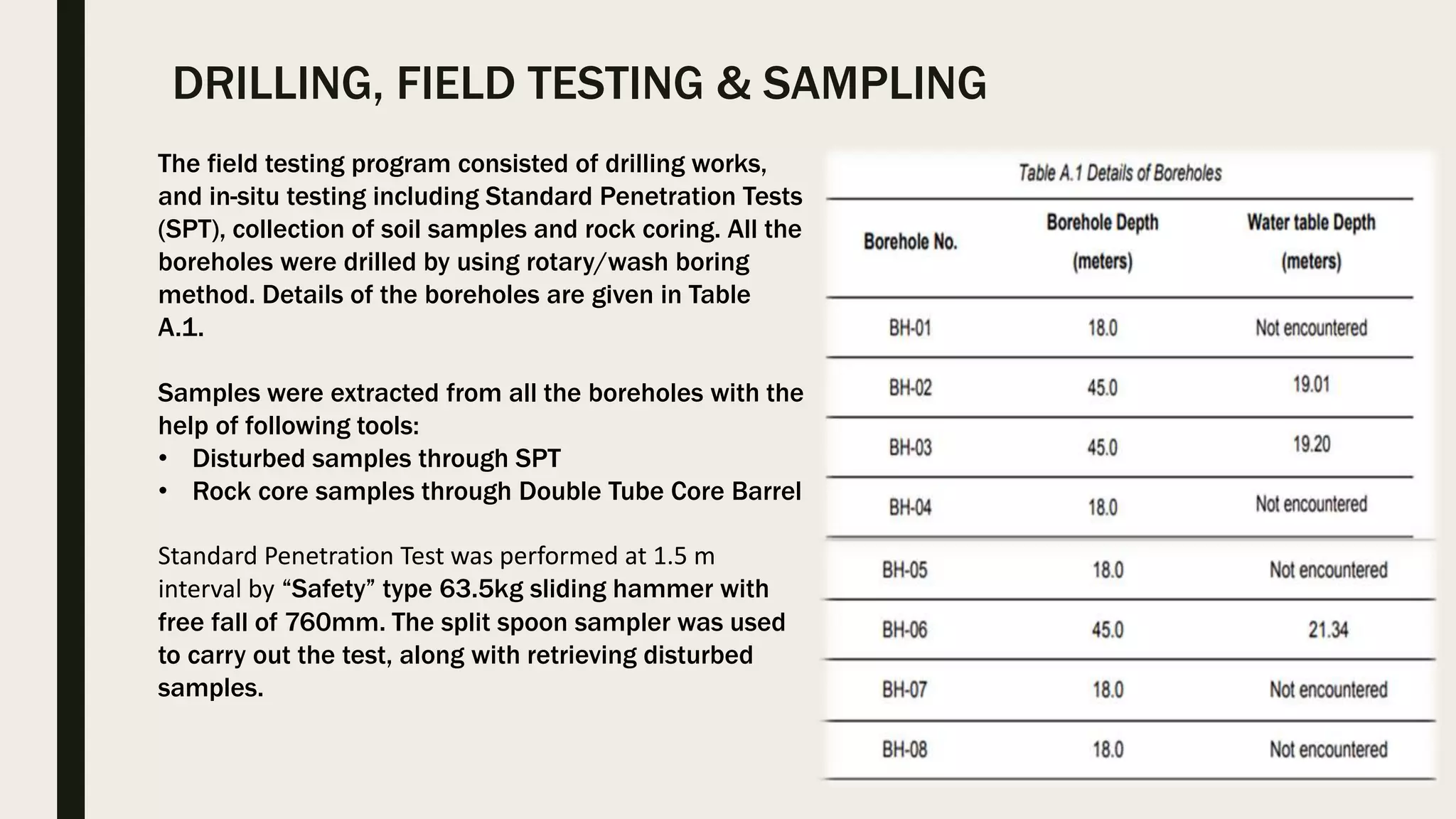
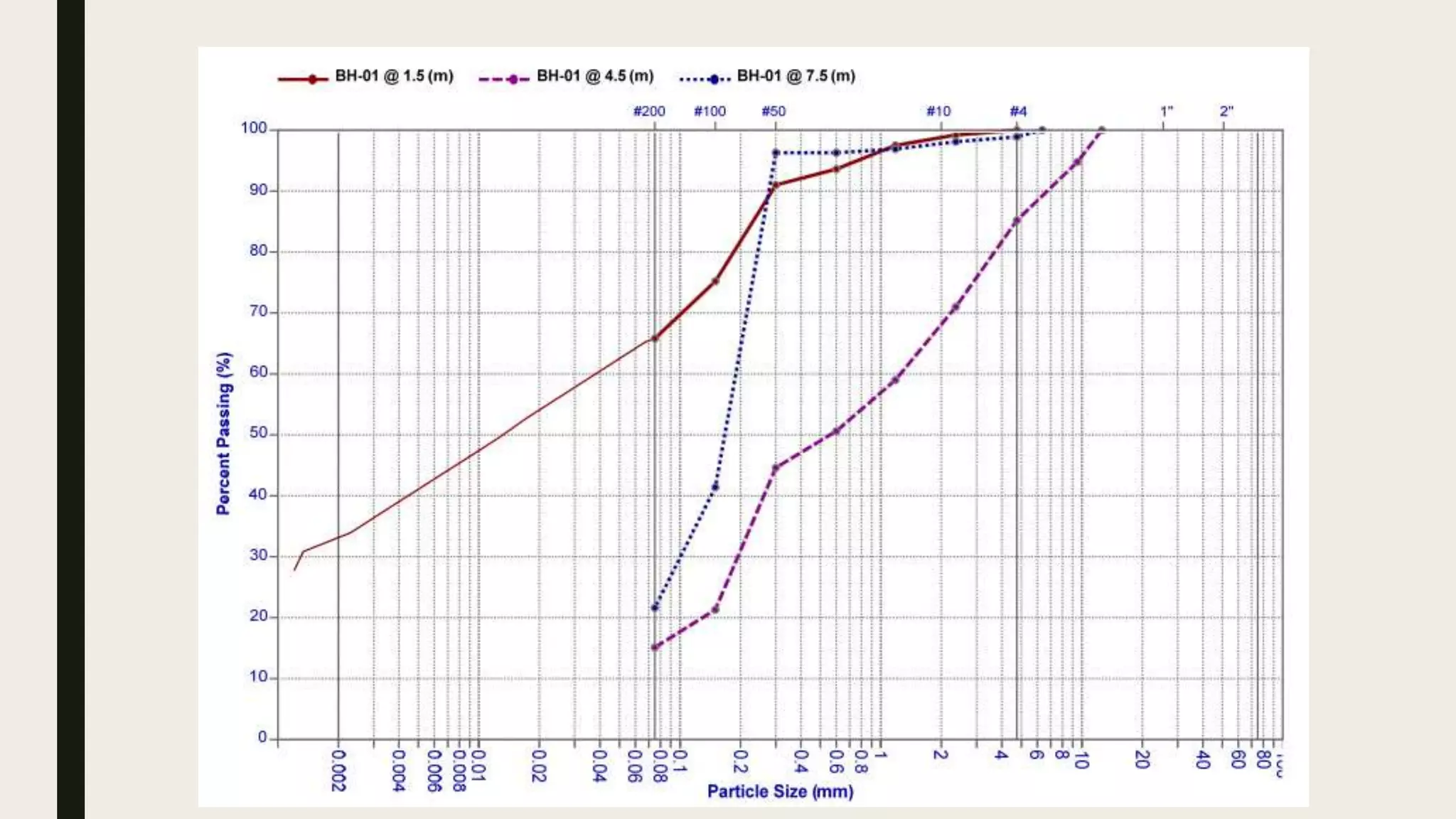
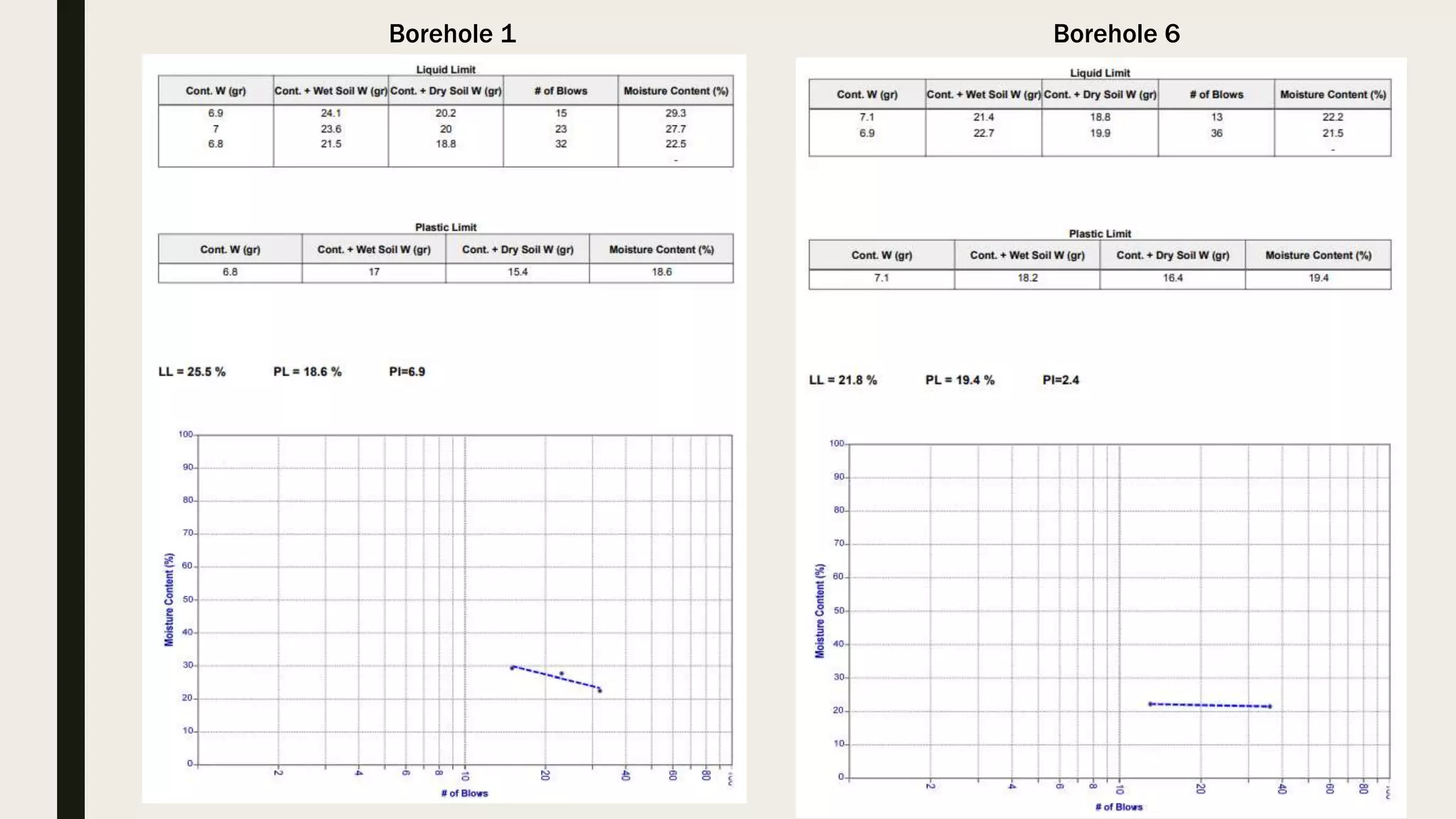
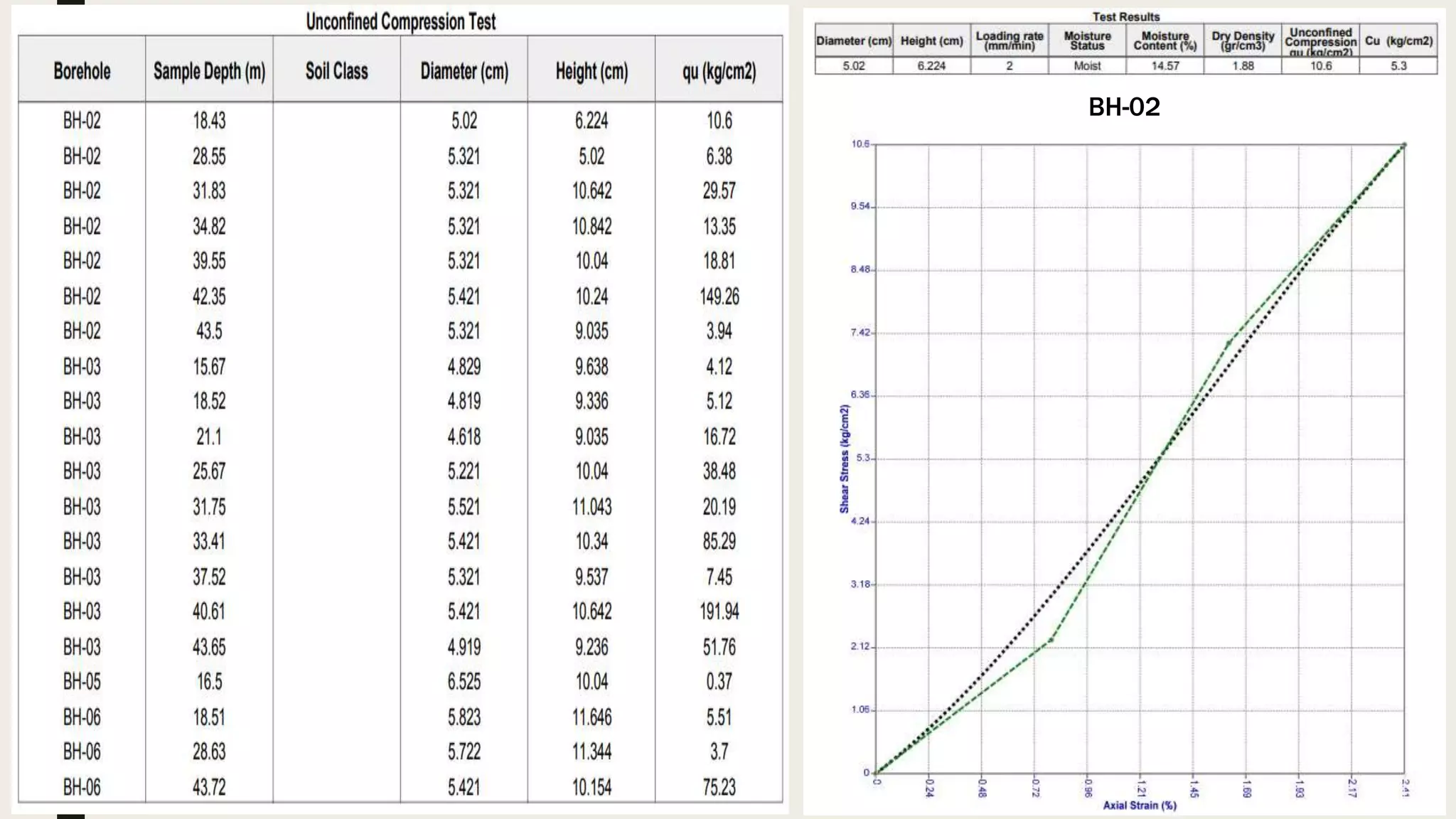
