The document discusses three software development life cycle models: the classical waterfall model, iterative waterfall model, and prototyping model.
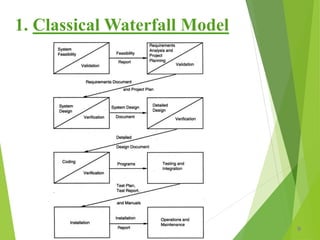
The classical waterfall model divides a project into sequential phases such as requirements, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. It has clear milestones but does not allow for overlap or feedback between phases.
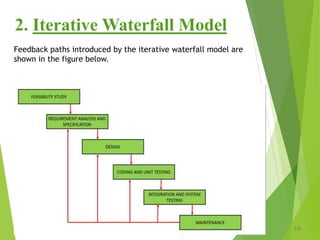
The iterative waterfall model incorporates feedback loops between phases to allow for error correction. However, it still requires freezing requirements before development and does not support incremental delivery.
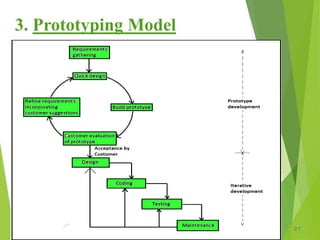
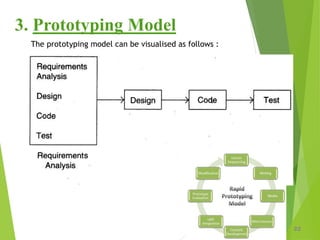
The prototyping model develops throwaway prototypes early to help understand requirements, which are then refined through a cycle of user feedback before full development. This allows new requirements to be accommodated more easily but can be costly in terms