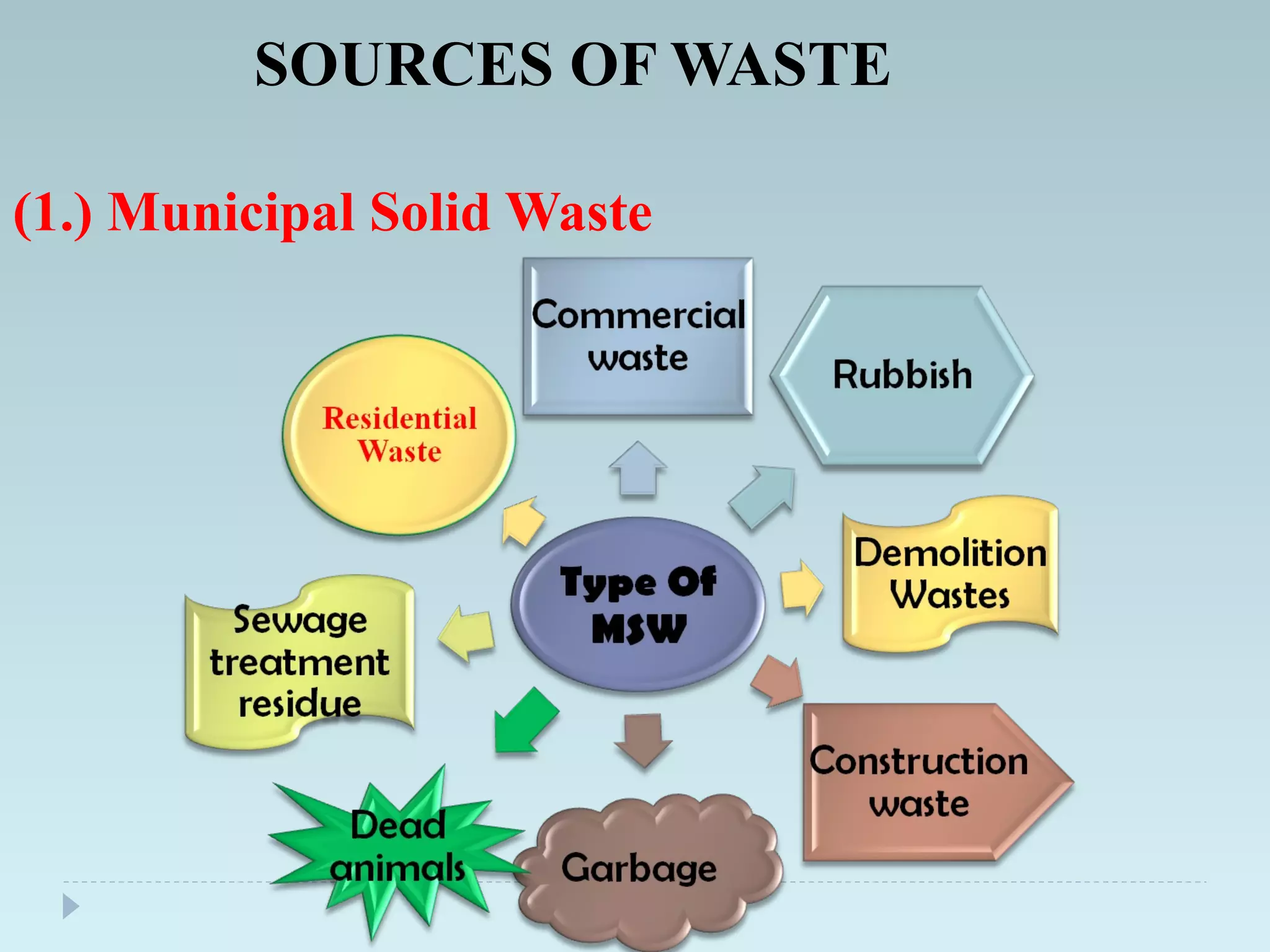
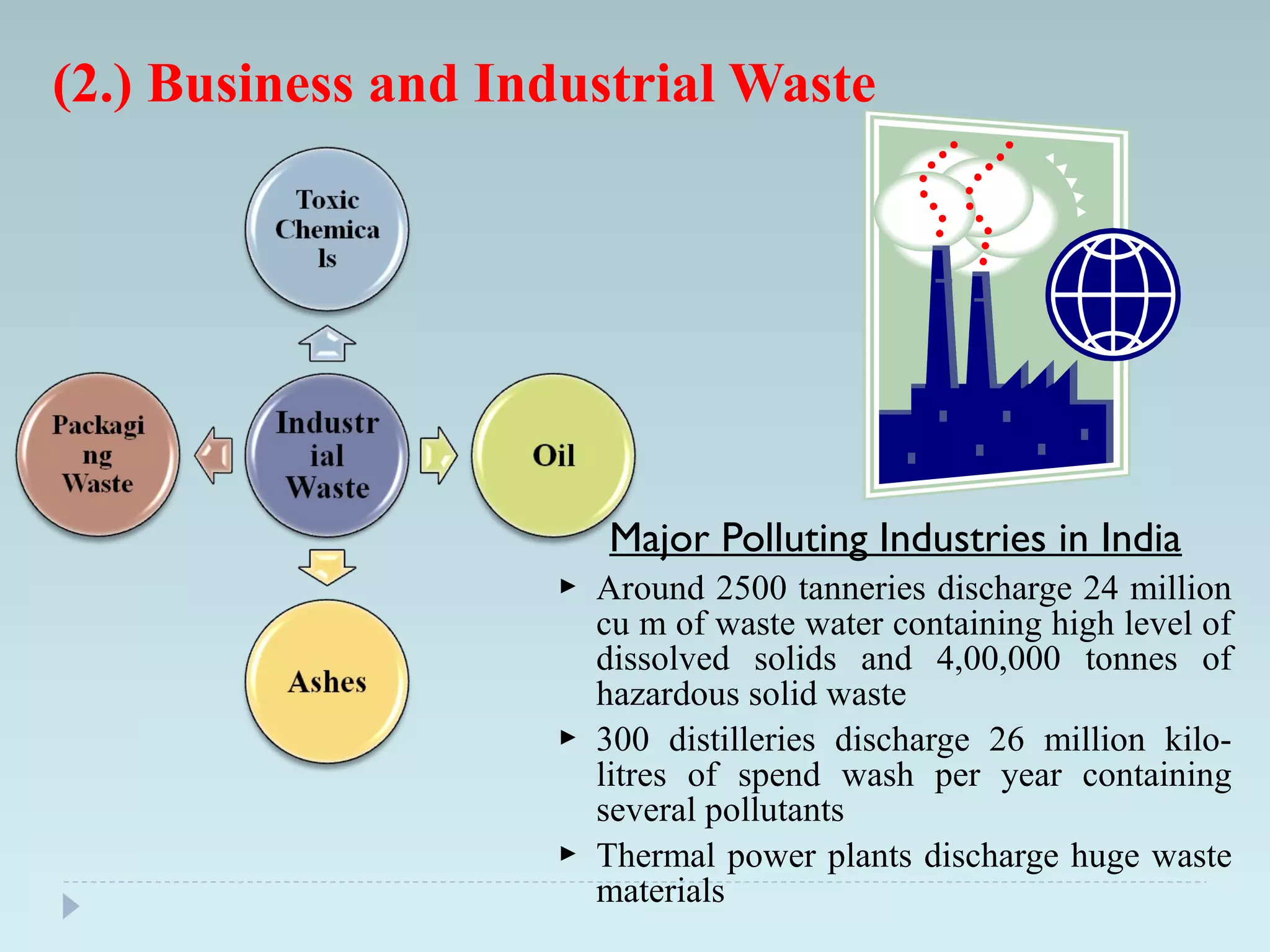
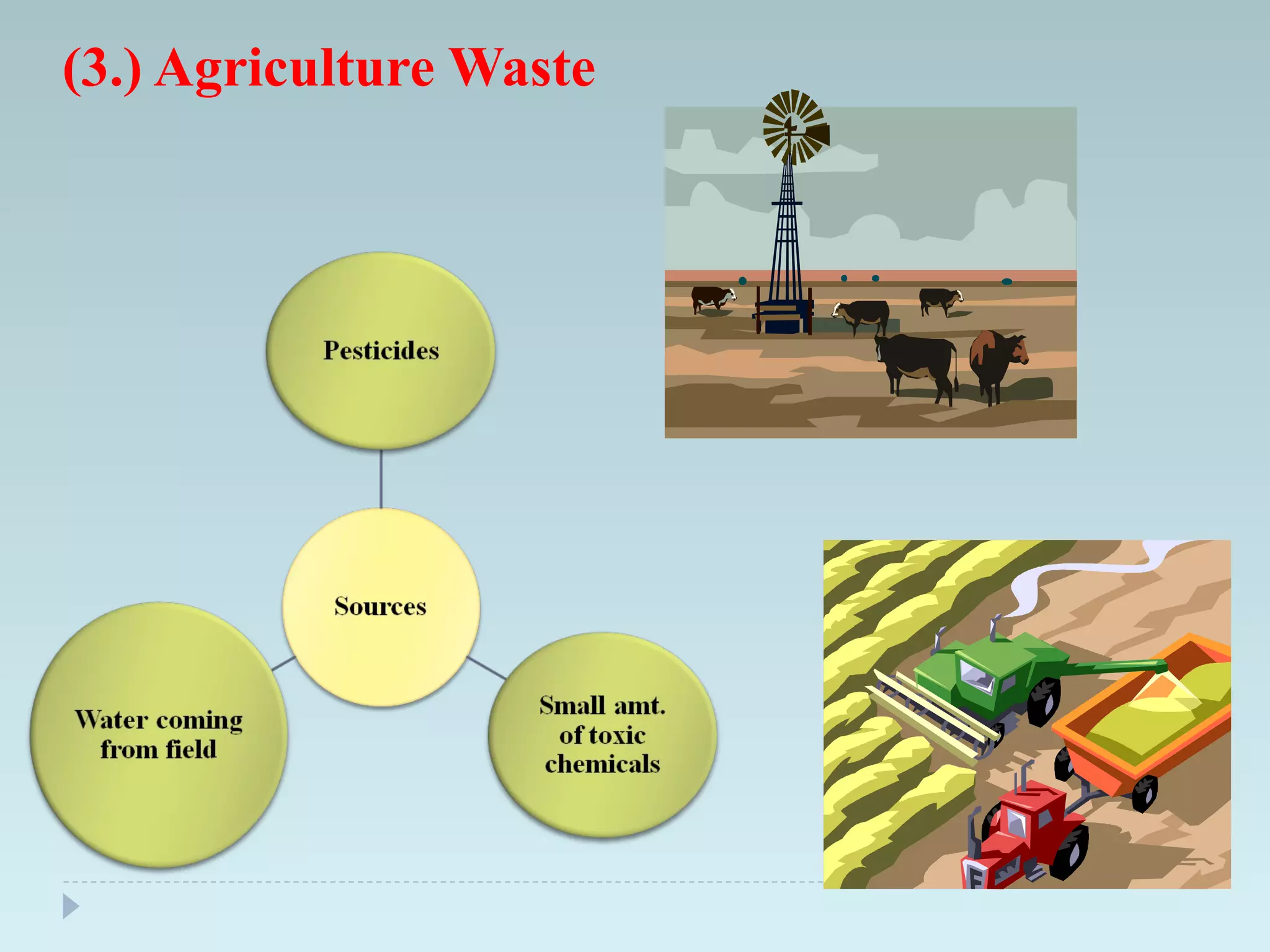
