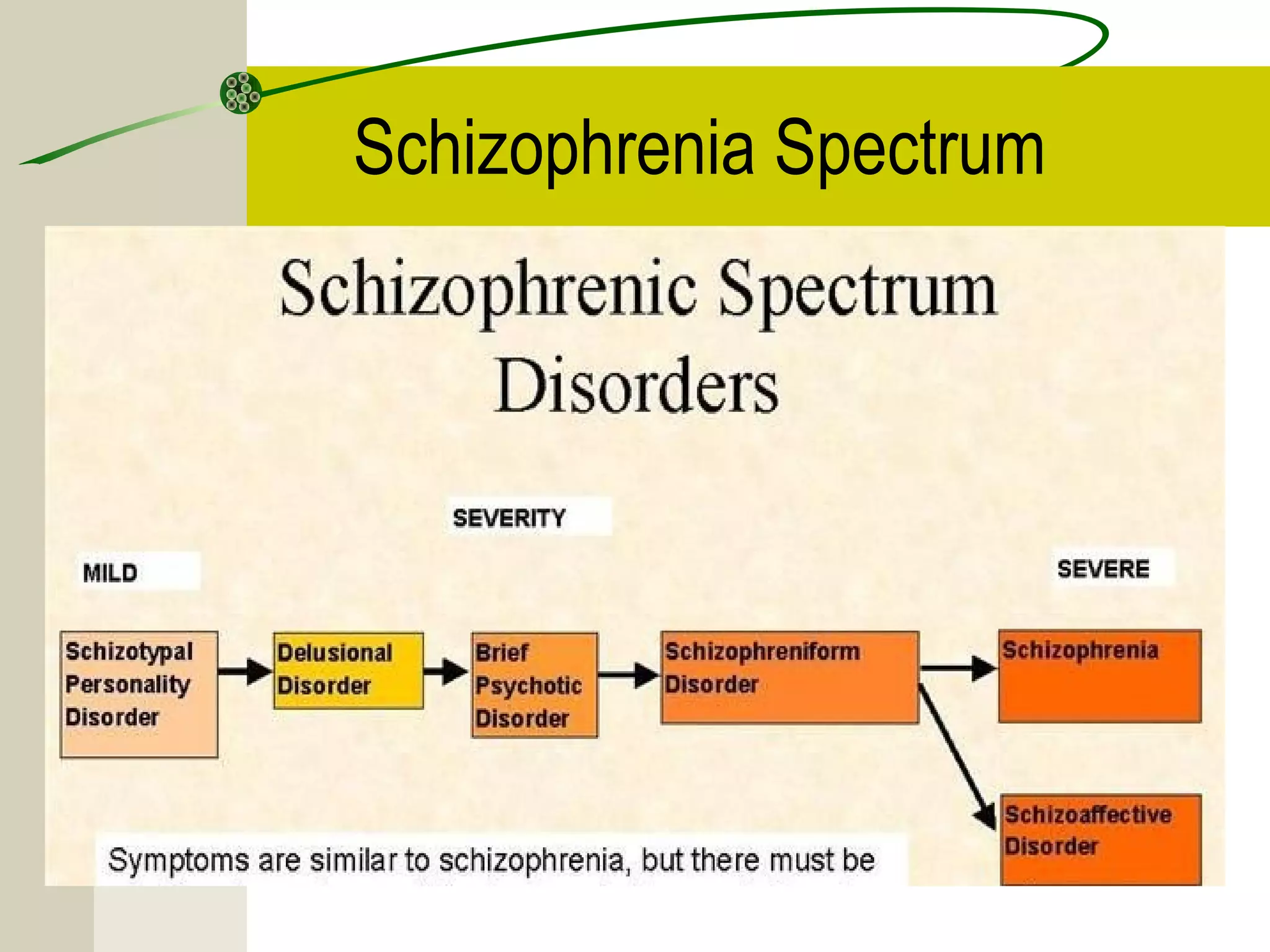
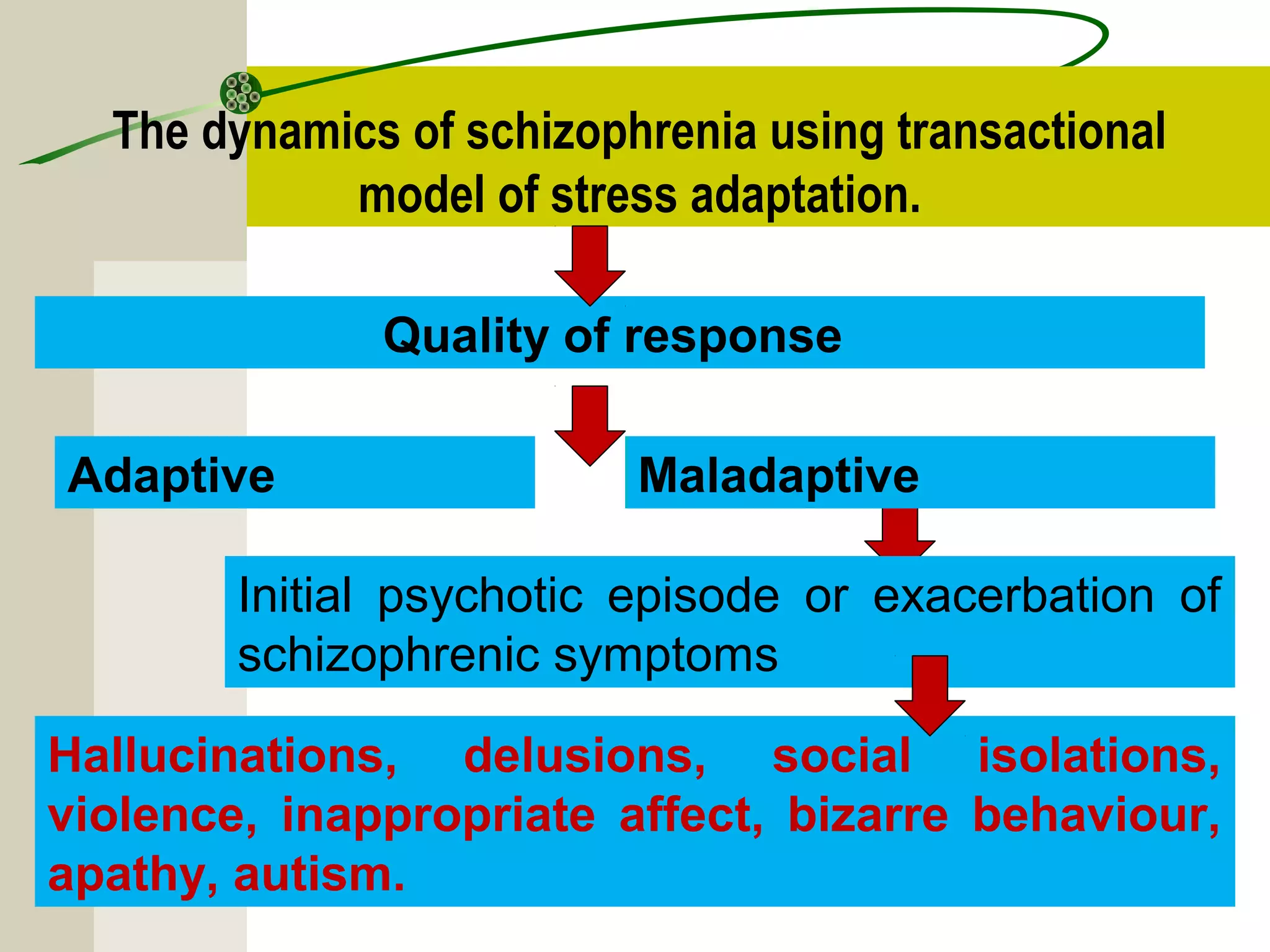
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders involve distortions in perception of reality and impairments in thinking, behavior, and emotion. The term schizophrenia was coined in 1908 and refers to a "split mind." Common types include paranoid schizophrenia, characterized by delusions and auditory hallucinations, and disorganized schizophrenia with loose and disordered thinking. Positive symptoms add characteristics like delusions and hallucinations, while negative symptoms remove characteristics and result in flattened affect and lack of motivation. Biological and environmental factors may contribute to the development of psychotic disorders.