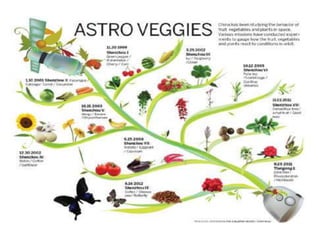
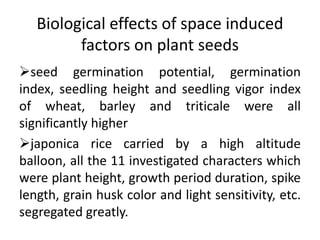
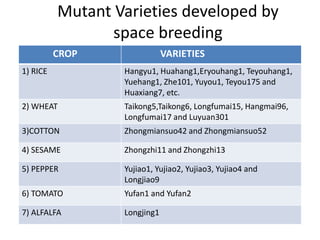
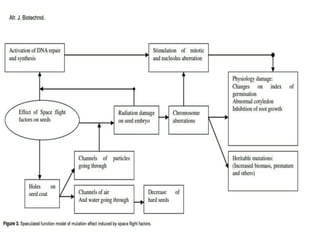
Space breeding involves sending seeds into low-Earth orbit to induce mutations from cosmic radiation and microgravity. Returning seeds are selected and bred to develop varieties with desirable traits like higher yield, disease resistance, and stress tolerance. China has been a pioneer in this area, sending over 400 plant species to space and developing commercial rice and vegetable varieties from space-bred seeds. The goals of space breeding are to efficiently produce new crop varieties with improved economic traits that are difficult to obtain through traditional breeding methods.