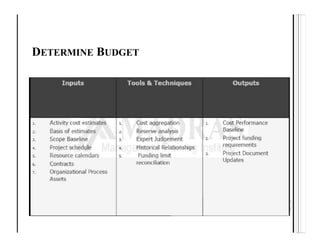
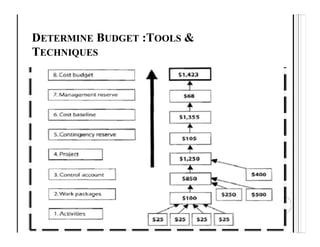
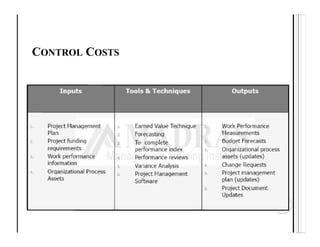
This document discusses key aspects of project cost management including estimating costs, determining budgets, and controlling costs. It provides details on processes, tools and techniques, and outputs for each aspect.
The main processes are estimate costs, determine budget, and control costs. Estimating costs involves tools like expert judgement, analogous estimating, bottom-up estimating, and reserve analysis. Determining the budget aggregates activity costs and includes contingency and management reserves. Controlling costs uses earned value management to track performance against the cost baseline and forecast estimates.





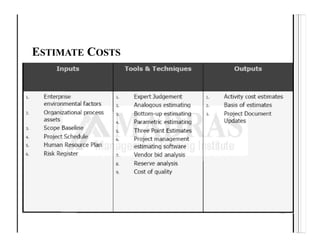




![THREE-POINT ESTIMATES (PERT)
5. Three Point Estimates
PERT analysis calculates An Expected c(E) activity
cost using a
weighted average of three estimates :
c(E) = [co+4cm+cp]/6
PERT analysis consider estimation uncertainties
and risks and hence accuracy of estimate is
improved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-projectcostmanagement-240223174458-f3a22e54/85/Software-Project-Cost-Management-and-estimation-11-320.jpg)