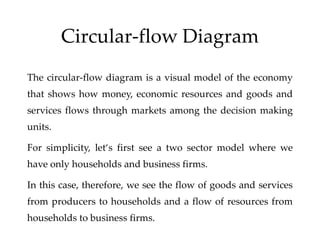
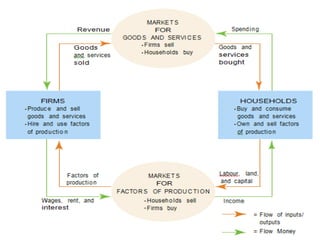
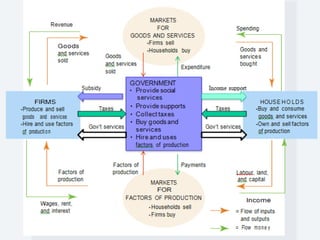
The document discusses different economic systems and concepts. It defines economic systems as how a society organizes and distributes resources and goods. The main factors of production are defined as land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. It then describes the three main economic systems - capitalist, command, and mixed economies - and compares their key features, advantages, and disadvantages.