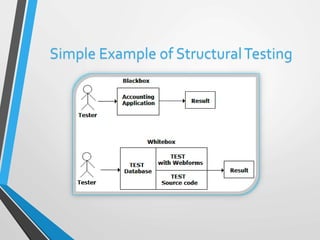
Black-box testing examines software functionality without knowledge of internal structures. It aims to find errors in functions, interfaces, data access, behavior, and initialization/termination. Black-box testing can be used at all testing levels and is most useful for larger systems. It has advantages of testing from a user perspective but limitations of only testing a small number of inputs.