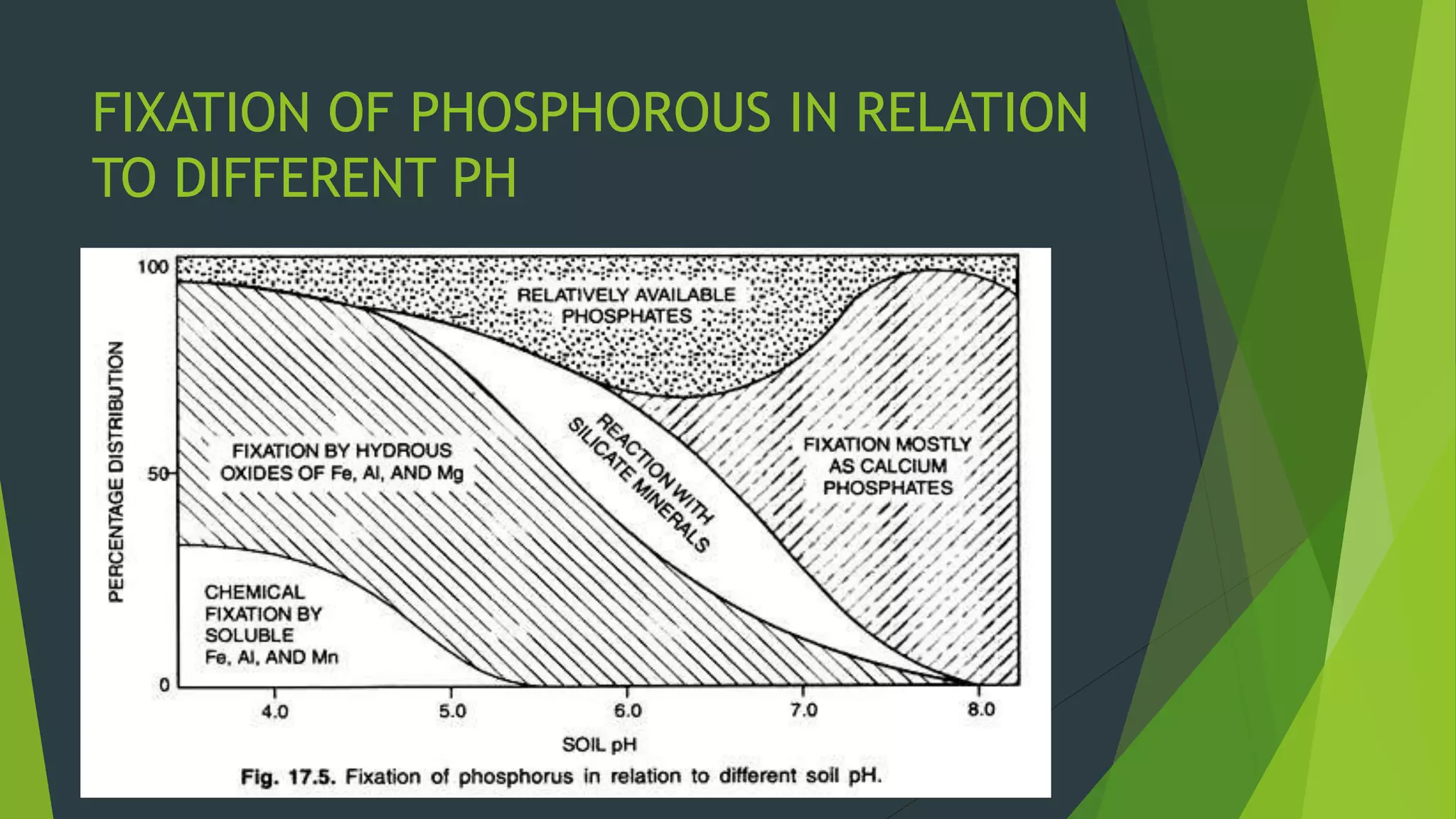
The document presents information on phosphate fixation in soils. It discusses how phosphorus is an essential nutrient for plant growth but is limited in about 40% of the world's soils due to fixation reactions. These reactions reduce the solubility and availability of phosphorus by adsorbing phosphate ions onto soil particles like iron, aluminum, and calcium compounds. The degree of fixation depends on soil properties like mineral composition, pH, and calcium carbonate content. Phosphate can be temporarily or permanently fixed depending on the reaction conditions, reducing phosphorus efficiency in soils to 10-20%.















