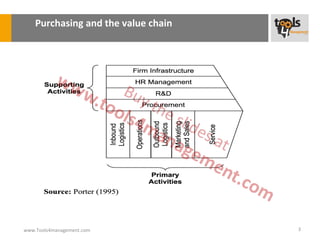
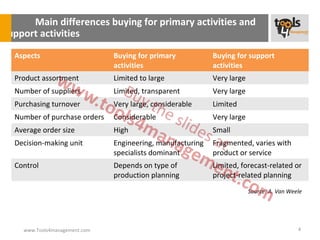
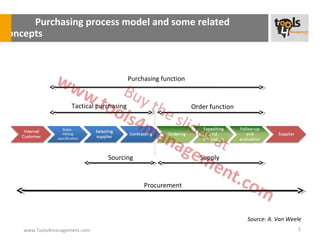
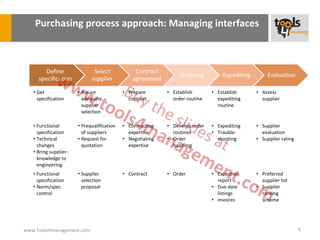
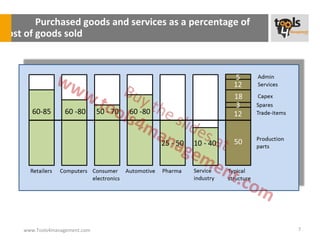
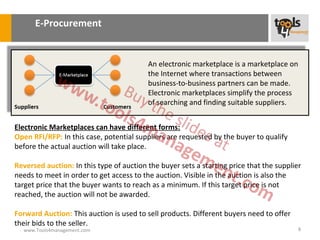
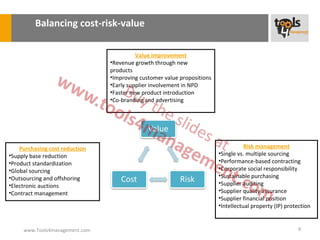
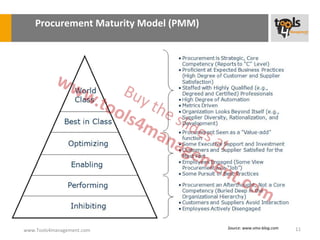
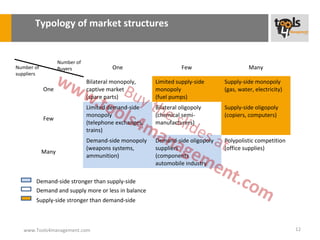
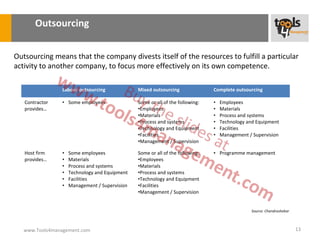
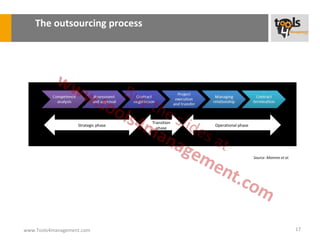
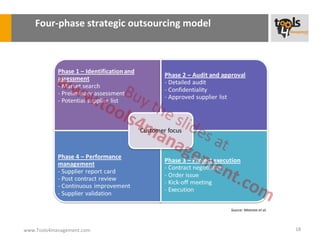
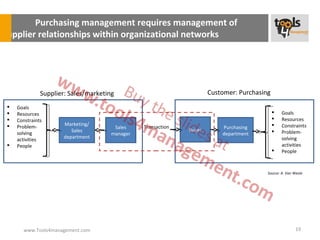
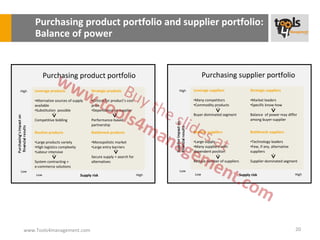
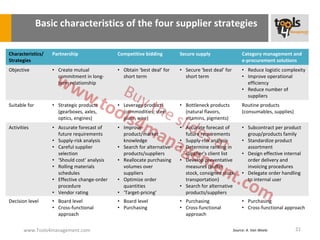
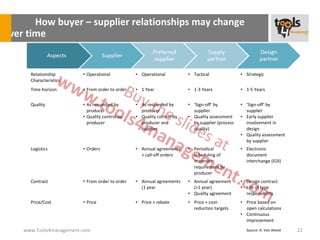
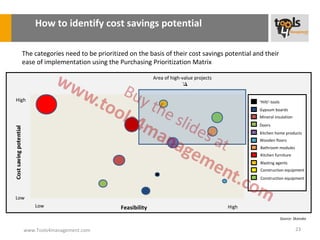
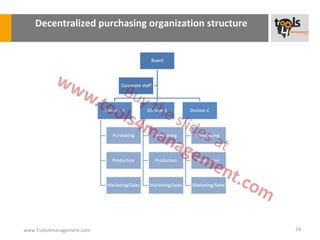
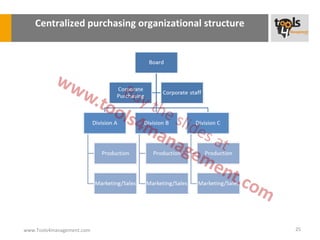
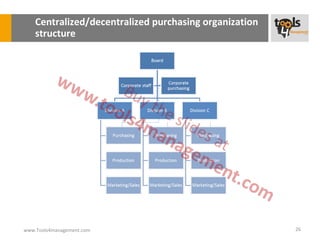
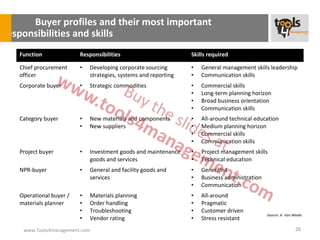
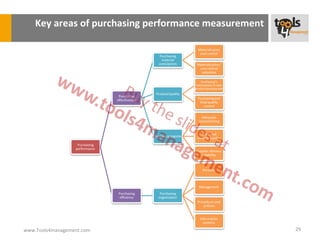
The document provides an overview of sourcing and purchasing management, outlining key concepts such as the differences between buying for primary and support activities, the purchasing process, and the impact of e-procurement. It discusses outsourcing strategies, supplier management, and the importance of balancing cost, risk, and value in procurement. Additionally, it explores organizational structures for purchasing and the roles of various buyer profiles within an organization.