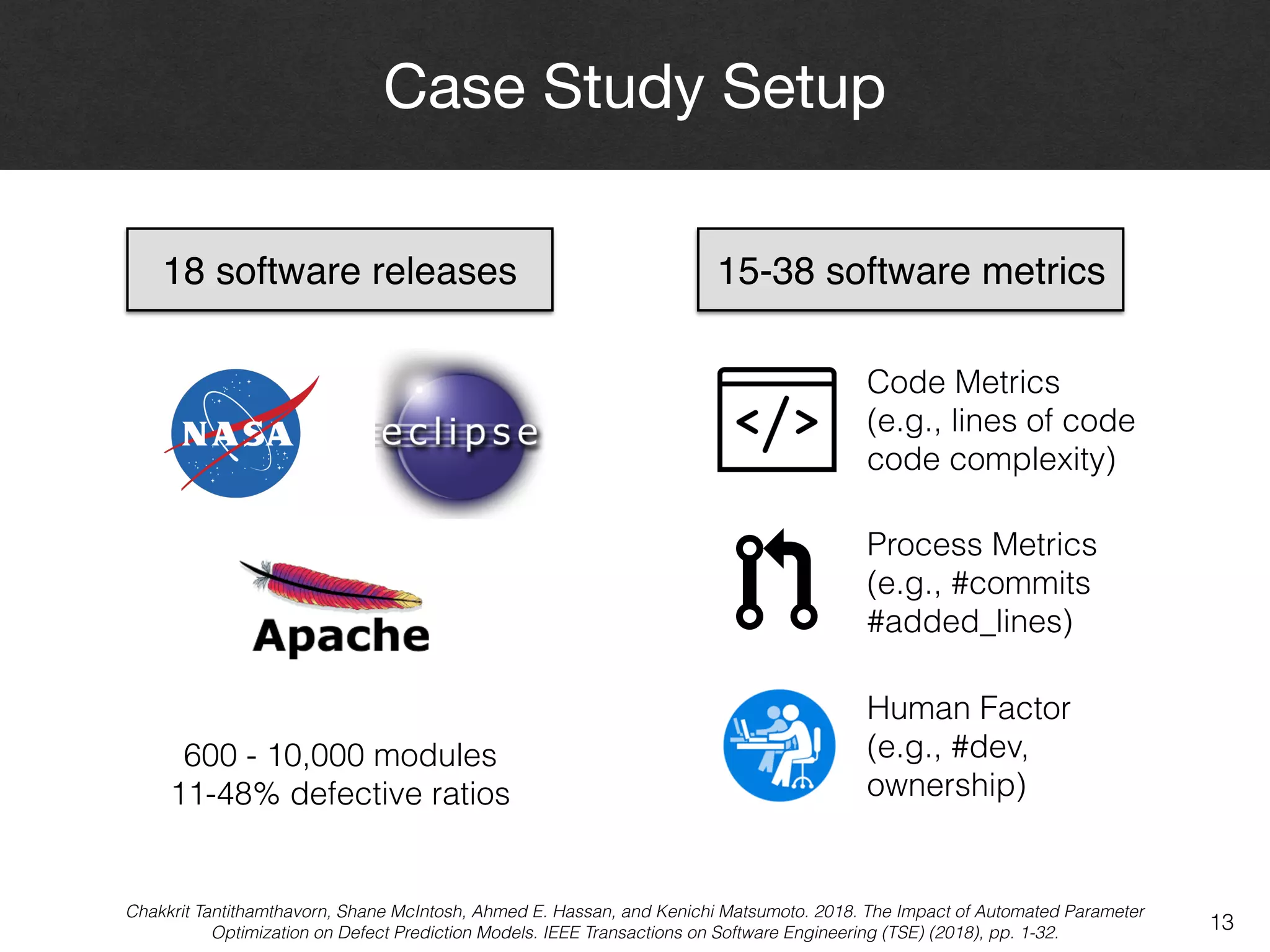
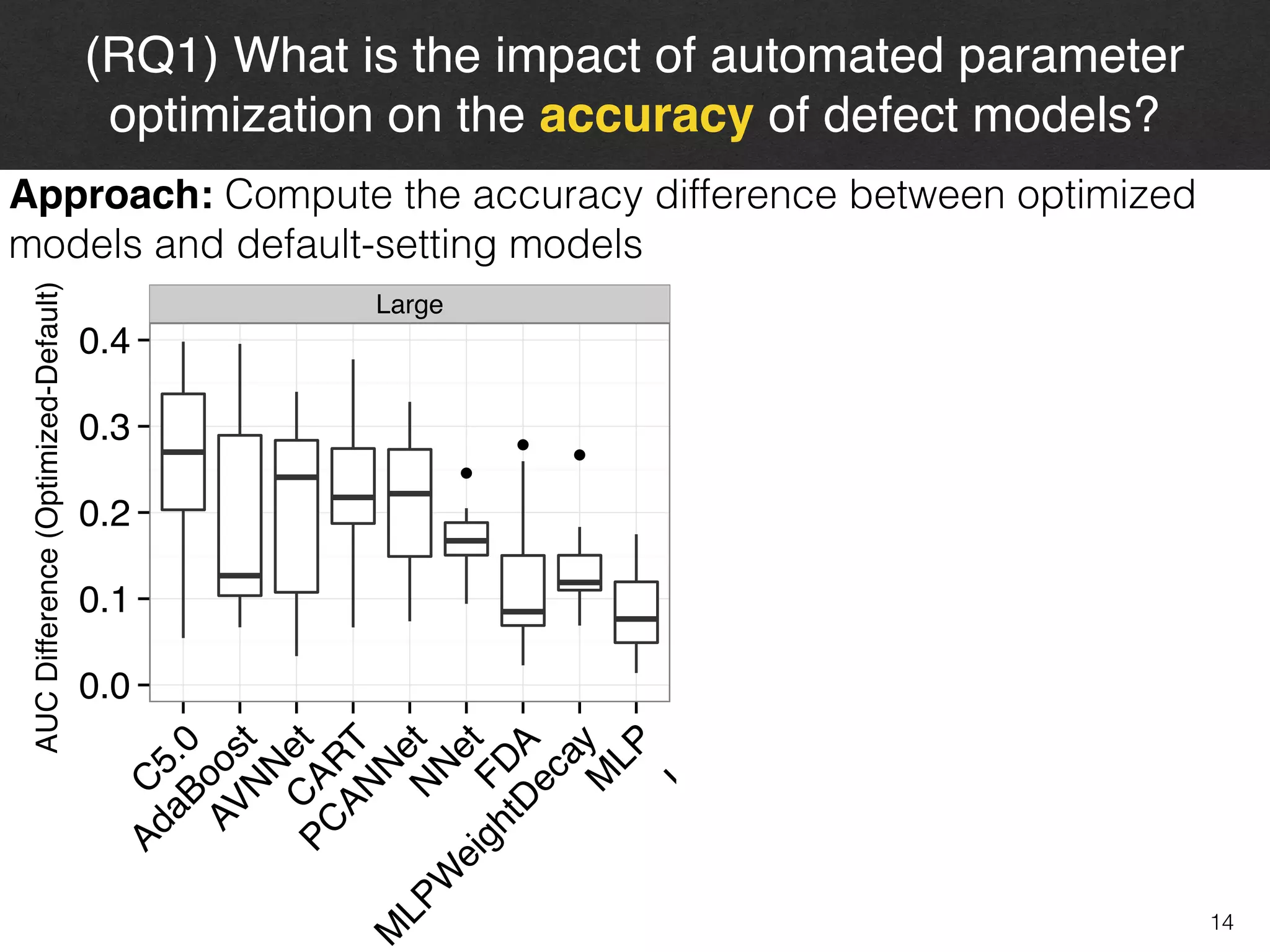
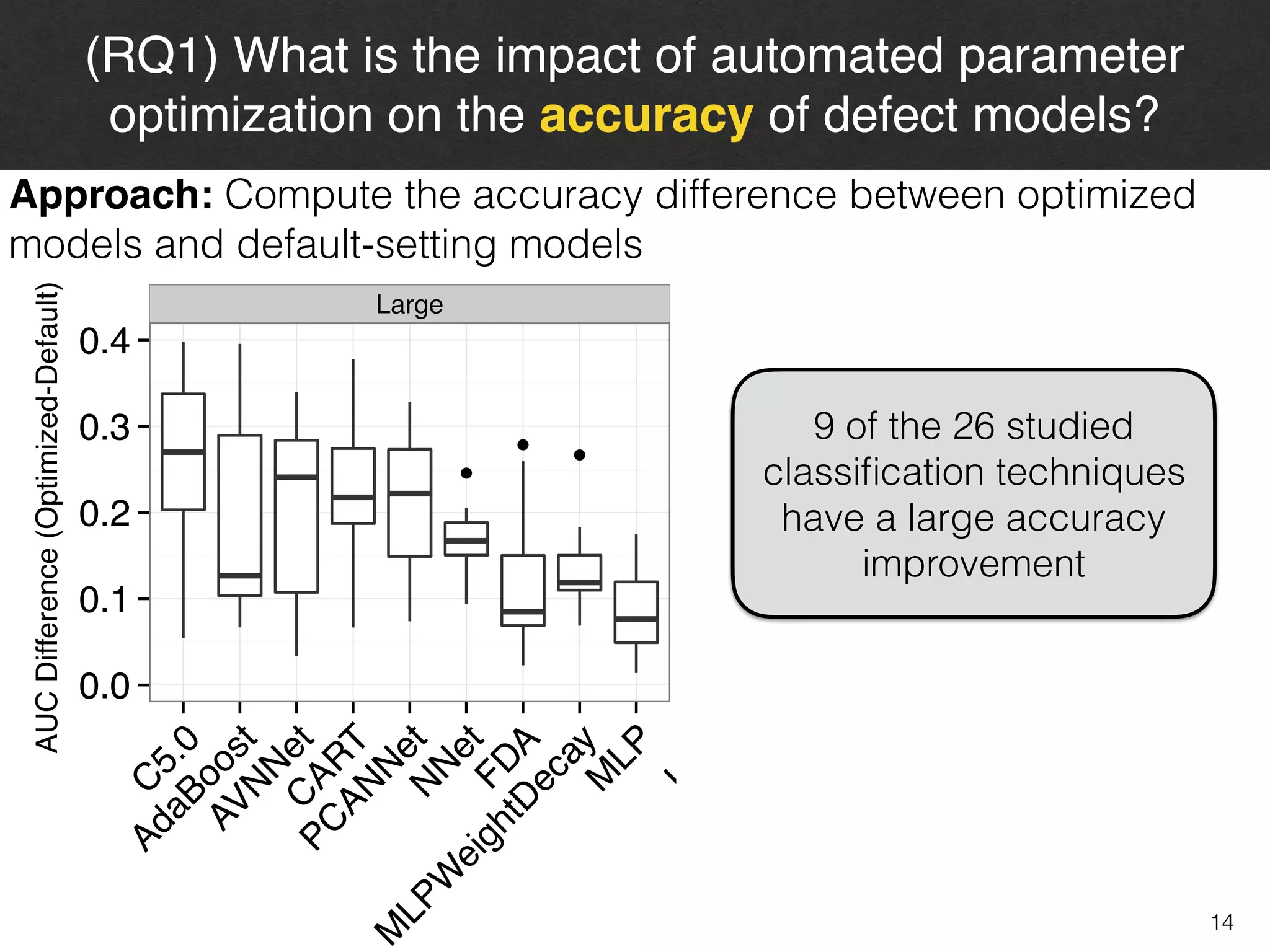
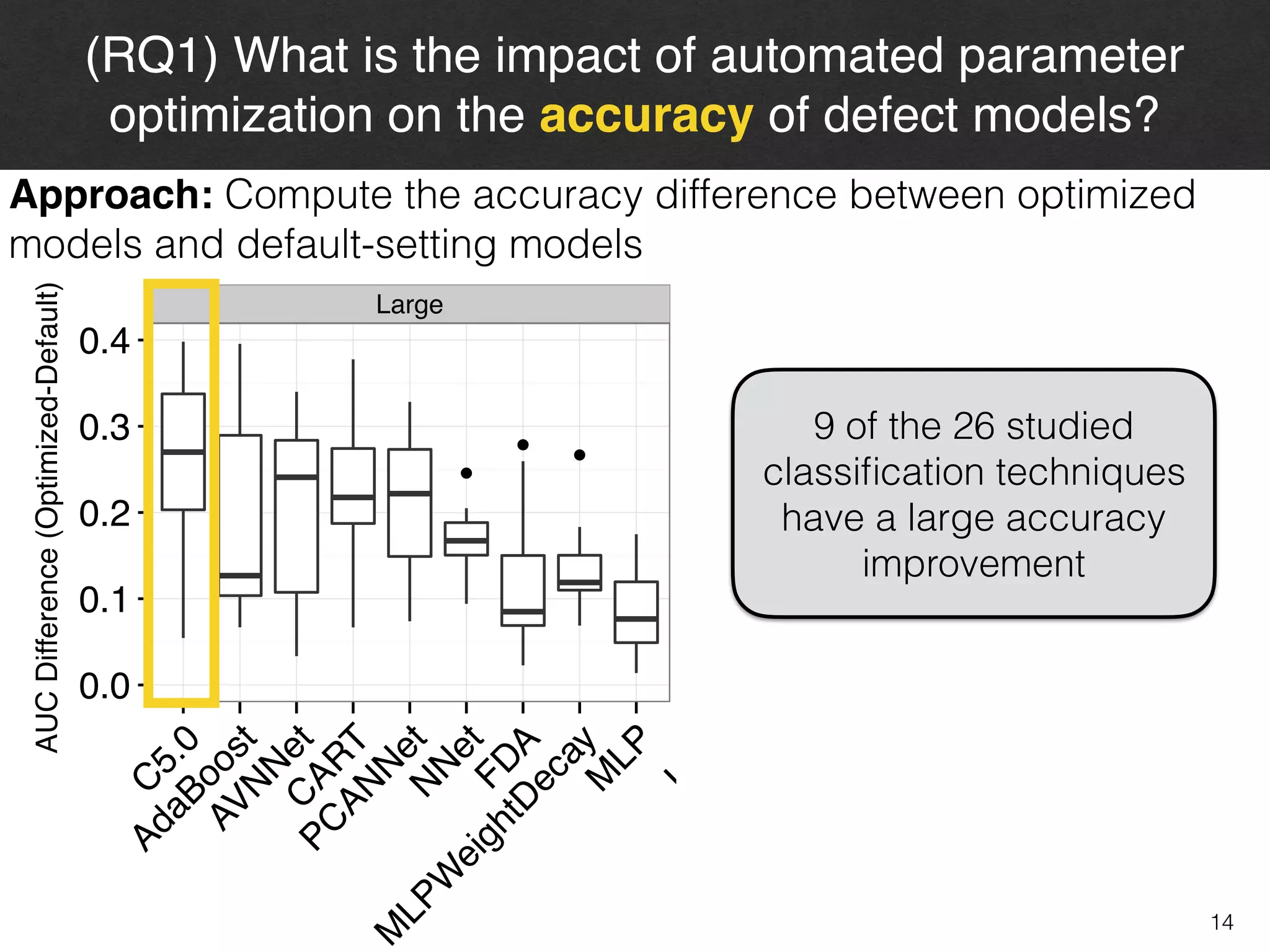
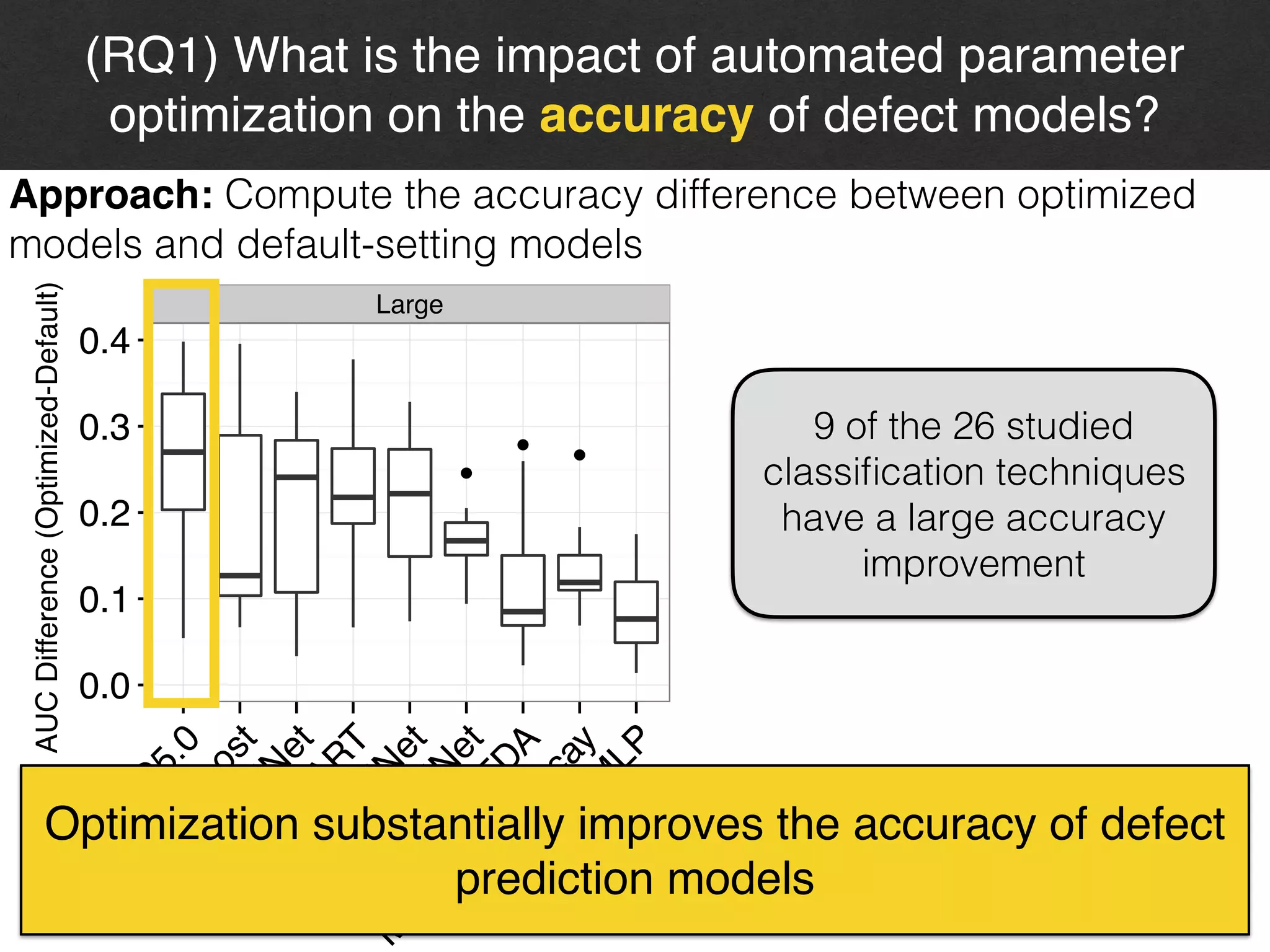
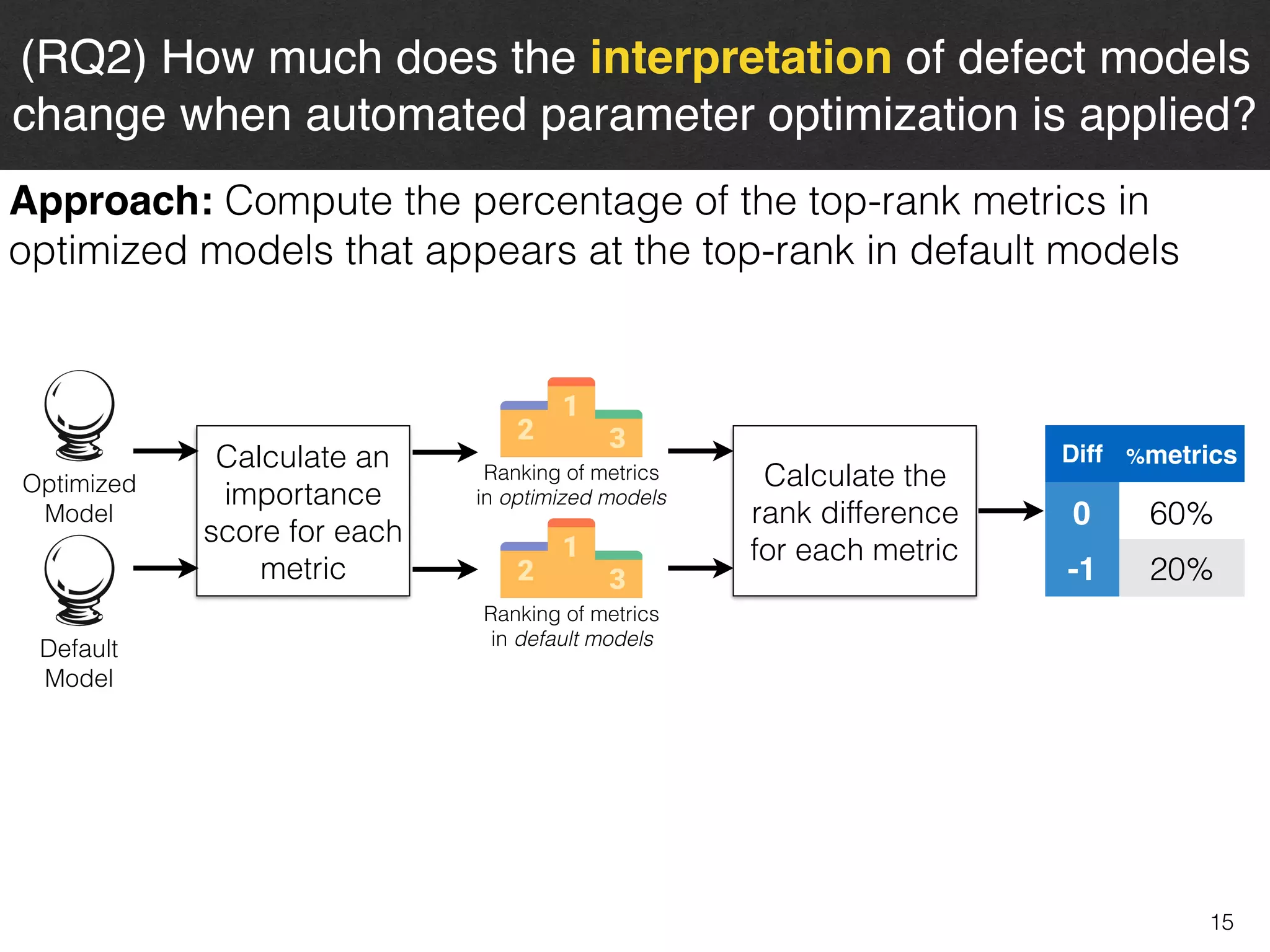
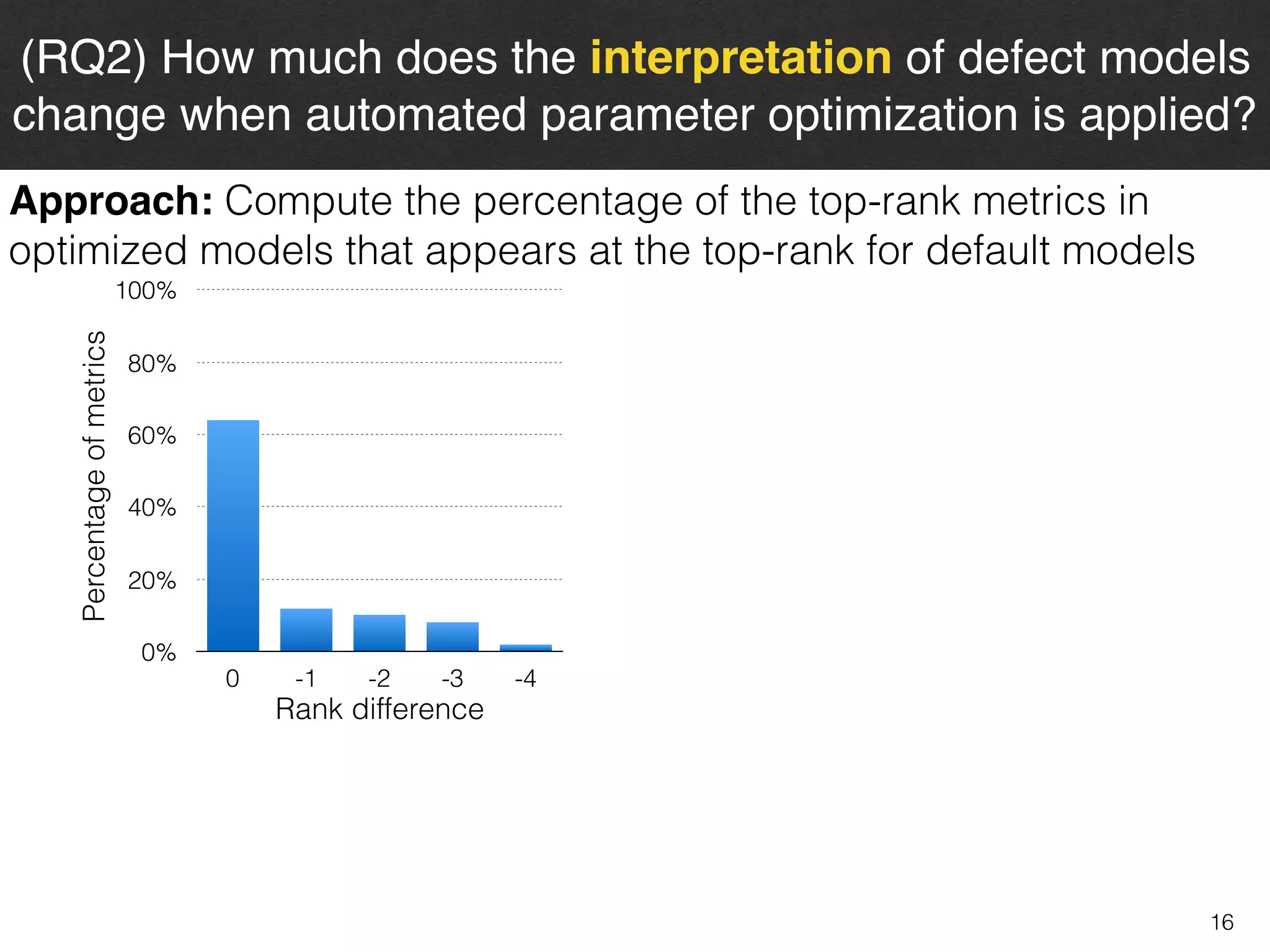
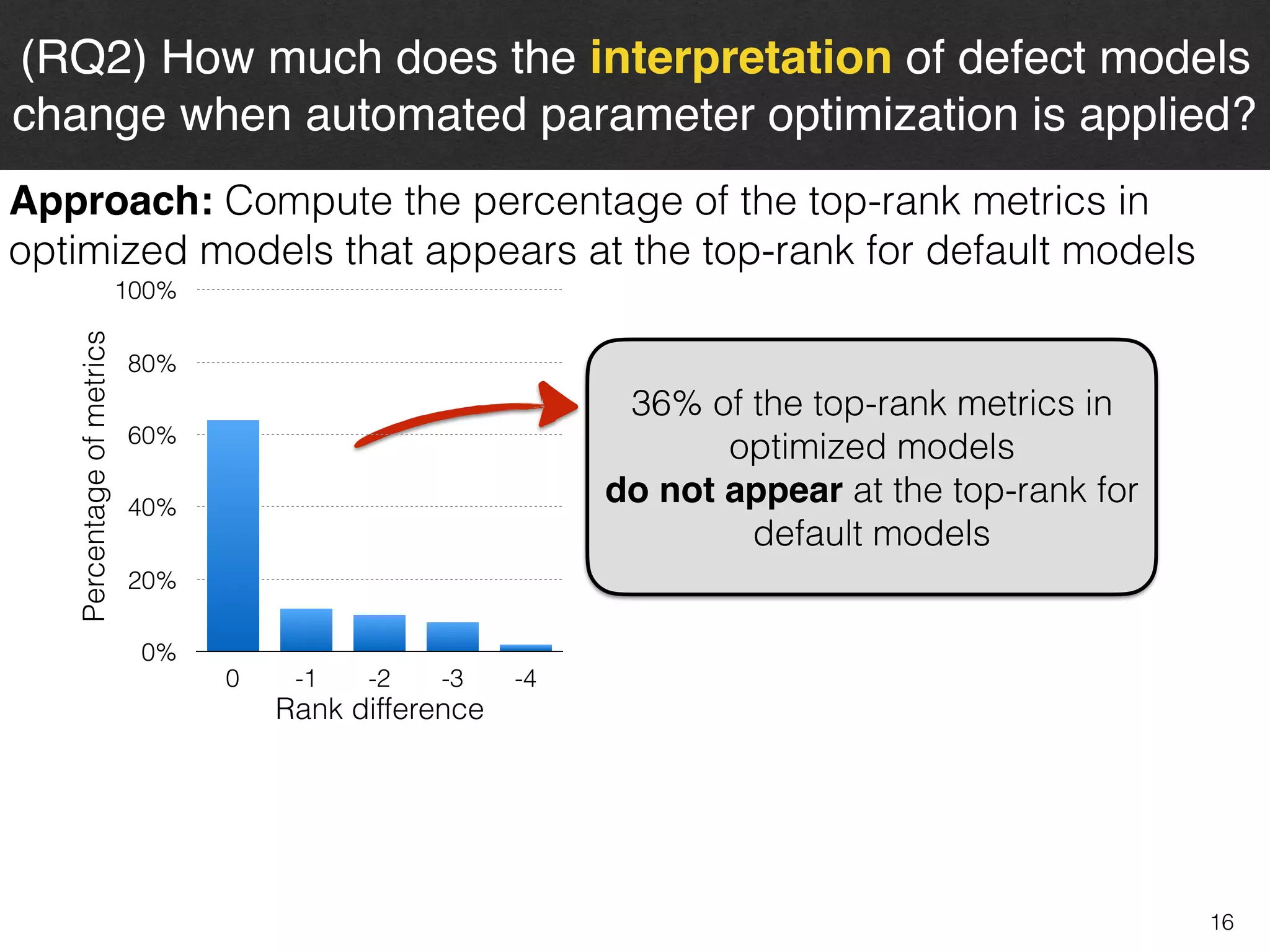
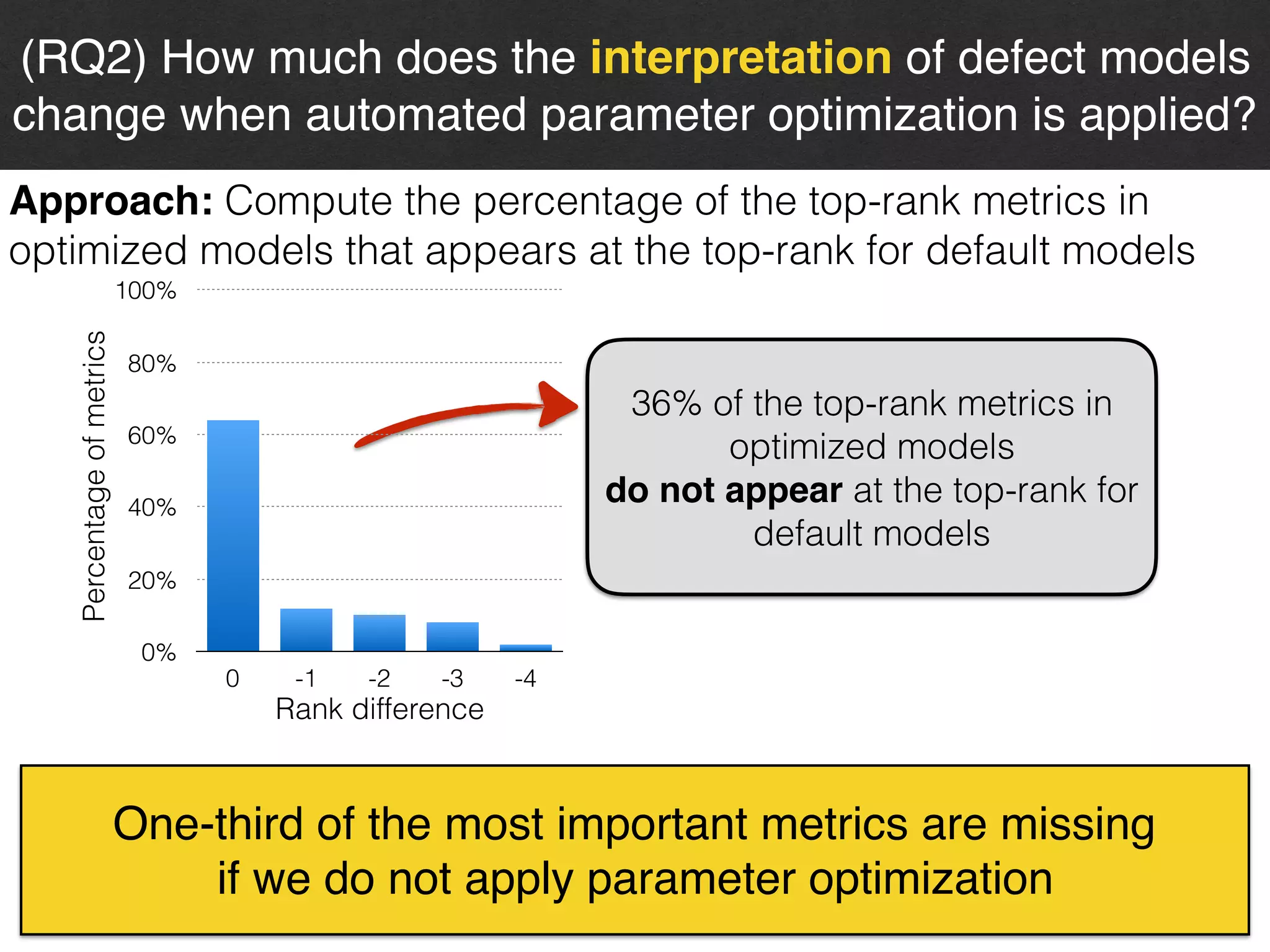
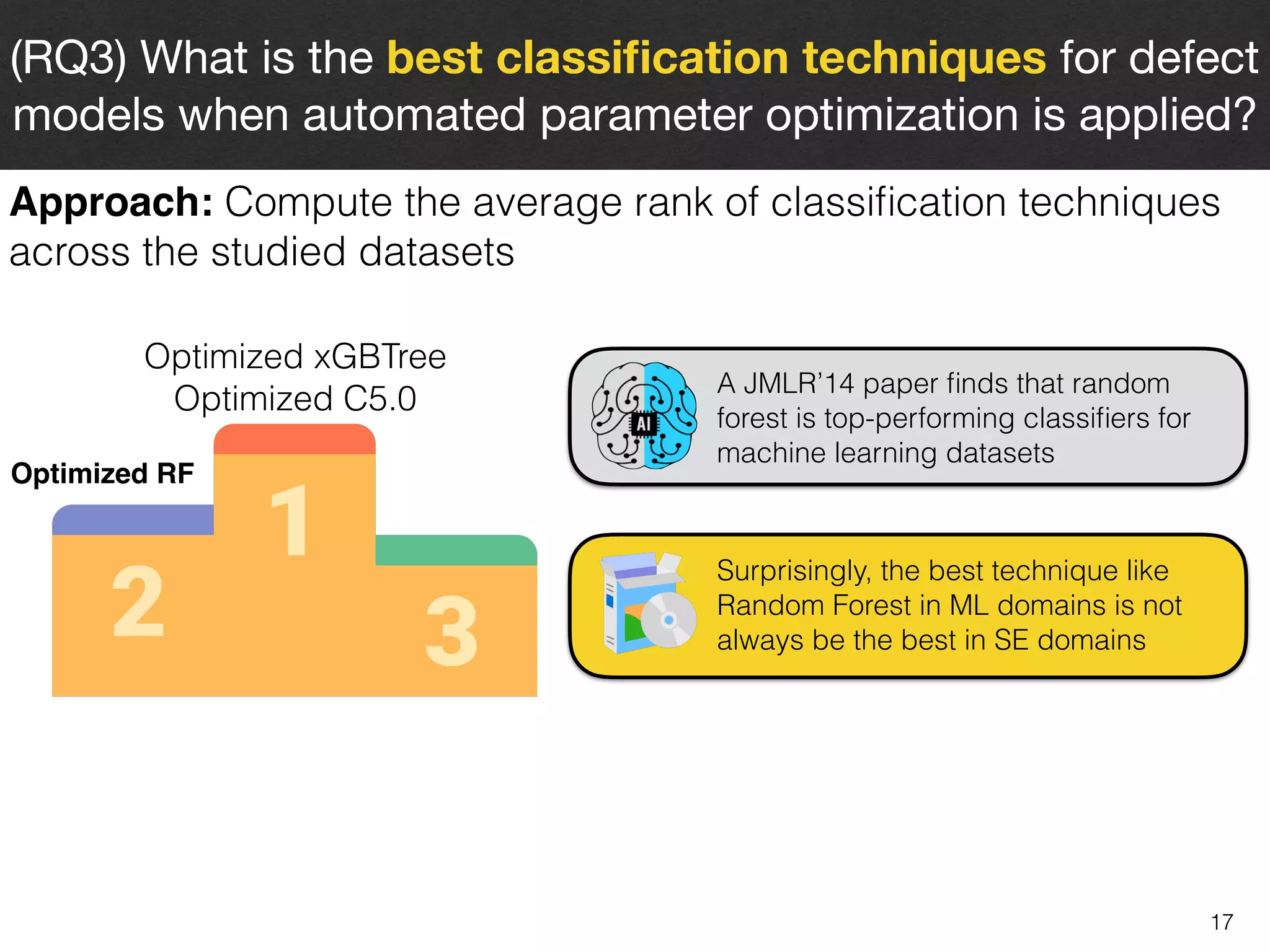
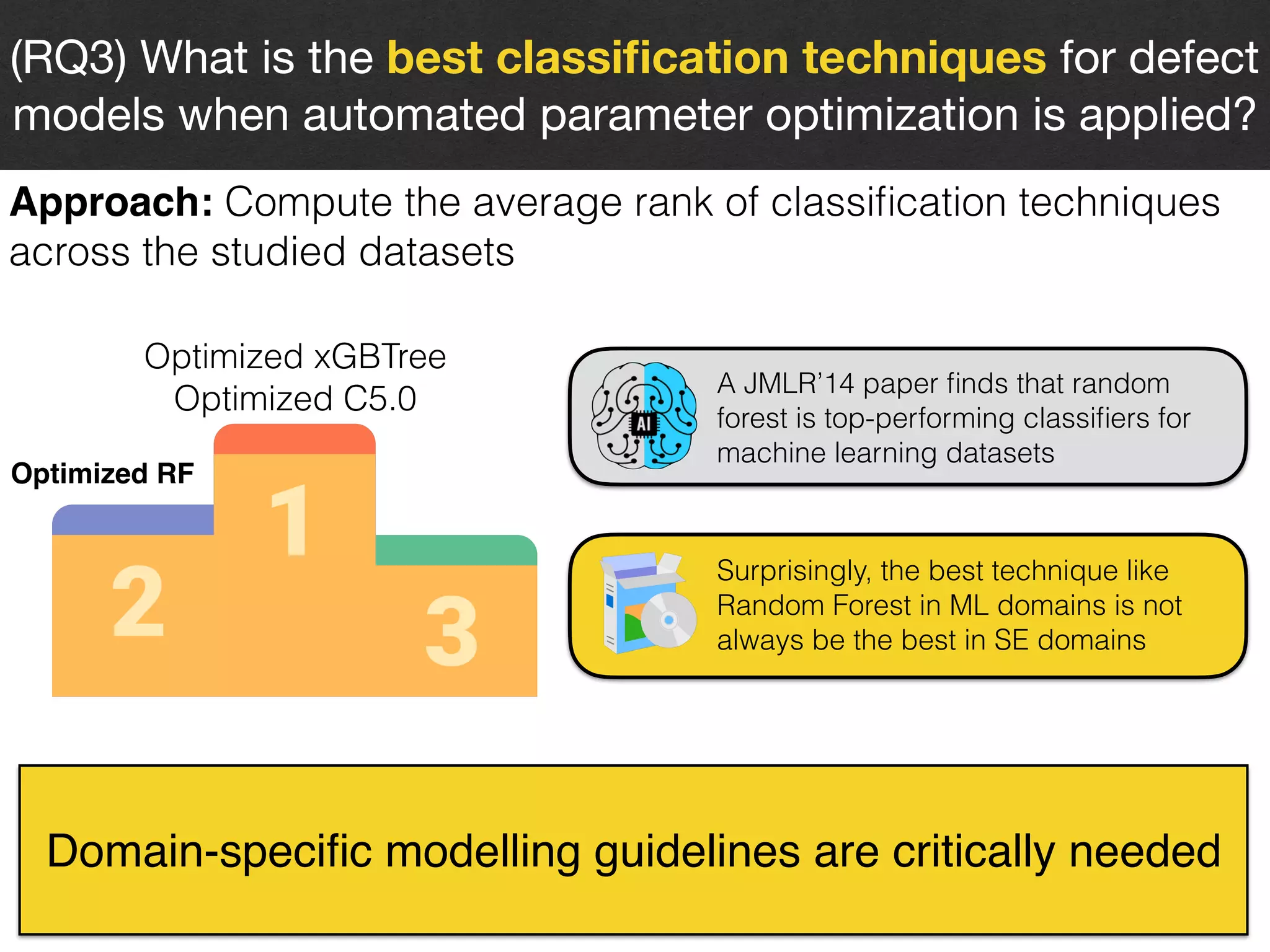
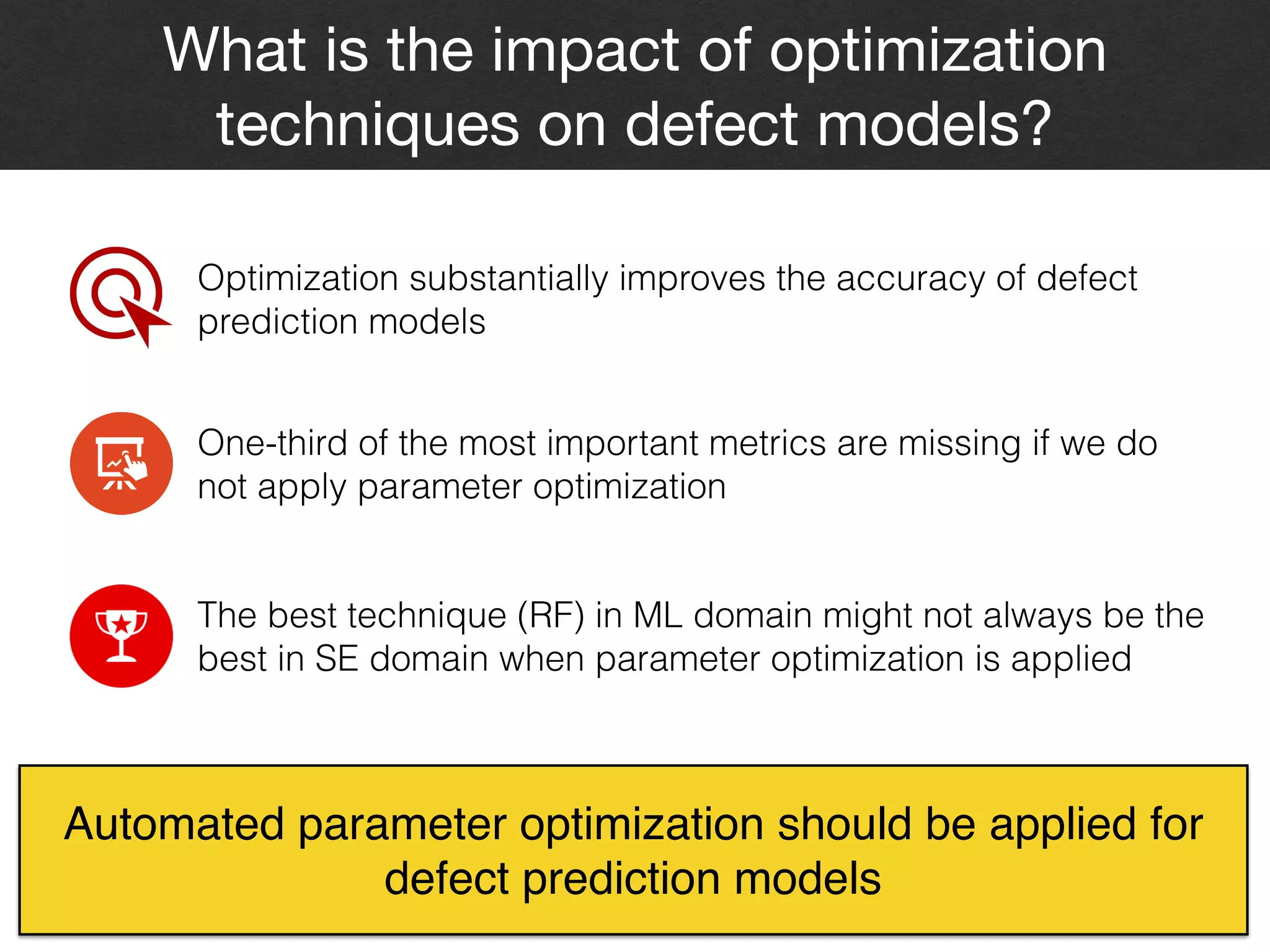
