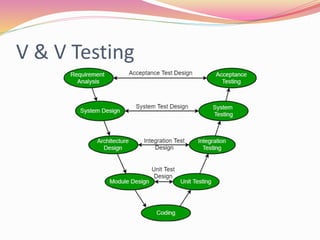
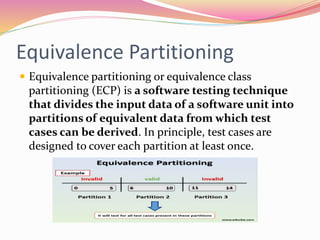
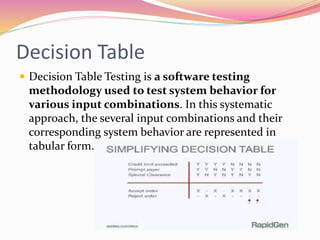
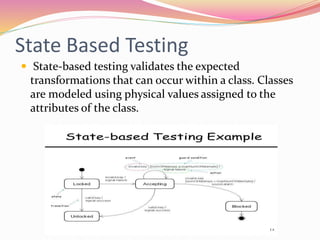
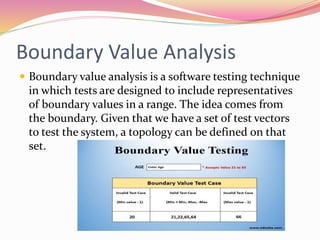
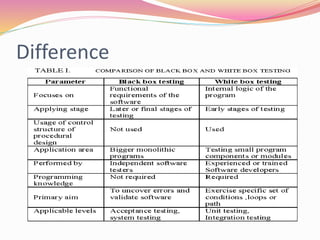
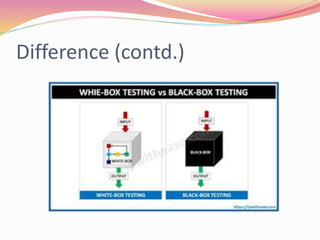
This document discusses various software testing methods, focusing on both black-box and white-box testing techniques. It highlights the importance of ensuring software quality through effective testing strategies, including structural and functional testing, with specific methodologies like equivalence partitioning and boundary value analysis. The document also outlines the advantages and disadvantages of each testing approach, emphasizing their roles in the software development lifecycle.