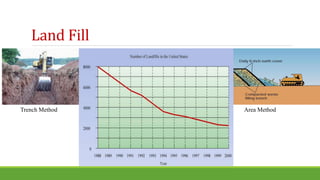
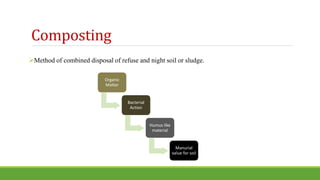
The document discusses various techniques for solid waste disposal and treatment including dumping, landfilling, composting, incineration, and recycling. Landfilling techniques include trench, ramp, and area methods. Composting can be done through various methods like Bangalore, mechanical, and vermicomposting. Incineration reduces waste volume by combustion and has different types like refuse-derived fuel and mass burn. Recycling processes used materials into new products to reduce consumption of raw materials and pollution. Common materials recycled include metals like steel and tin cans, and paper products.