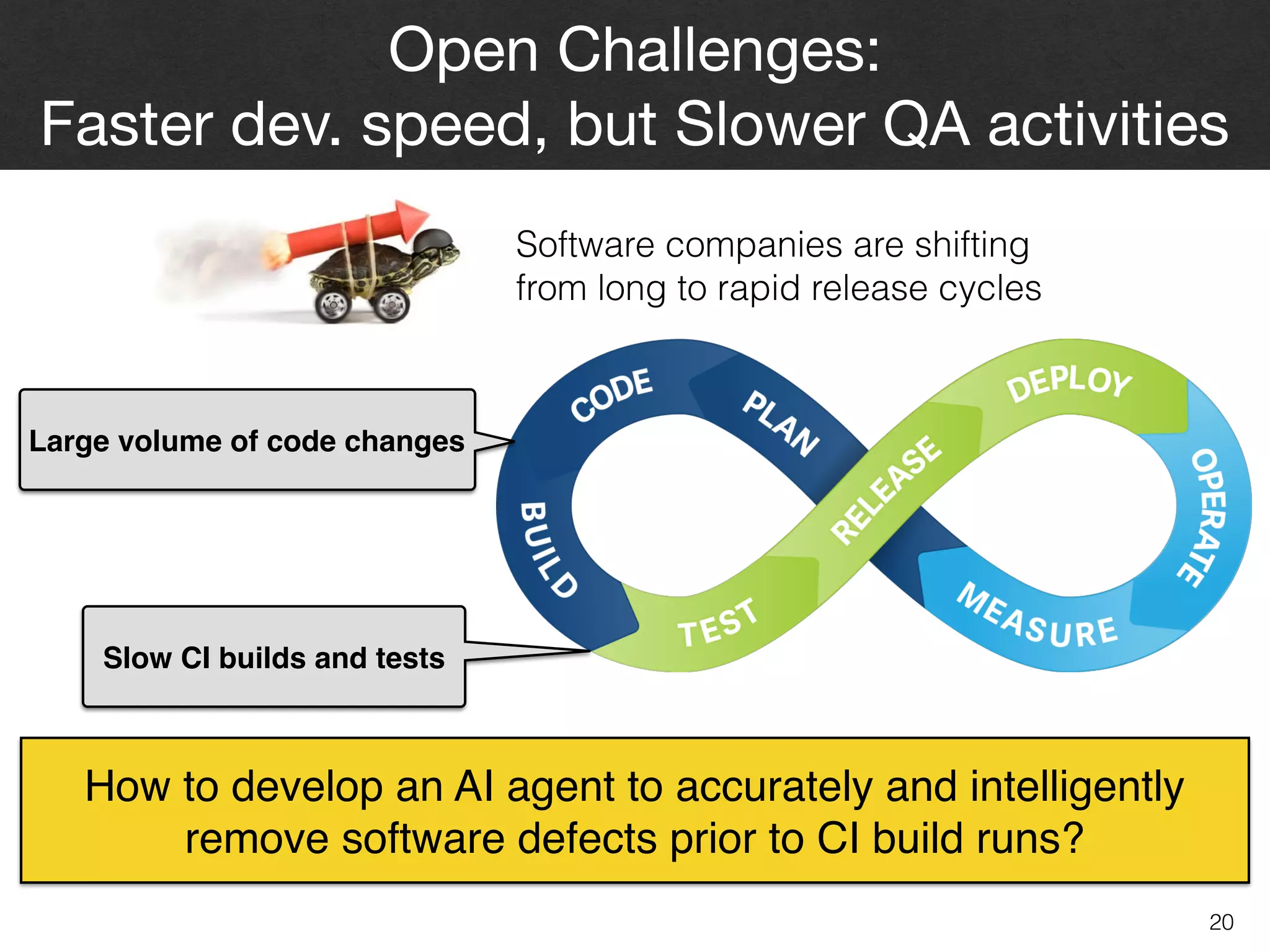
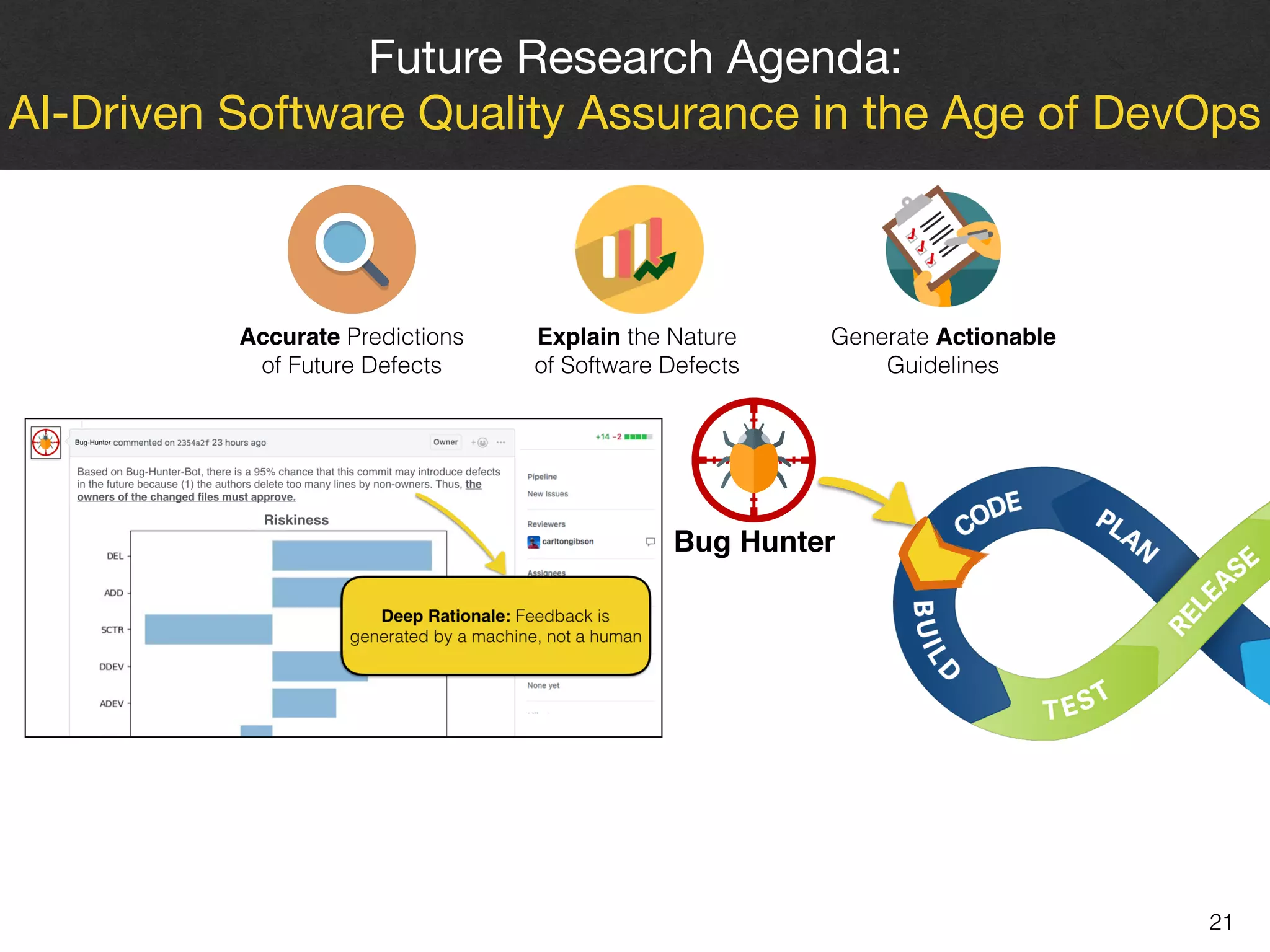
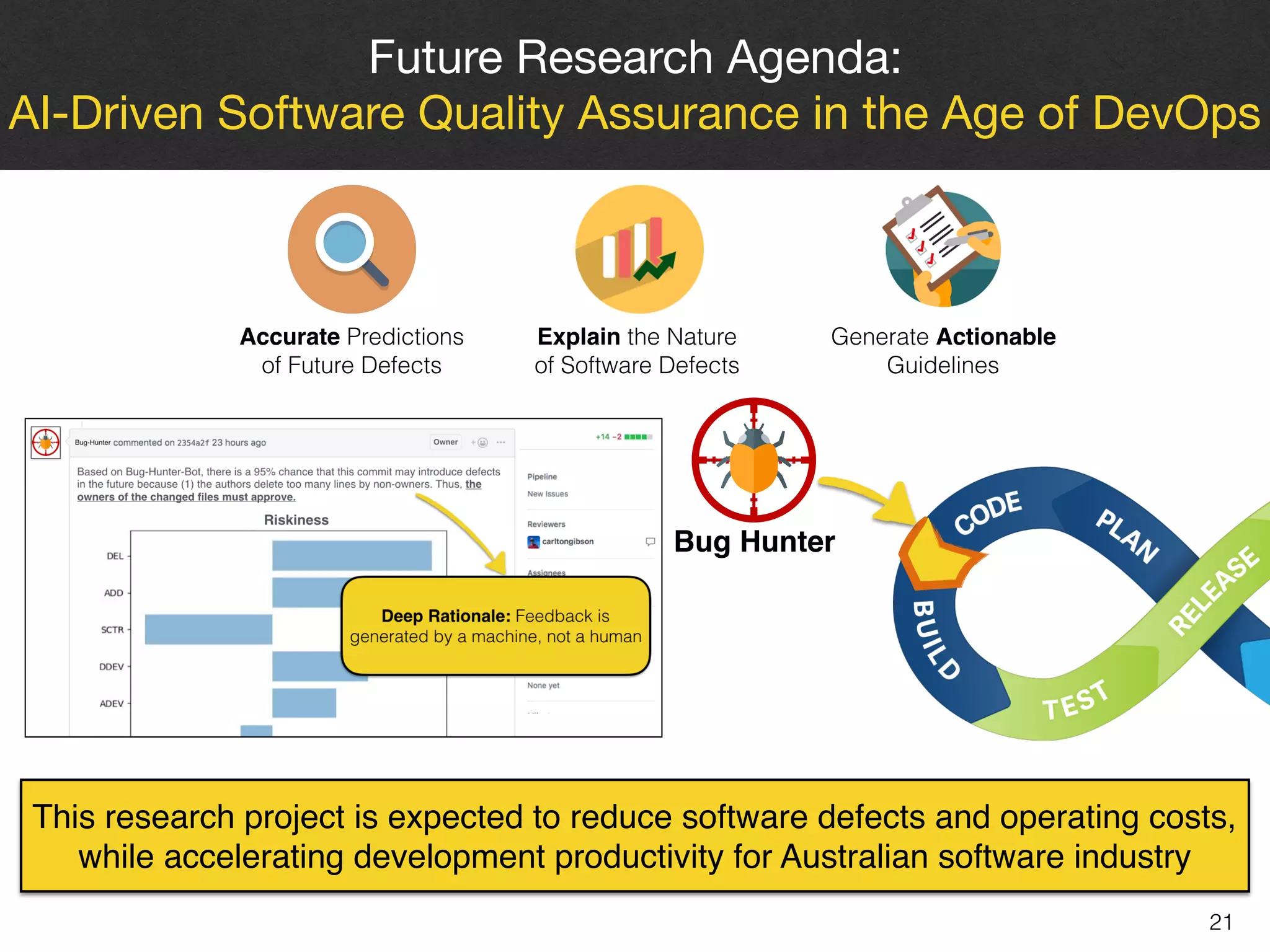
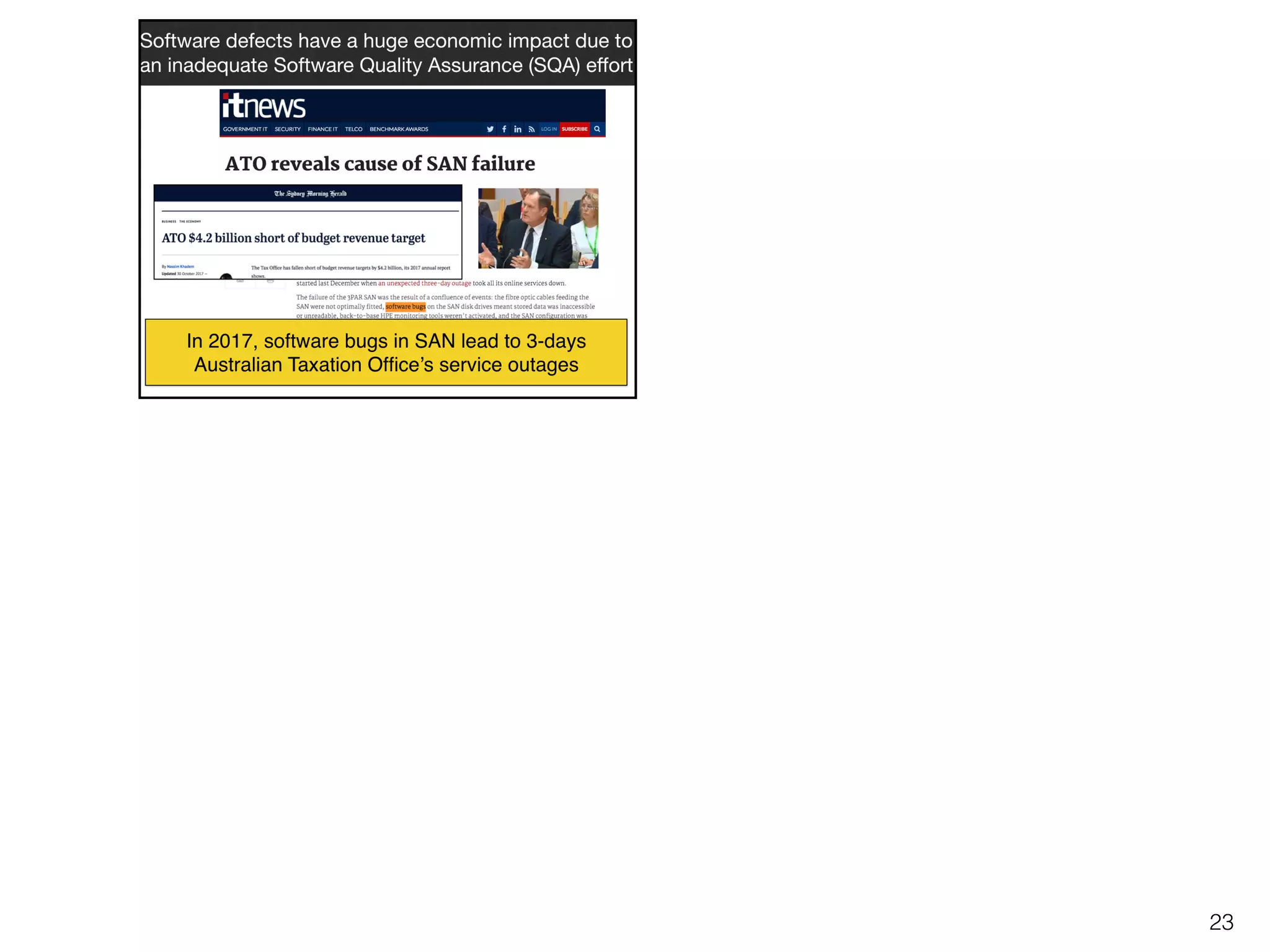
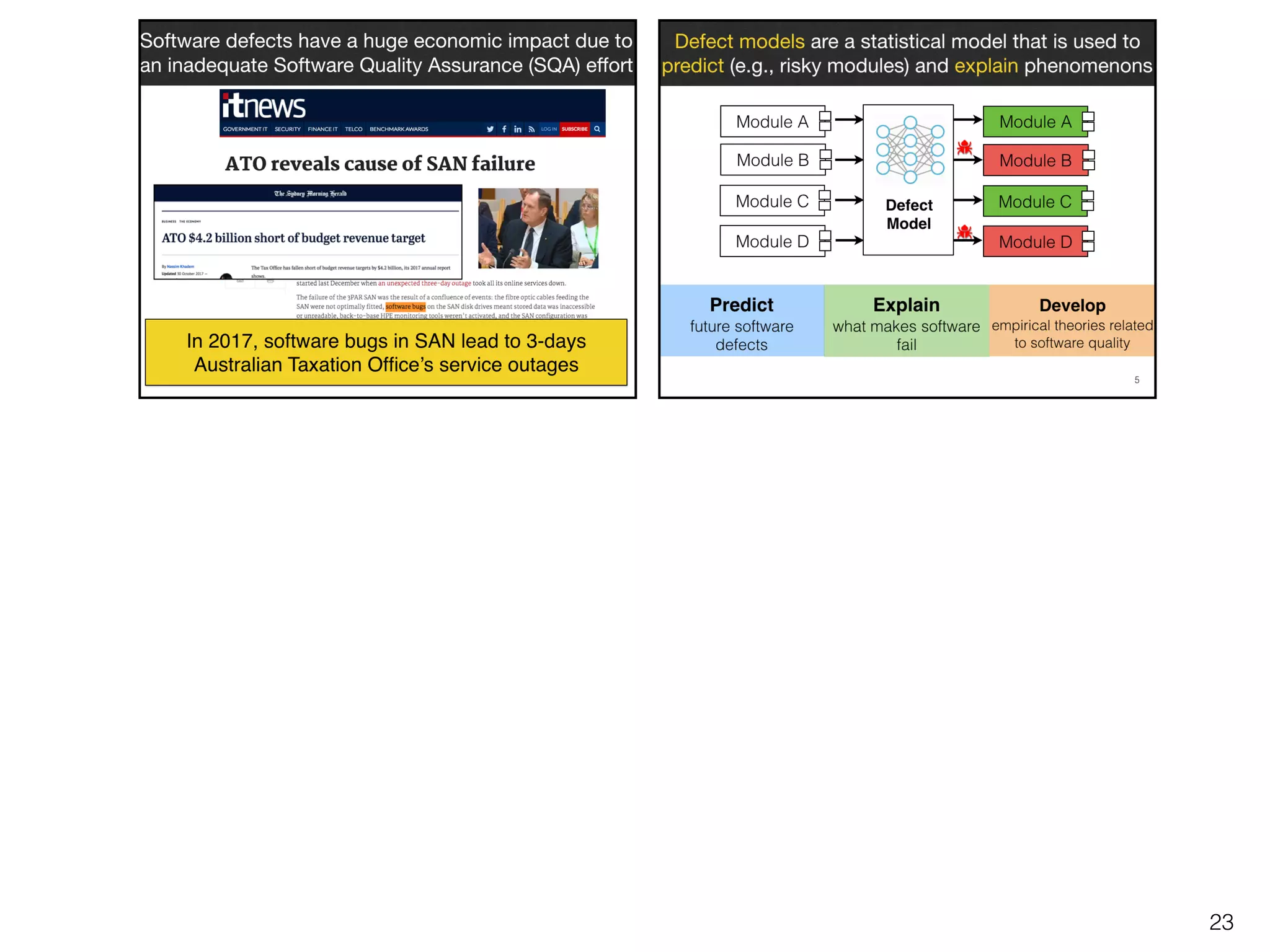
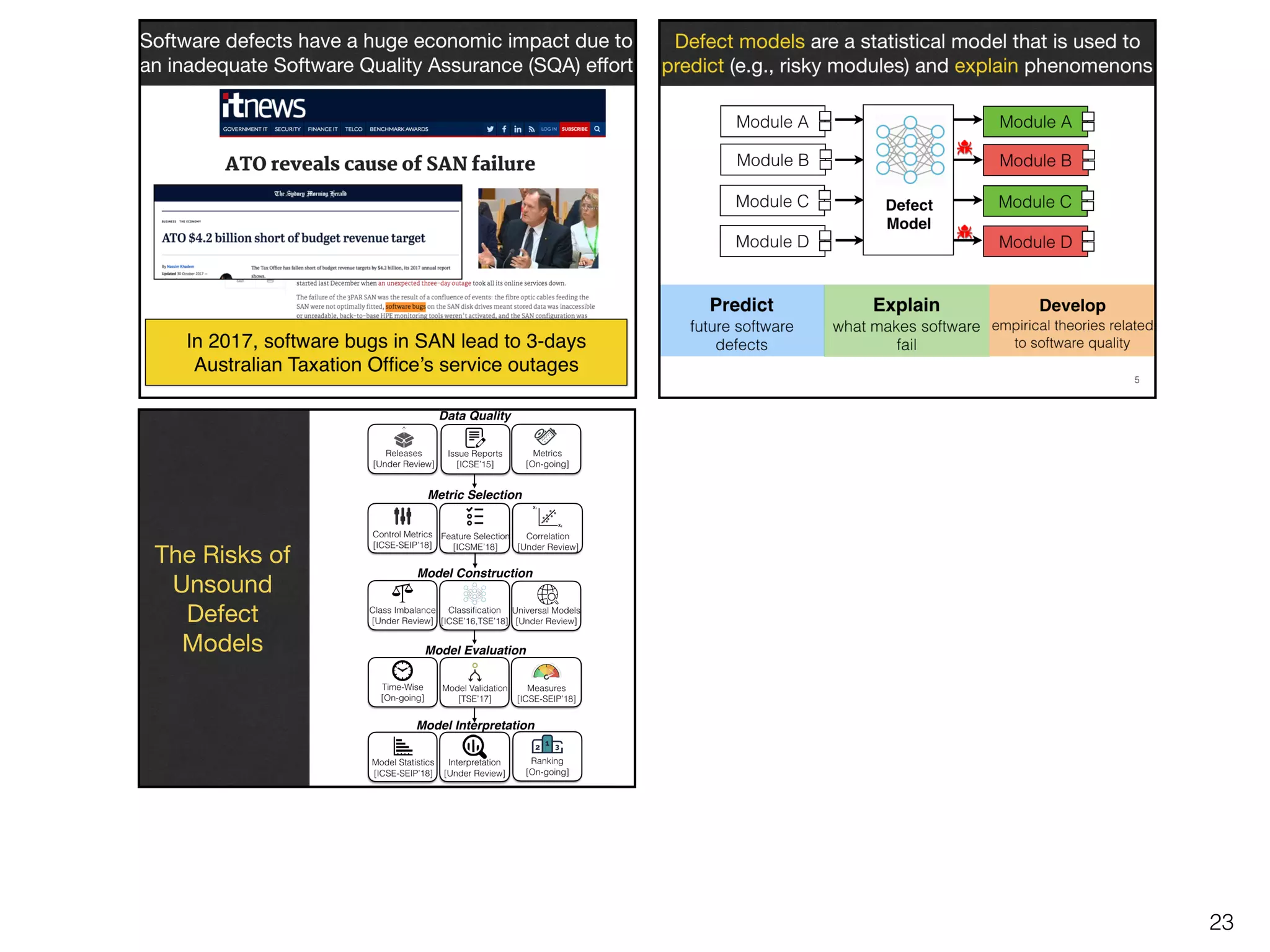
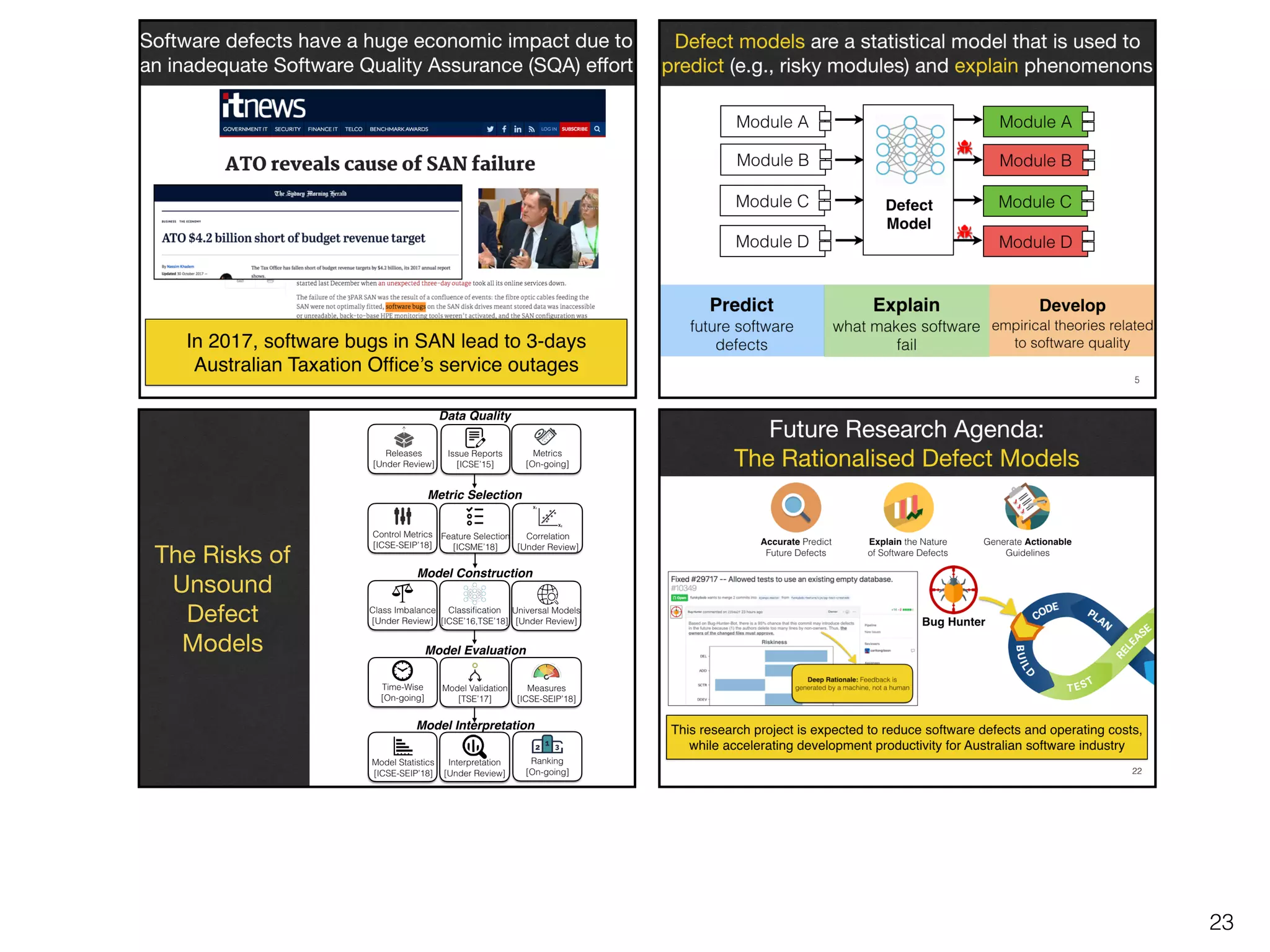
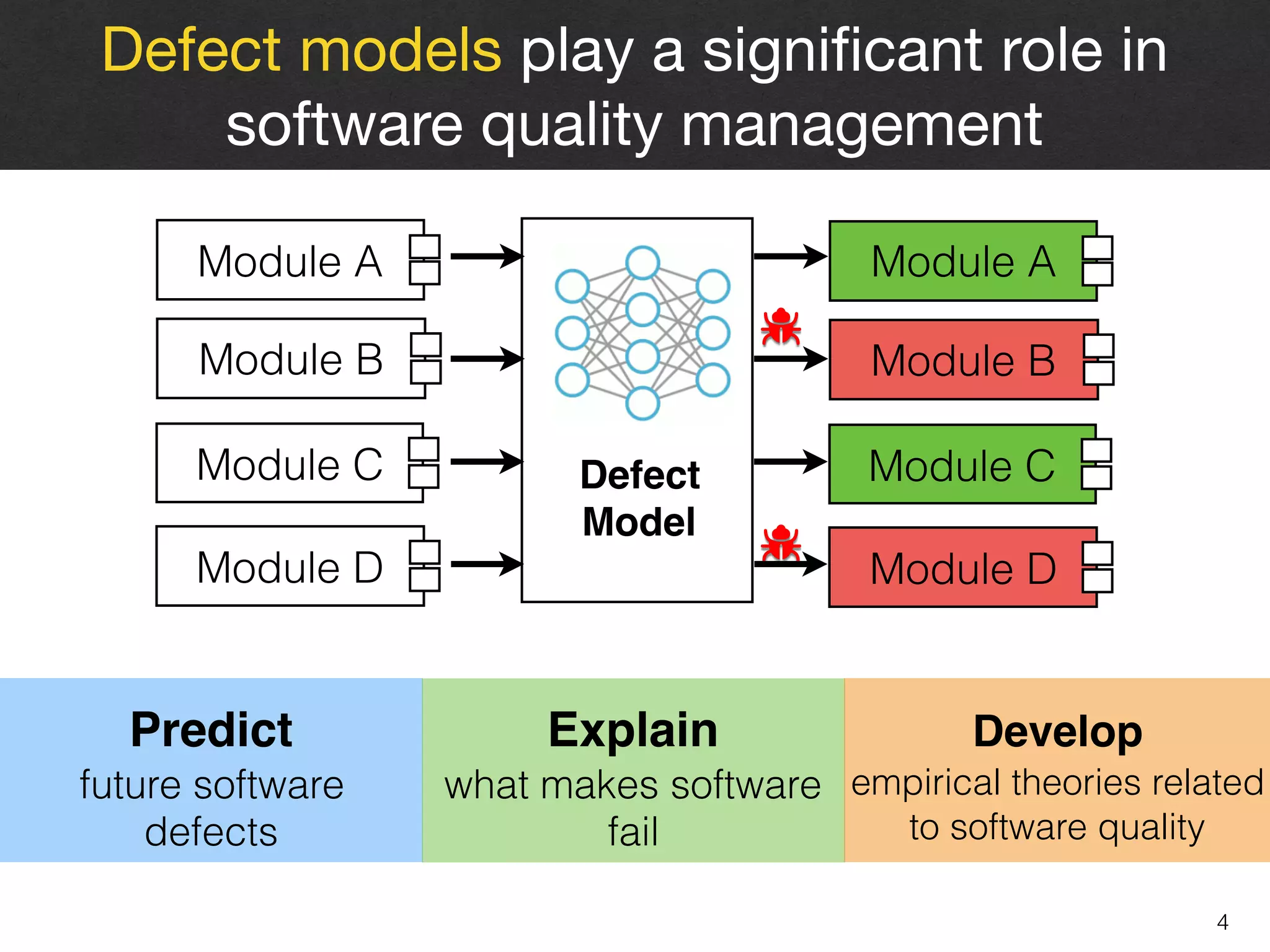
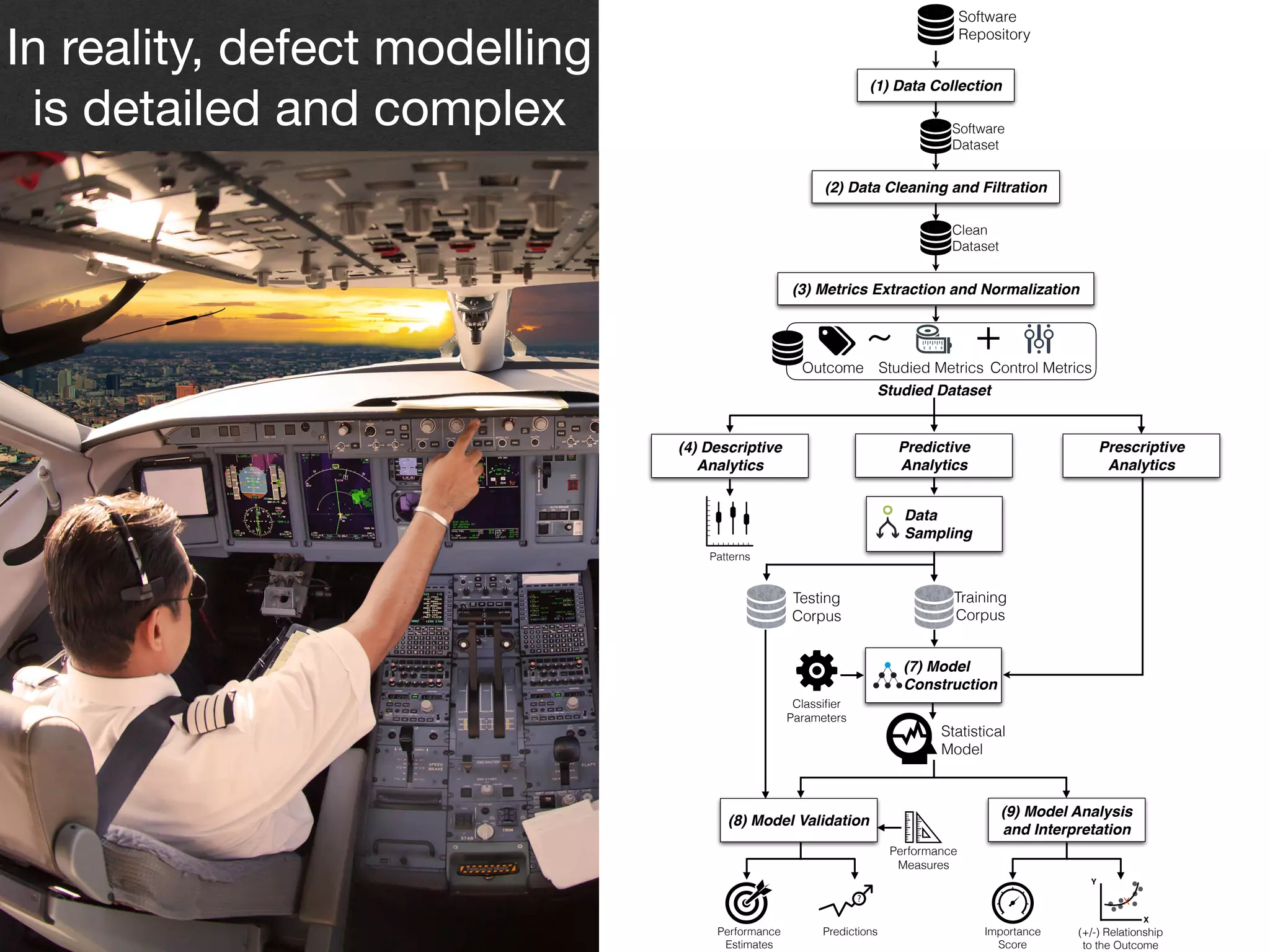
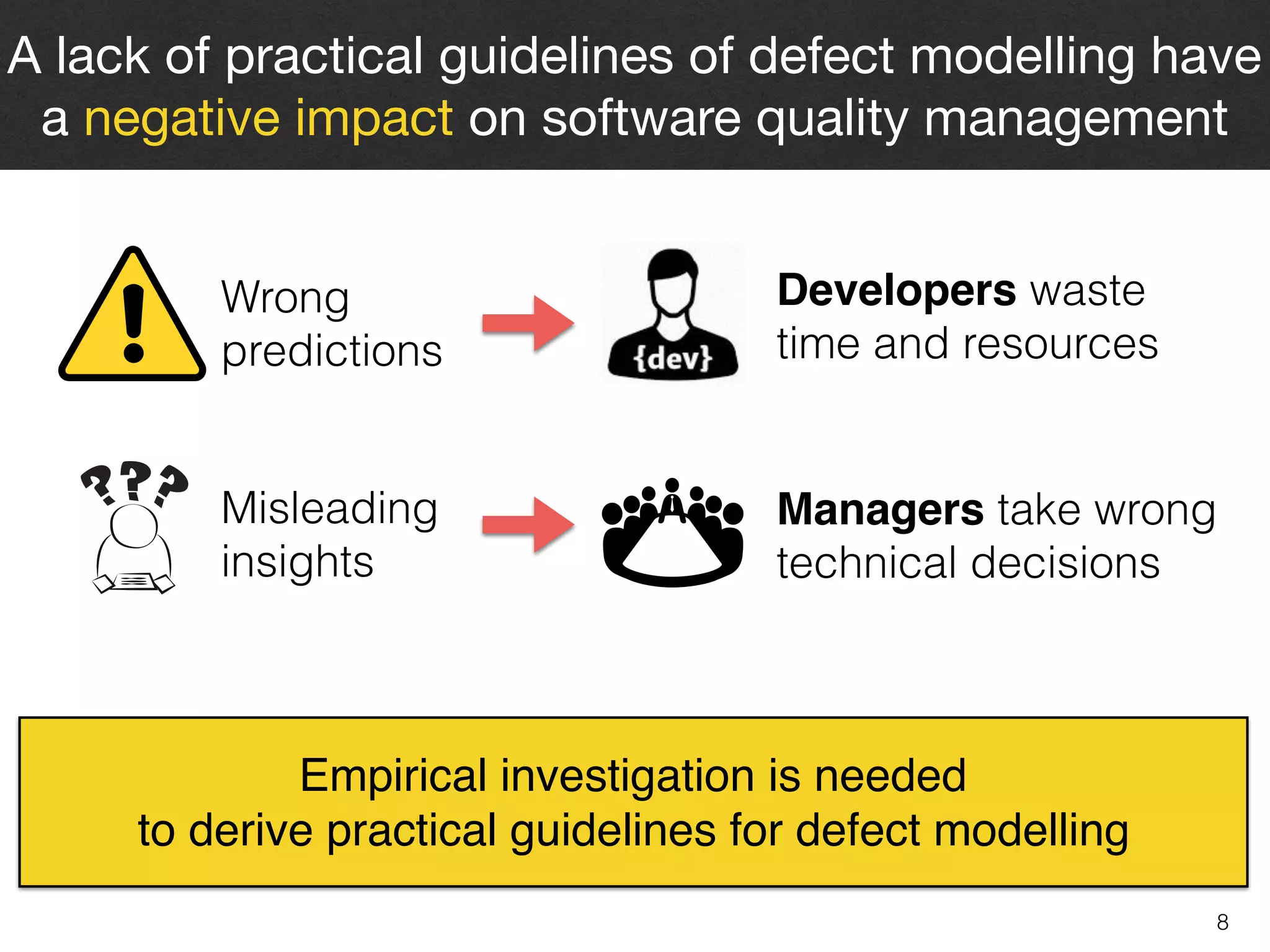
The document discusses the challenges and methodologies surrounding software