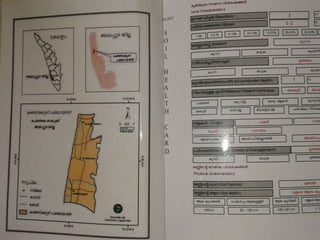
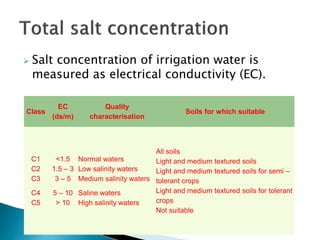
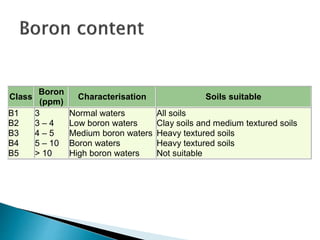
The document discusses soil health management in Kerala. It notes that soil health cards are provided to farmers to evaluate soil quality based on physical, chemical and biological characteristics. The cards are intended to help farmers monitor soil health and make informed management decisions. They provide information on soil type, nutrients, pH, and recommendations to improve soil quality. The overall goal is to support sustainable land management and increase agricultural productivity.