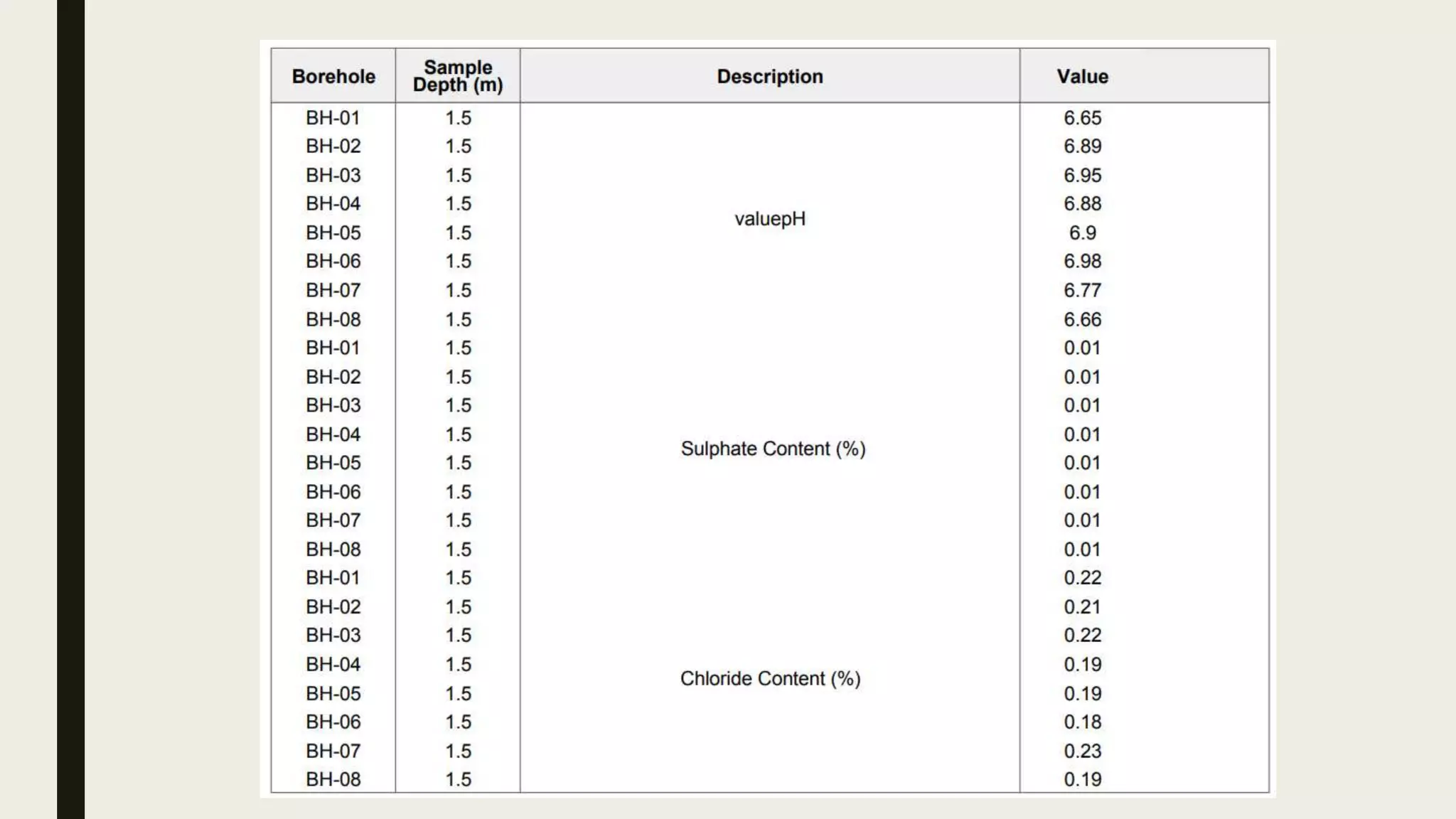
This geotechnical investigation report summarizes soil testing performed for the construction of a shopping mall and residential building in Karachi, Pakistan. Field testing included borehole drilling, standard penetration testing, and soil sampling. Laboratory tests analyzed grain size, Atterberg limits, unconfined compression strength, density, moisture content, direct shear strength, and chemistry. The direct shear tests determined cohesion and angle of friction values for soil samples from 8 boreholes ranging from 0-1.0 kg/cm2 and 12.1-36.4 degrees, respectively. The report provides details of the field and laboratory testing done to characterize the soil conditions at the construction site.