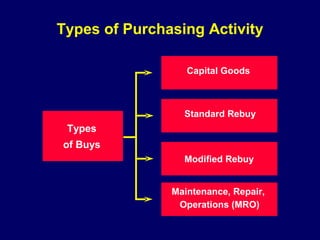
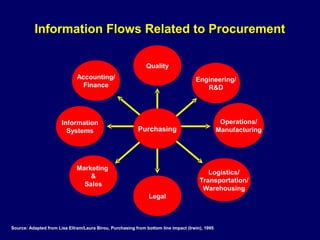
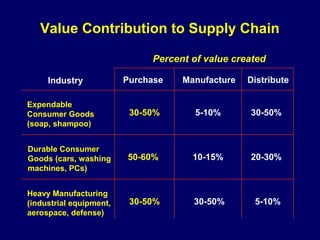
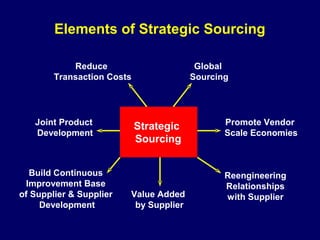
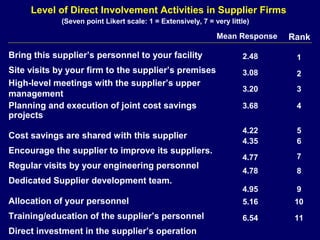
This document discusses how procurement impacts logistics operations. It defines key terms like purchasing, procurement, and strategic sourcing. Strategic sourcing focuses on developing supply channels at the lowest total cost while aligning purchasing with business goals. Improved supply chain planning can reduce inventory and transaction costs through closer collaboration with suppliers. Measuring metrics like inventory velocity and conducting supplier assessments are important aspects of strategic sourcing.