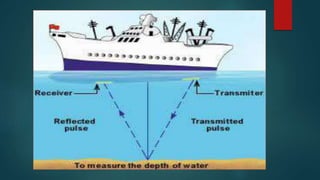
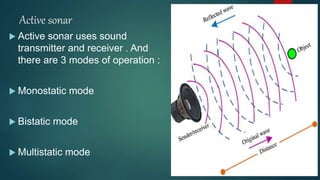
This document provides an overview of sonar technology. It discusses the history of sonar, beginning with its use by animals and early experiments by Leonardo Da Vinci and others. It describes the main types of sonar - active and passive. Applications include ocean mapping, locating ships and submarines, and underwater security. Limitations include impacts on marine life and noise pollution. New innovations are described, including a technique called Finger IO that allows interaction with mobile devices by writing or gesturing on nearby surfaces using built-in microphones and speakers.