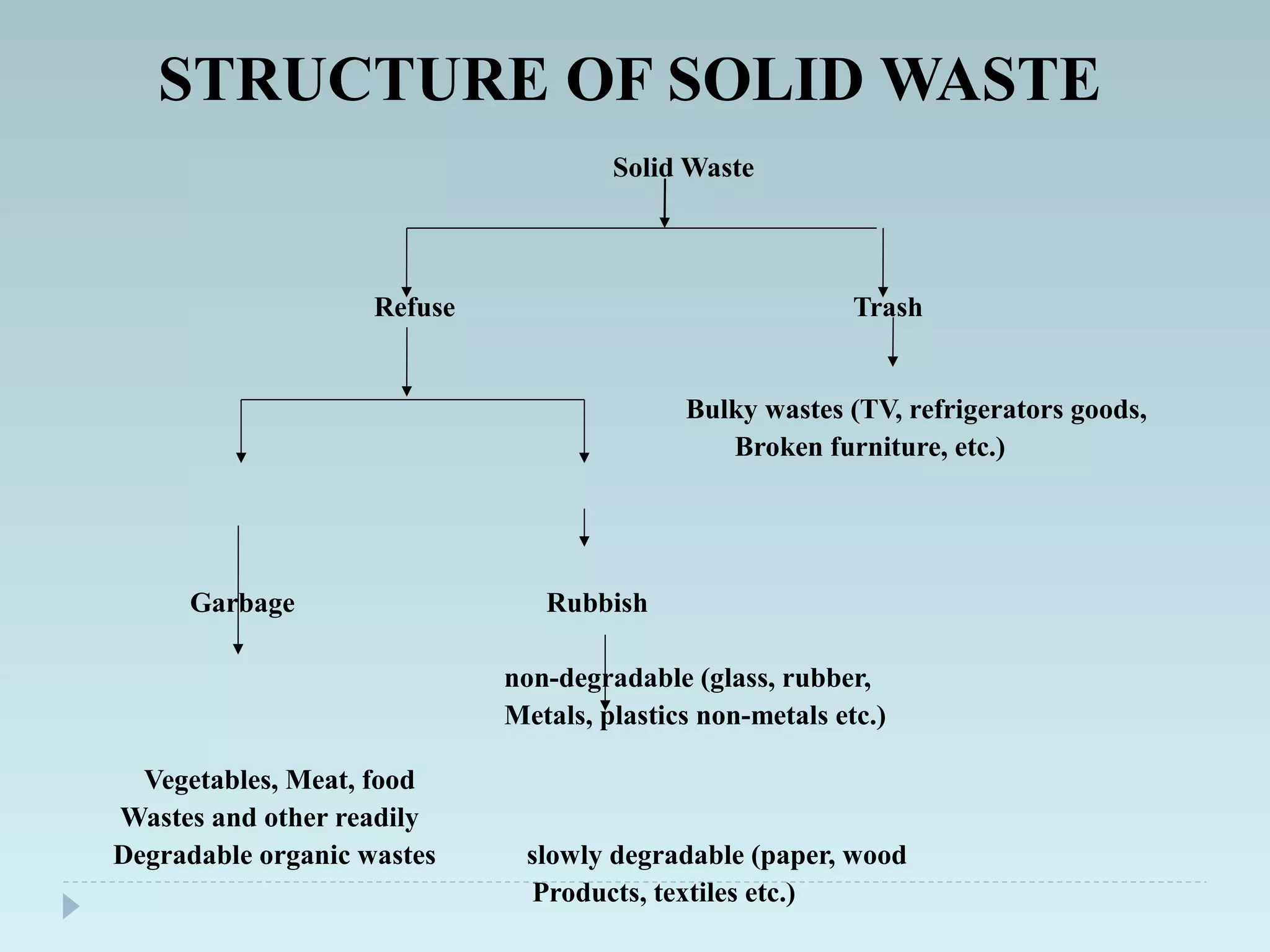
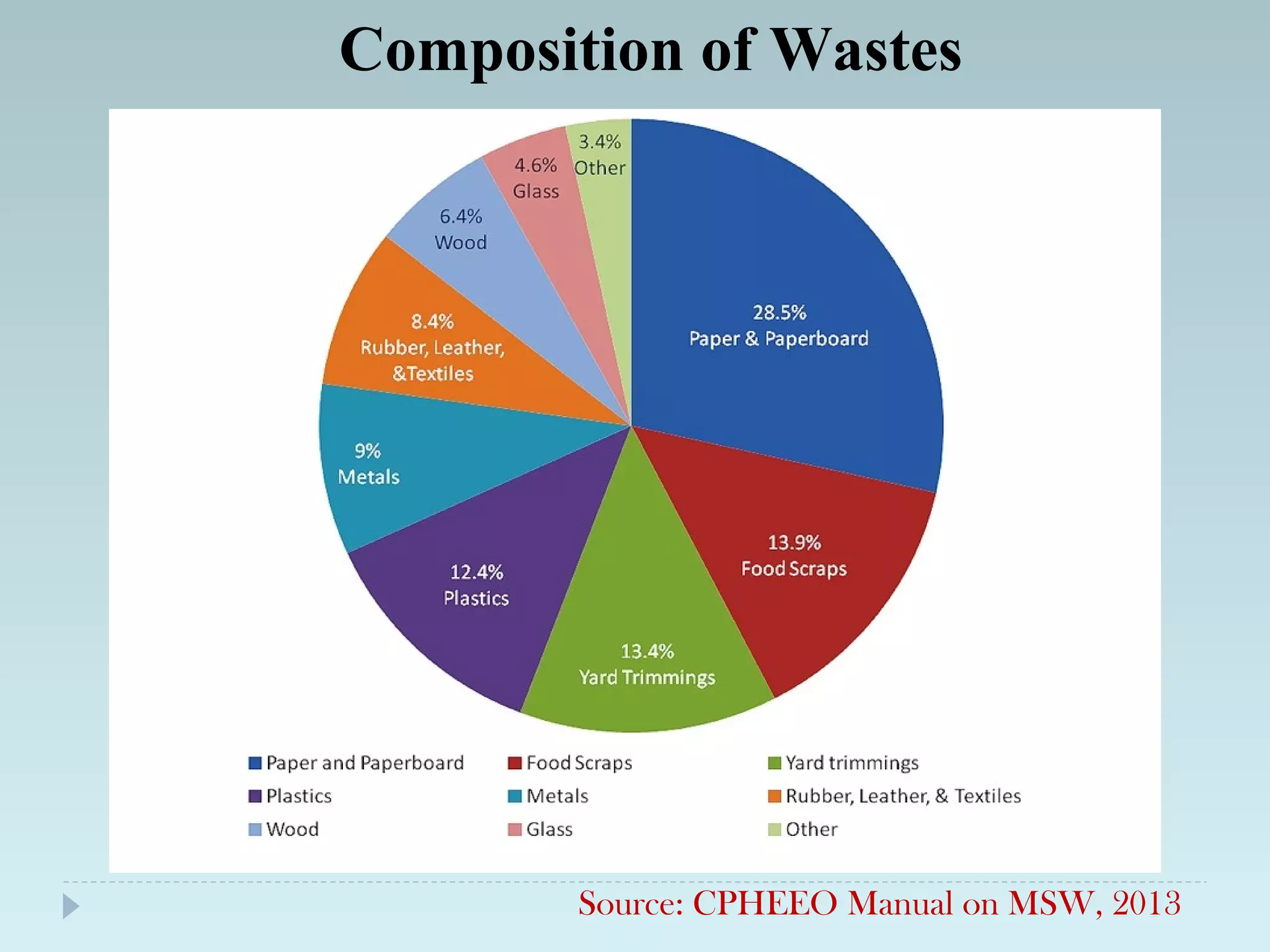
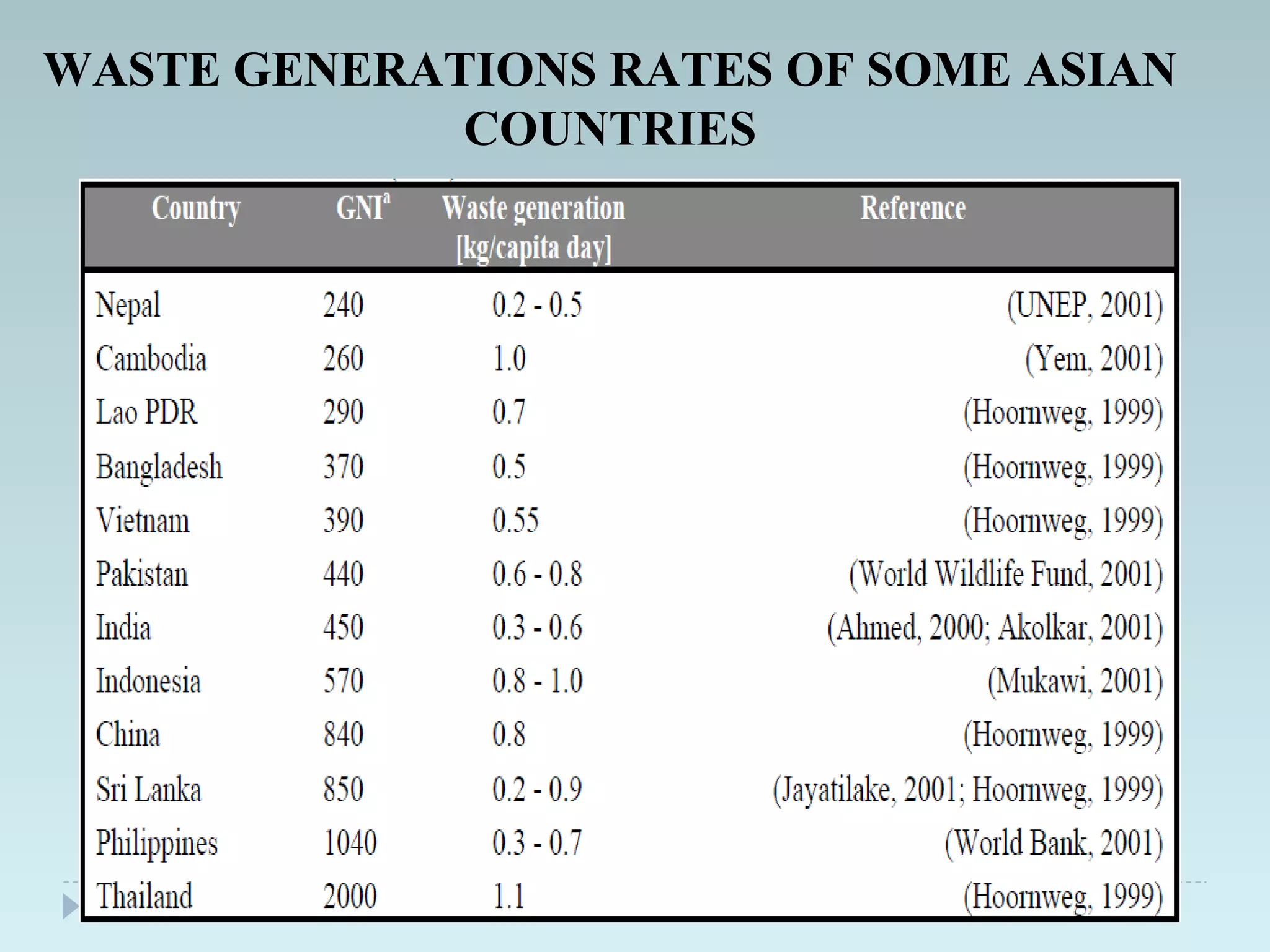
