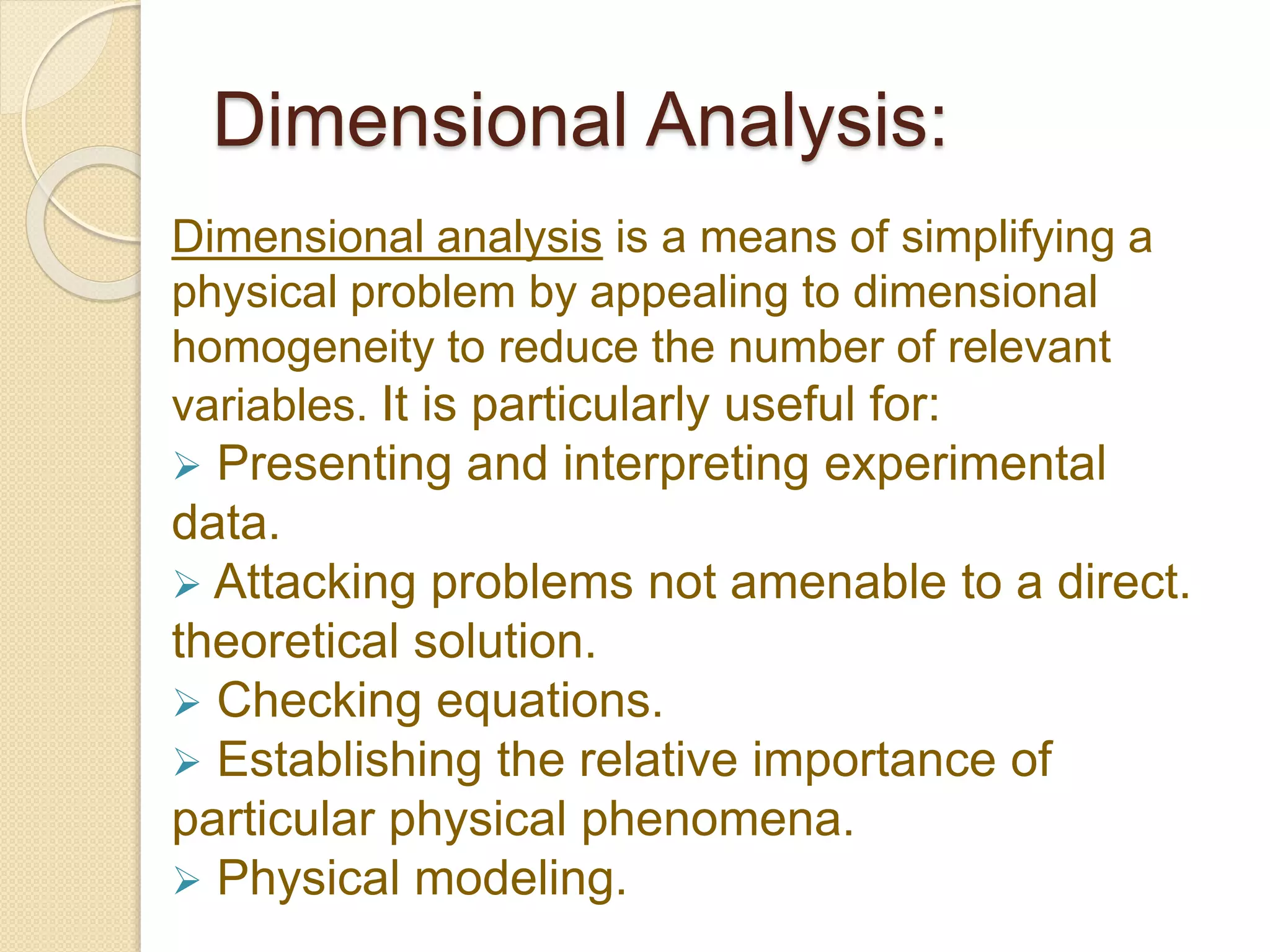
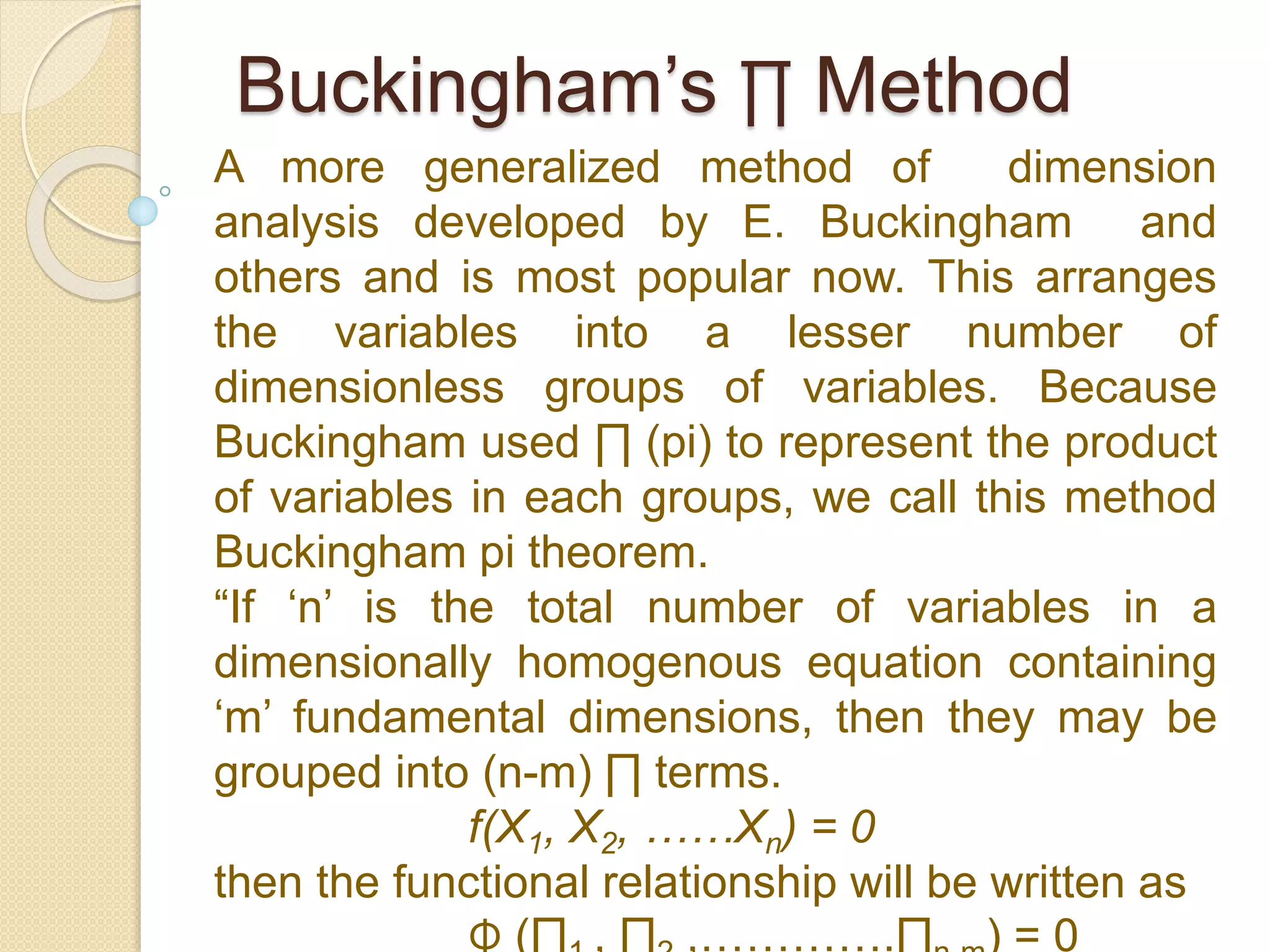
Dimensional analysis is a technique for simplifying physical problems by reducing the number of variables. It is useful for presenting experimental data, solving problems without exact theories, checking equations, and establishing relative importance of phenomena. Dimensional analysis refers to the physical nature and units of quantities. It can be used to develop equations for fluid phenomena, convert between unit systems, and reduce variables in experiments. Two common methods are Rayleigh's method, which determines expressions involving a maximum of four variables, and Buckingham's π-method, which arranges variables into dimensionless groups. Dimensional analysis provides a partial solution and requires understanding the relevant phenomena.





![Method Involves The Following Steps:
1.Gather all the independent variables which
govern variation of dependent variables.
2.Write the functional relationship with the given
data
3.Write the equation in terms of a constant with
exponents(power) a,b,c.....
Where , K is a dimensionless co- efficient and
a,b,c....are the arbitrary powers.
4. Apply principal of dimensional homogeneity, and
),.......,,( 321 nxxxxfY
,.......])(,)(,)[( 321
cba
xxxKY ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dimensionalanalysis-200127095458/75/Dimensional-analysis-7-2048.jpg)


![Method Involves The Following
Steps:
List all physical variables and note ‘n’ and ‘m’.
n = Total no. of variables
m = No. of fundamental dimensions (That is, [M], [L],
[T])
Compute number of ∏-terms by (n-m)
Write the equation in functional form.
Write equation in general form.
Select repeating variables. Must have all of the ‘m’
fundamental dimensions and should not form a ∏
among themselves.
Solve each ∏-term for the unknown exponents by
dimensional homogeneity.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dimensionalanalysis-200127095458/75/Dimensional-analysis-11-2048.jpg)




