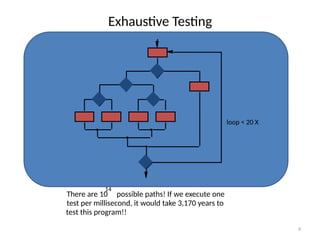
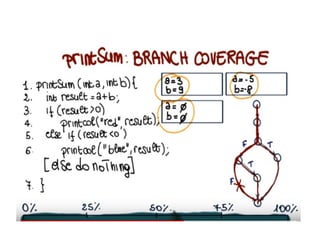
The document outlines various software testing techniques, categorizing software bugs and their potential impacts on programs. It discusses the importance of testing activities, different methodologies such as black-box and white-box testing, as well as specific techniques like boundary value analysis and error guessing. Additionally, it covers the stages of testing including alpha and beta testing, as well as the significance of both functional and non-functional testing in ensuring software quality.