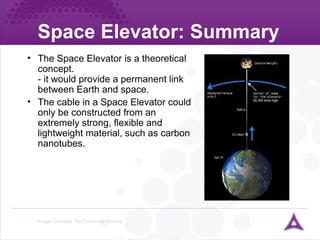
The document discusses the concept of a space elevator, which would provide a permanent link between Earth and space. A space elevator would require an extremely strong yet lightweight material, such as carbon nanotubes, to construct the cable. Carbon nanotubes have properties like strength and flexibility that make them a promising material for building a space elevator.









![Properties Of Carbon Nanotubes Image: [email_address] Strong – 200 times stronger than steel. – the first synthetic material to have greater strength than spider silk. Light – 1 square kilometre = 30kg Flexible – Compared to most materials. Heat resistant – resists burning like a metal.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spaceelevatormodule-1227487211235927-9/85/Space-Elevator-Module-11-320.jpg)
![Carbon Nanotubes? Image: [email_address] How can we explain the properties of carbon nanotubes? What about other forms of carbon?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spaceelevatormodule-1227487211235927-9/85/Space-Elevator-Module-12-320.jpg)
![Experiment 1 Forms Of Carbon Use these molecular images to do the Forms of Carbon Experiment Image: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spaceelevatormodule-1227487211235927-9/85/Space-Elevator-Module-13-320.jpg)



![Forms Of Carbon: Graphite Images Clockwise: Wikipedia , orangeacid@flickr, compujeramey @flickr, [email_address] Properties: light, super lubricating, conductor Molecular structure: sheets of carbon atoms in regular, flat structure Application: pencil, sport equipment, electronics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spaceelevatormodule-1227487211235927-9/85/Space-Elevator-Module-17-320.jpg)