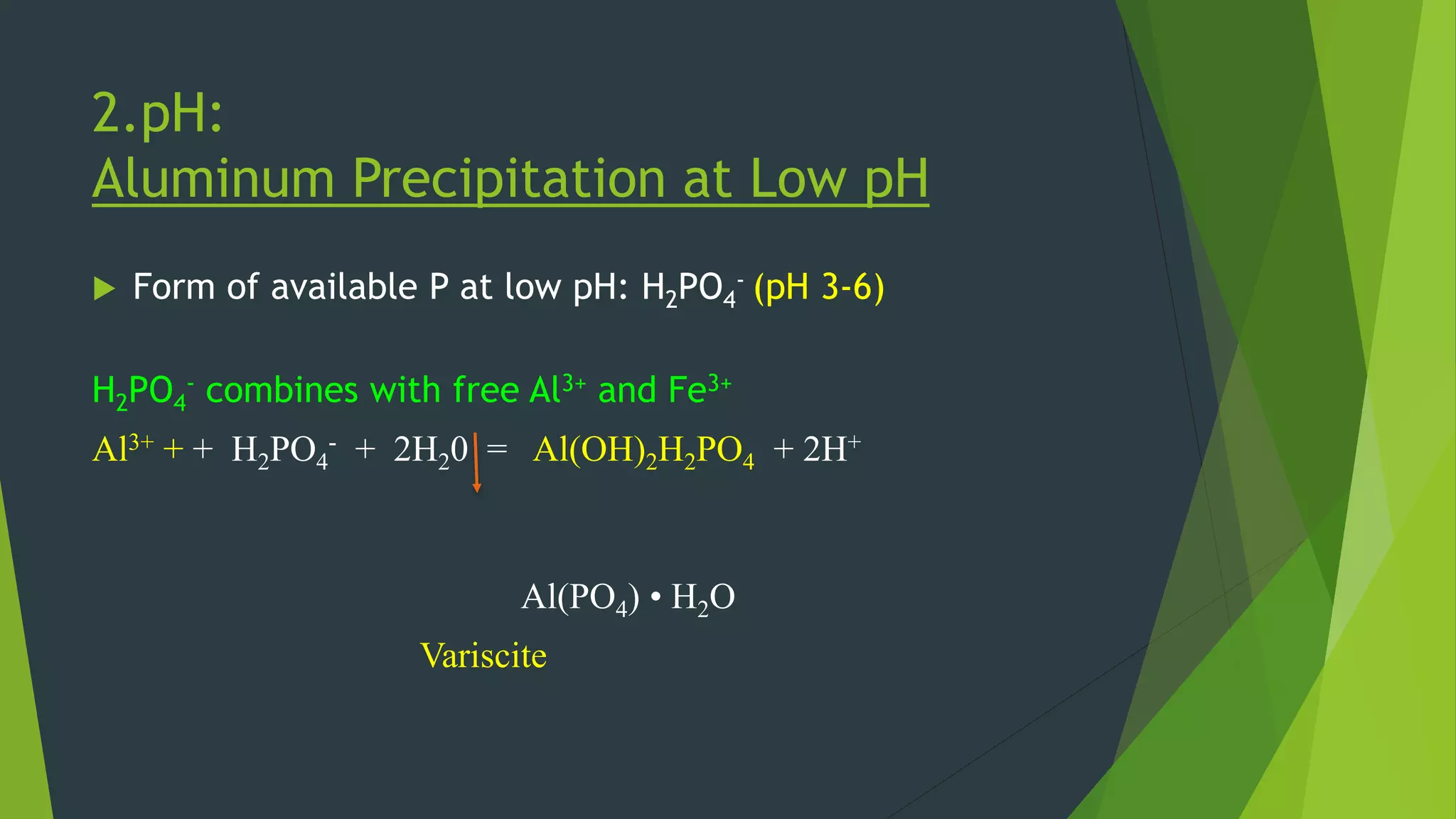
![Calcium Binding in Basic Soils
CaCO3
CaCO3 + 2H2(PO4)- = Ca [H2(PO4)]2 + CO3
2-
CaHPO4
Ca5(PO4)3OH (Apatite mineral)
(higher calcium availability)
H2(PO4)- is the available form of P](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phosphatefixatiionsoilfertilitynew-180310184633/75/Phosphate-fixation-18-2048.jpg)