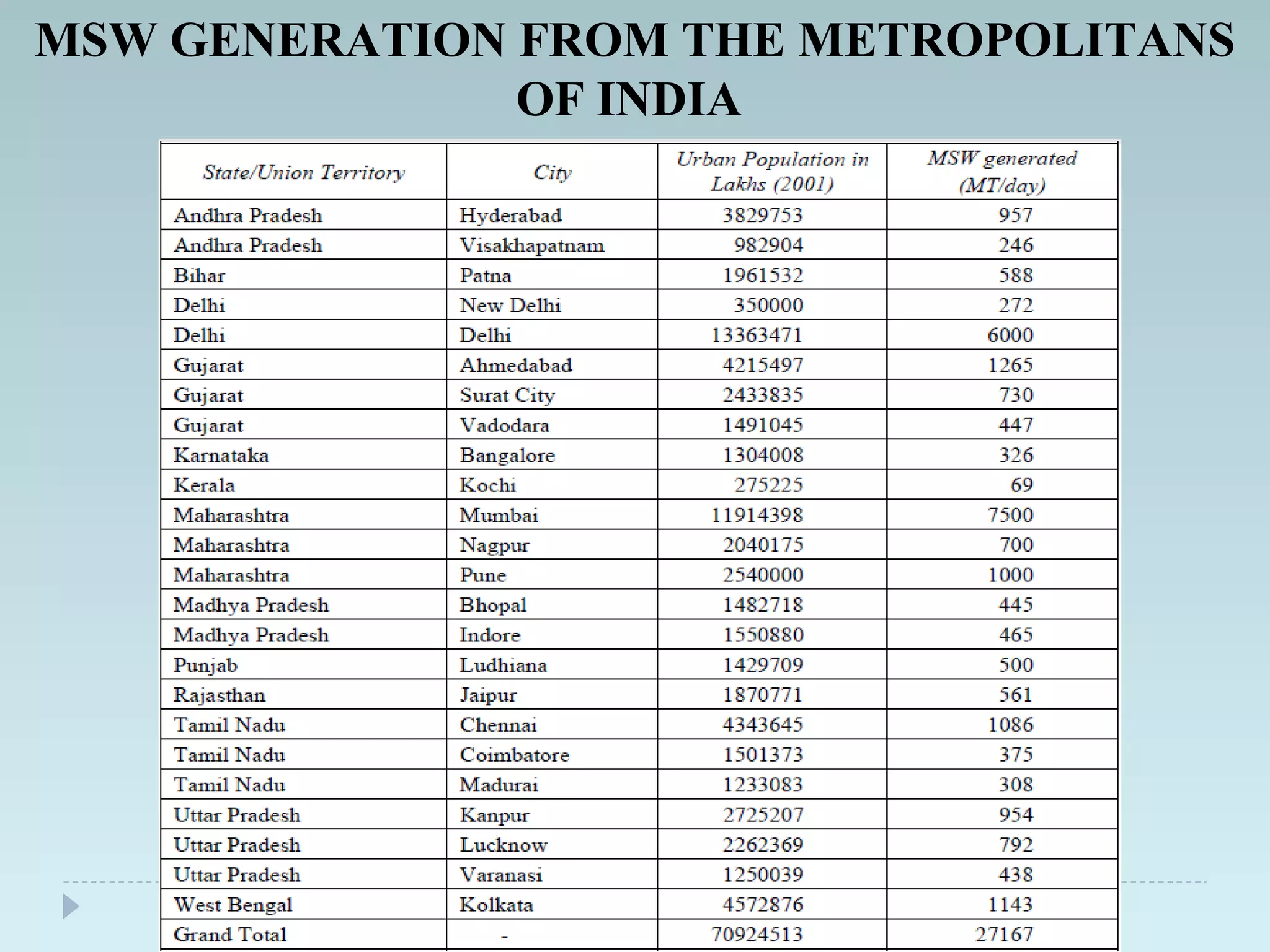
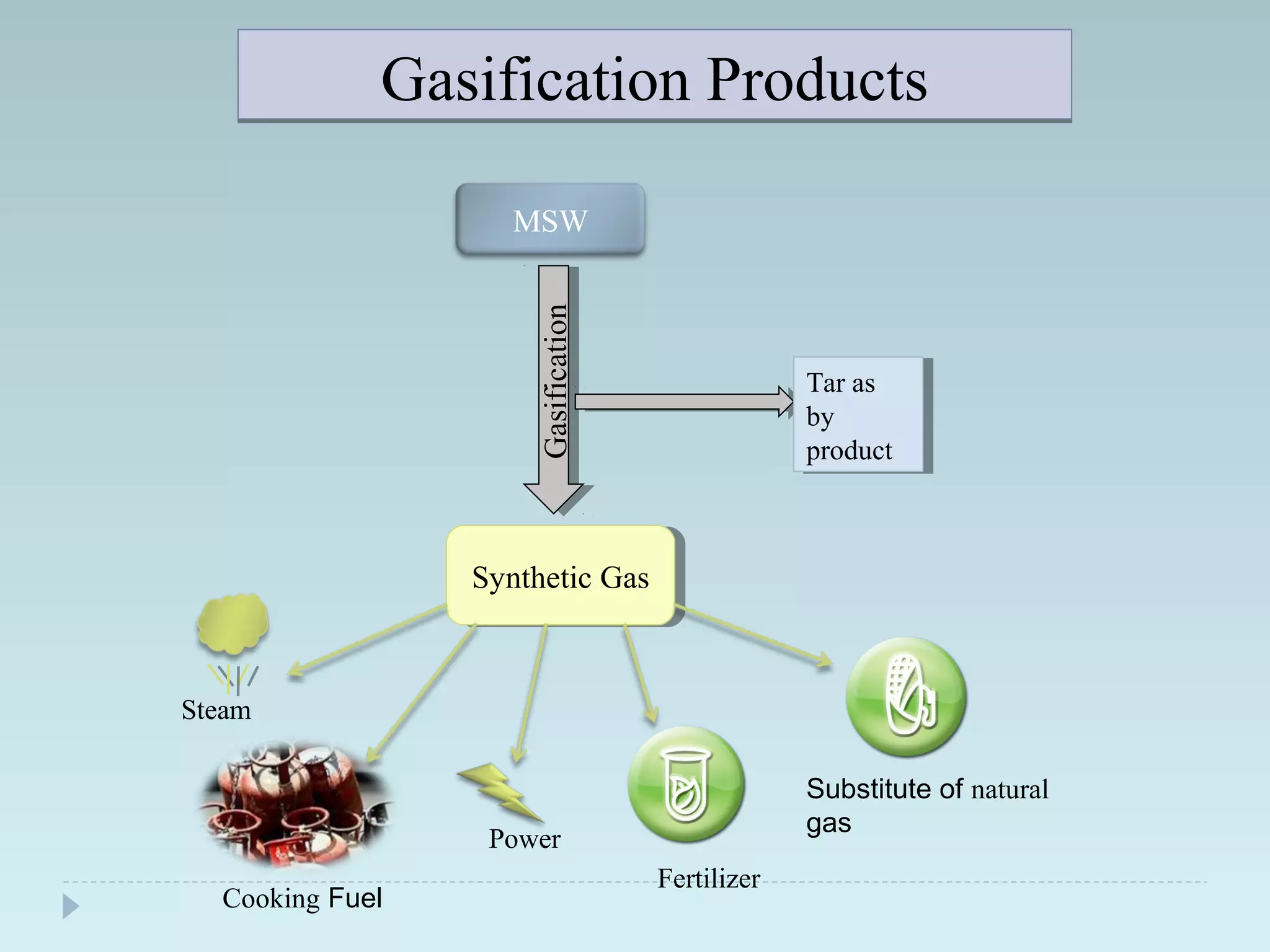
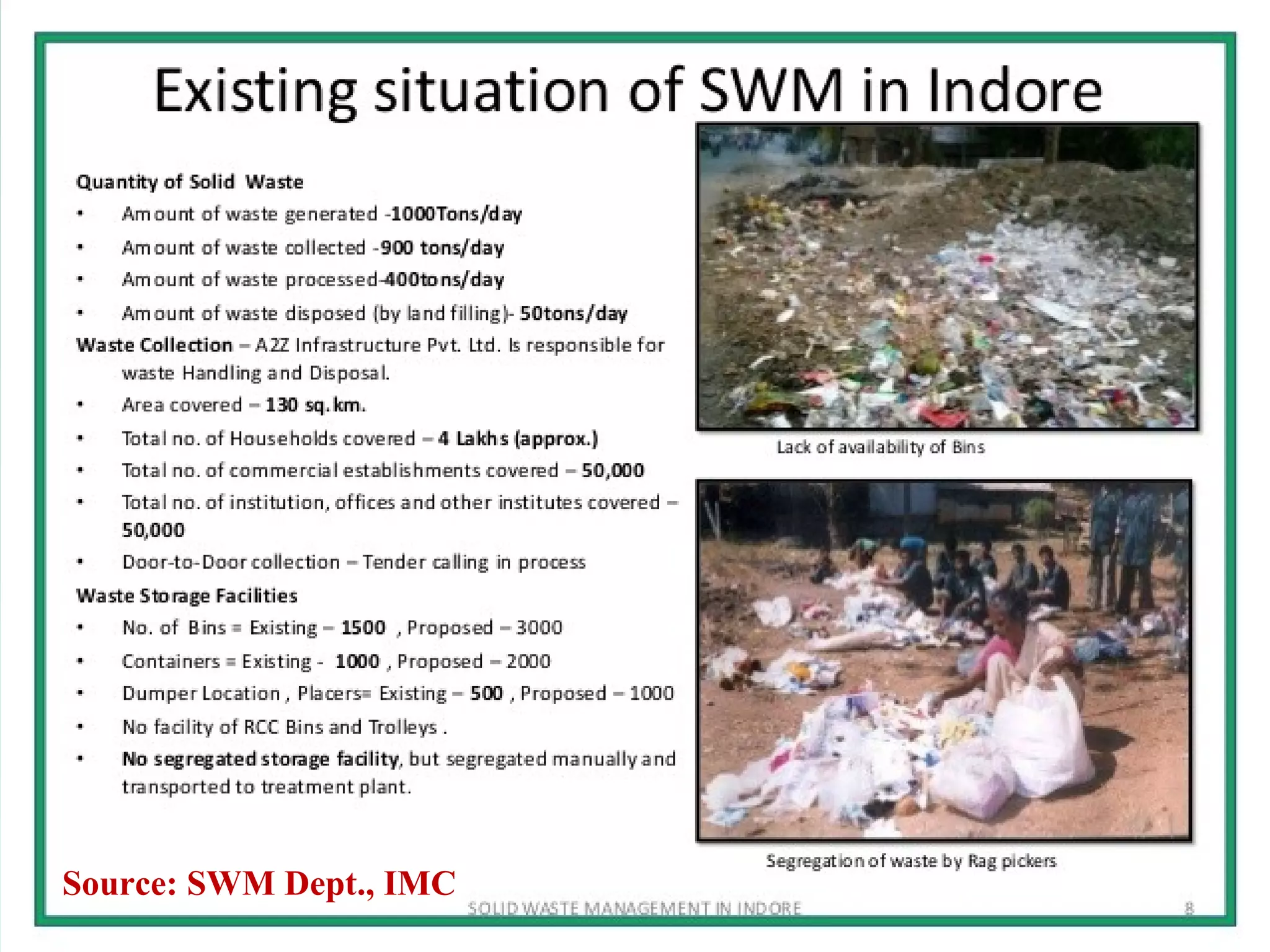
