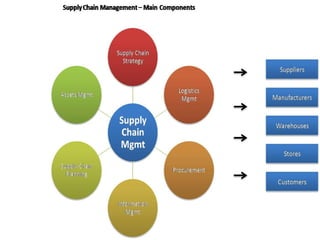
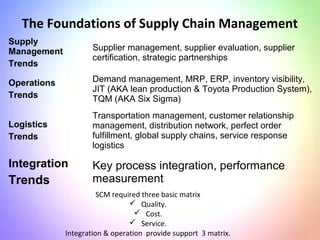
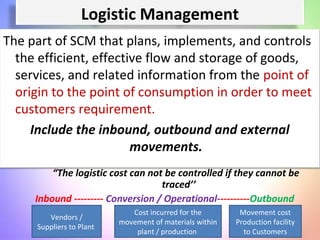
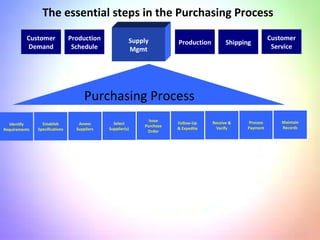
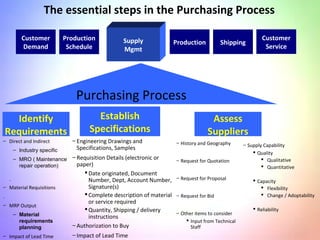
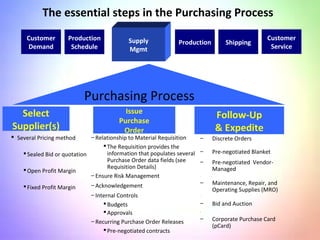
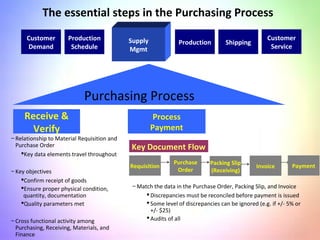
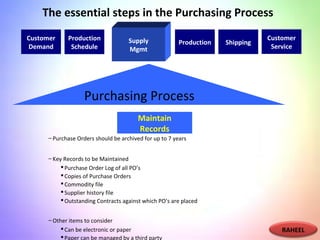
This document contains information about a group project on supply chain management. It includes the names of group members Arsalan Gulzar, Imdad, Farhan, and Raheel. It then covers various topics related to supply chain management including definitions, trends in areas like procurement, sourcing strategies, logistics management, the purchasing process, and the importance of information systems and purchasing.