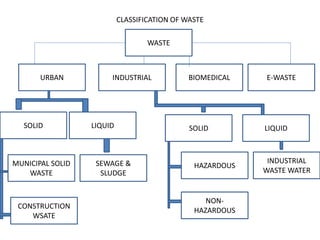
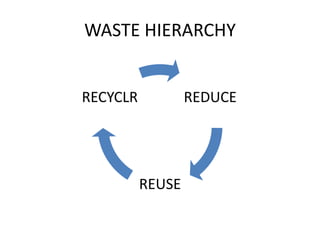
The document provides an overview of waste management, including activities such as collection, transportation, segregation, recycling, and disposal of different types of waste. It classifies waste into categories such as municipal solid waste, construction waste, industrial waste, biomedical waste, and e-waste, while also outlining relevant laws and disposal methods like landfilling and incineration. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of managing waste effectively through new technologies and promotes a waste hierarchy of reduce, reuse, and recycle.