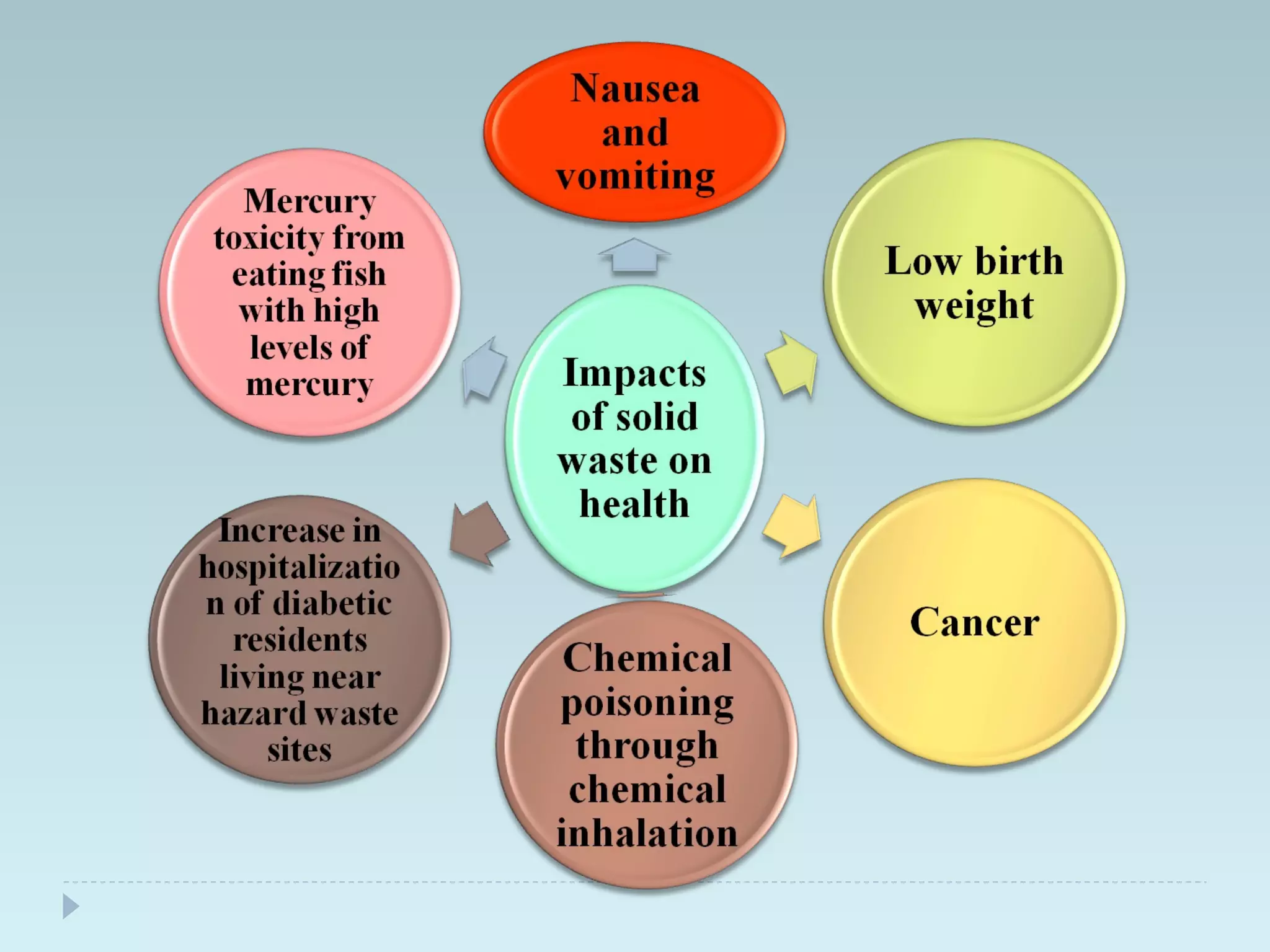
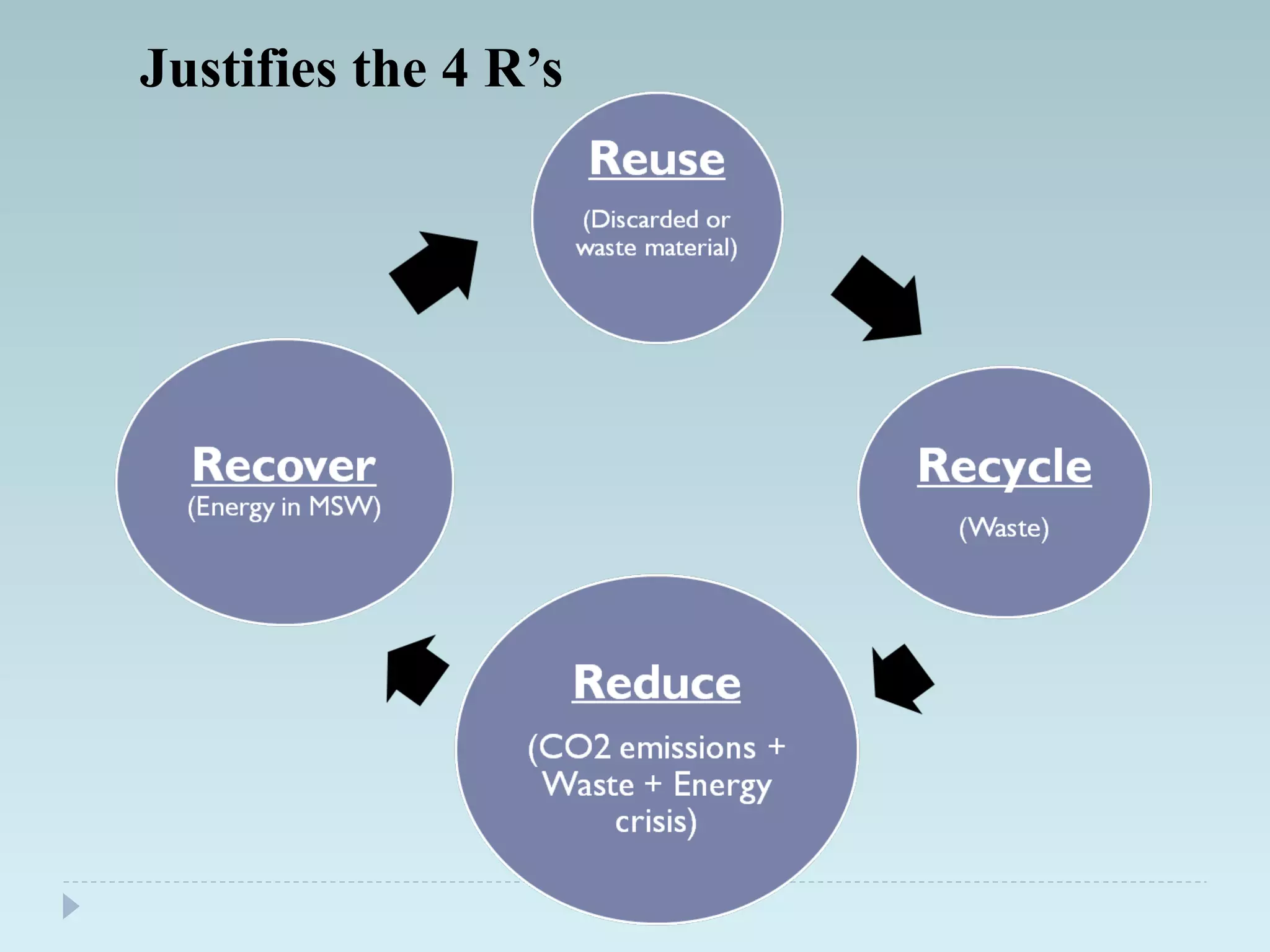
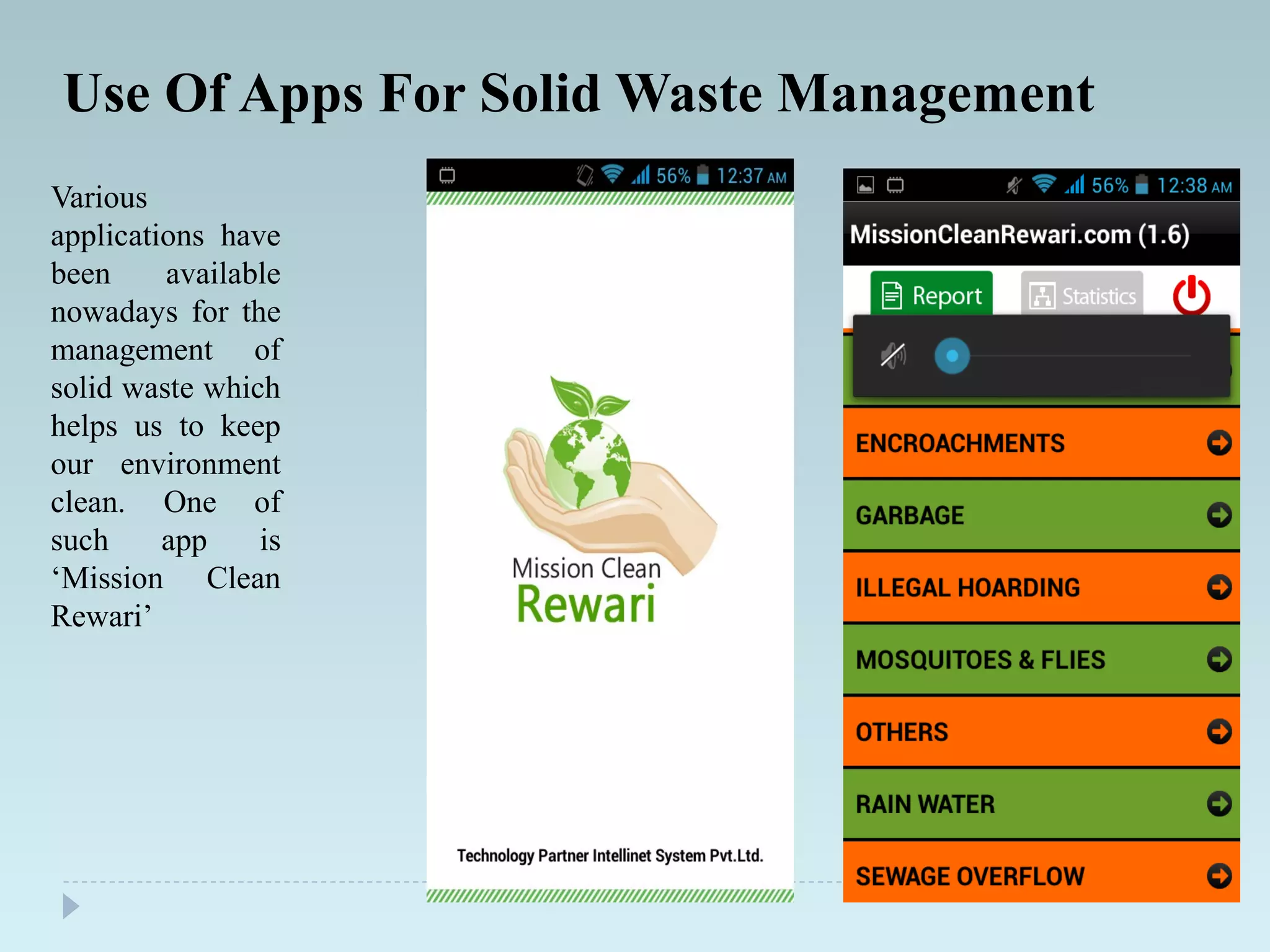
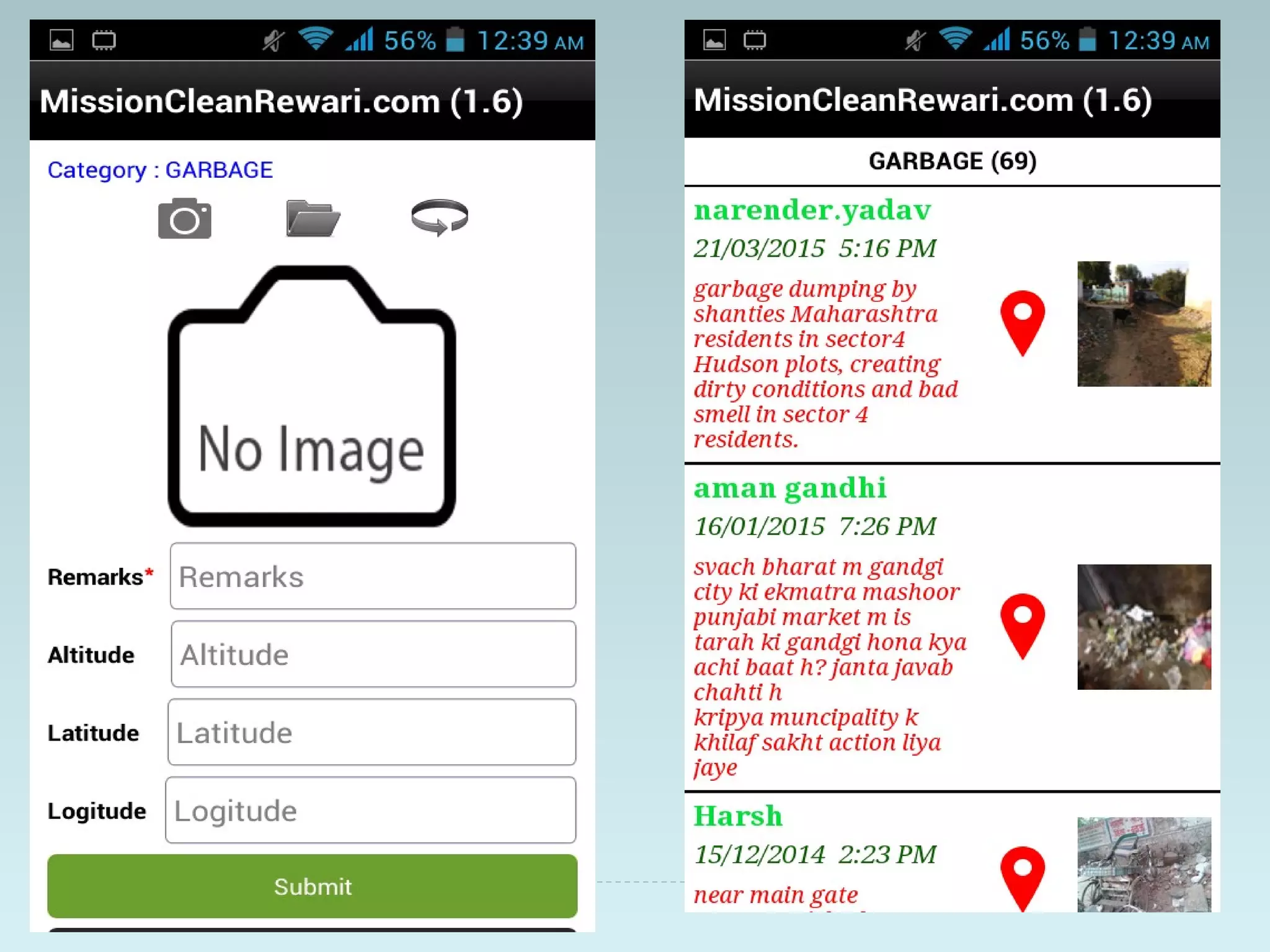
The document outlines an extensive study on solid waste management, highlighting its goals, sources, and various disposal methods including landfill, incineration, and composting. It discusses the growth and characteristics of solid waste in India, emphasizing the environmental implications and the need for effective management practices. Additionally, the report covers case studies, preventive measures, and technological solutions like the use of apps for improvement in waste management systems.