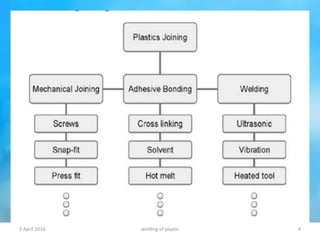
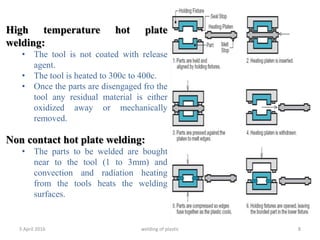
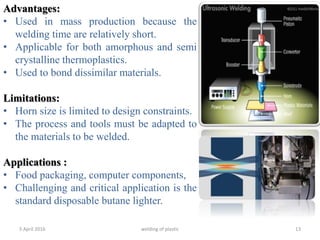
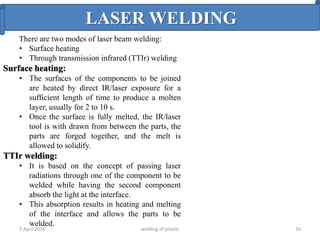
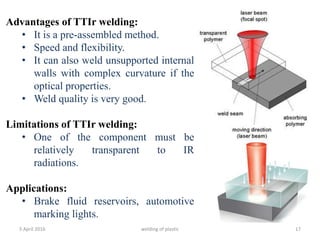
This document summarizes various plastic welding techniques including: hot plate welding, which uses heated plates to weld plastic; hot gas welding, which uses a heated gas stream; ultrasonic welding, which uses high frequency vibrations; friction welding, which generates heat through rotational friction; and laser welding, which uses a laser beam. It discusses the basic mechanisms, advantages, limitations, and applications of each technique. The document is a presentation on plastic welding given by Shyed Farhan Ali, a chemical engineering student.