quality assurance, particularly in the context of defect prediction models. It emphasizes the impact of automated parameter optimization on the accuracy and interpretation of these models, highlighting that incorrect application can lead to misleading insights and poor decisions. The research indicates that while some statistical techniques perform well, guidance specific to software engineering is essential for effective implementation.





![9
Metric Selection
Model Construction
Model Evaluation
Control Metrics
[ICSE-SEIP’18]
Correlation
[TSE’16]
Model Statistics
[ICSE-SEIP’18]
Model Interpretation
Class Imbalance
[Under Review]
The Risks of
Unsound
Defect
Models
Data Quality
Issue Reports
[ICSE’15]
Feature Selection
[ICSME’18]
Interpretation
[Under Review]
Model Validation
[TSE’17]
Measures
[ICSE-SEIP’18]
Releases
[Under Review]
Metrics
[On-going]
Universal Models
[Under Review]
Ranking
[On-going]
Time-Wise
[On-going]
Parameters
[ICSE’16,TSE’18]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qa-in-devops-181223103604/75/AI-Driven-Software-Quality-Assurance-in-the-Age-of-DevOps-14-2048.jpg)
![9
Metric Selection
Model Construction
Model Evaluation
Control Metrics
[ICSE-SEIP’18]
Correlation
[TSE’16]
Model Statistics
[ICSE-SEIP’18]
Model Interpretation
Class Imbalance
[Under Review]
The Risks of
Unsound
Defect
Models
Data Quality
Issue Reports
[ICSE’15]
Feature Selection
[ICSME’18]
Interpretation
[Under Review]
Model Validation
