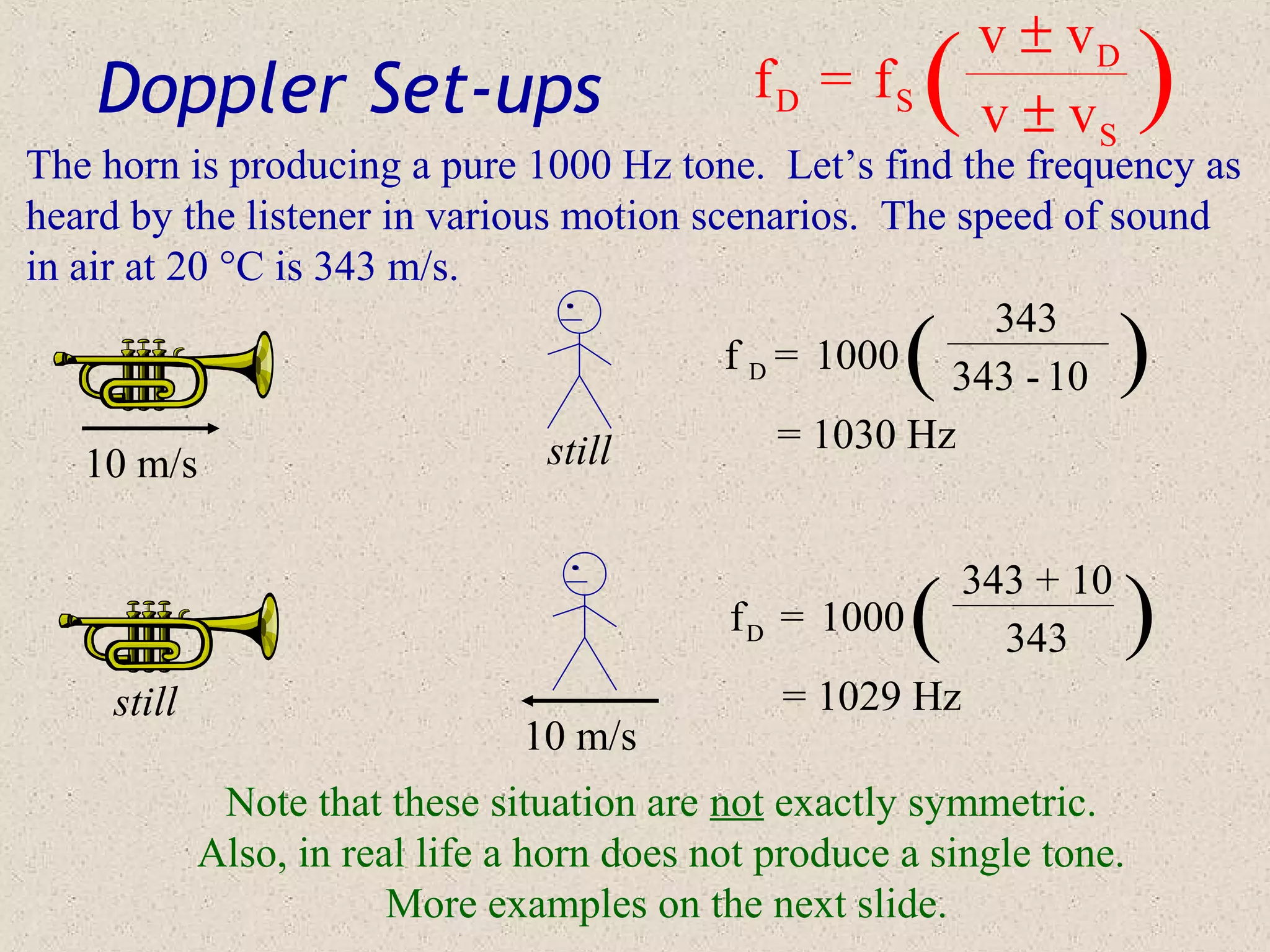
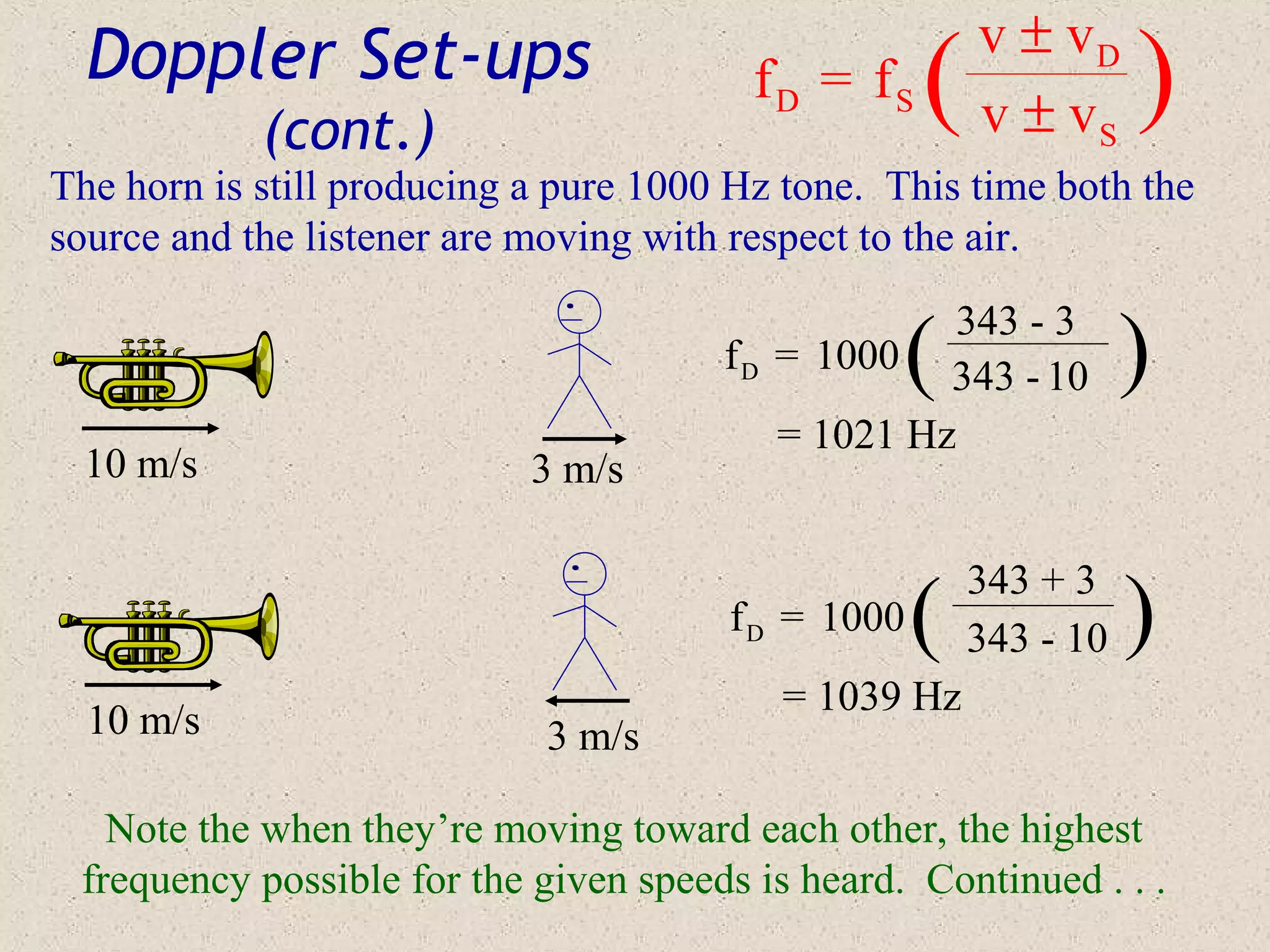
The Doppler effect describes how the observed frequency of a sound or electromagnetic wave is different from its emitted frequency due to relative motion between the source and observer. The Doppler equation accounts for the speeds of both the source and observer relative to the medium, and whether their motion causes the observed frequency to increase or decrease. Examples are provided of how the Doppler effect changes observed sound frequencies for different source-observer motion scenarios, including cases where both are moving.