[TSE’17]
Measures
[ICSE-SEIP’18]
Releases
[Under Review]
Metrics
[On-going]
Universal Models
[Under Review]
Ranking
[On-going]
Time-Wise
[On-going]
Parameters
[ICSE’16,TSE’18]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qa-in-devops-181223103604/75/AI-Driven-Software-Quality-Assurance-in-the-Age-of-DevOps-15-2048.jpg)


![10
Defect prediction models have configurable
parameters that control their characteristics
Most of the widely-used classification techniques
require at least one parameter setting
Based on the literature analysis of
300+ defect studies
#trees for
random forest
#clusters for
k-nearest neighbors
80% of top-50 highly-cited defect studies
rely on a default setting [IST’16]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qa-in-devops-181223103604/75/AI-Driven-Software-Quality-Assurance-in-the-Age-of-DevOps-18-2048.jpg)
![10
Defect prediction models have configurable
parameters that control their characteristics
Most of the widely-used classification techniques
require at least one parameter setting
Based on the literature analysis of
300+ defect studies
#trees for
random forest
#clusters for
k-nearest neighbors
80% of top-50 highly-cited defect studies
rely on a default setting [IST’16]
Even within the R toolkit, 2 random forest
packages have different default settings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qa-in-devops-181223103604/75/AI-Driven-Software-Quality-Assurance-in-the-Age-of-DevOps-19-2048.jpg)